-
What Is SQL Server Database Compatibility Level?
-
Why Compatibility Level Matters in SQL Server?
-
How to Check Compatibility Level in SQL Server?
-
How to Change Compatibility Level in SQL Server?
-
Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Your Databases
-
SQL Server Database Compatibility Level FAQs
-
Conclusion
Have you ever upgraded SQL Server but noticed your database still acts like it did years ago? This often happens because of the database compatibility level. This setting tells SQL Server how to interpret queries and which features to use for each database. Knowing how to manage compatibility levels is key for smooth upgrades, stable performance, and unlocking new features. In this guide, we’ll explain what compatibility level means, why it matters, and how you can manage it step by step.
What Is SQL Server Database Compatibility Level?
The SQL Server database compatibility level is a property set at the individual database level. It directs SQL Server to apply the rules, behaviors, and supported features from a specific version—even if your server runs a newer release. Think of it as a “version lens” that shapes how SQL Server sees your data.
For example, suppose you restore a SQL Server 2012 database onto a SQL Server 2022 instance. The restored database can still operate in compatibility level 110 (which matches 2012). This helps older applications keep working after upgrades because their expected behaviors remain unchanged. Importantly, the compatibility level only affects the chosen database—not the entire server or other databases.
Why Compatibility Level Matters in SQL Server?
Why should you care about compatibility level? Because it shapes how your database works every day. The compatibility level controls which T-SQL features are available, how queries are optimized by the engine, and even how some built-in functions behave.
When you upgrade SQL Server itself, existing databases keep their old compatibility levels by default. This avoids breaking changes that might disrupt legacy applications or business processes. However, staying on an old level can also prevent you from using new query optimizations or advanced features introduced in later versions.
Real-World Scenarios Where Compatibility Level Impacts Operations
Let's look at some common situations where compatibility levels make a difference:
Suppose your application relies on older syntax or deprecated functions that were changed in newer versions of SQL Server. Keeping an older compatibility level ensures these functions still work as expected after an upgrade.
On the other hand, if you want to use new features—like STRING_AGG (introduced in level 130) or intelligent query processing (available from level 150)—you must raise your database’s compatibility level first.
Sometimes raising the compatibility level changes query plans or optimizer behavior. This can improve performance but may also reveal hidden bugs or inefficiencies in legacy code.
How to Check Compatibility Level in SQL Server?
Before making any changes, you need to know your current settings. There are two main ways: using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or running a T-SQL query.
Start with SSMS by connecting to your instance. In Object Explorer, expand Databases, then right-click your target database and select Properties. In the Database Properties window, click Options. You’ll see Compatibility level listed on the right side as a drop-down menu showing current and supported values.
If you prefer T-SQL:
SELECT name, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'YourDatabaseName';
Replace 'YourDatabaseName' with your actual database name. The result shows a number matching one of the version codes above.
If you want to check all databases at once:
SELECT name, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases;
This displays every user and system database along with its current setting.
How to Change Compatibility Level in SQL Server?
Ready to update the compatibility level? You have two main options: through SSMS or with T-SQL commands. Always test changes first in a non-production environment since altering this setting can affect query results and application logic.
Using SSMS:
1. Open SSMS and connect to your server.
2. In Object Explorer, right-click your target database.
3. Select Properties.
4. Go to Options.
5. In Compatibility level, pick the desired value (such as SQL Server 2022 (160)).
6. Click OK to apply changes.
With T-SQL:
ALTER DATABASE YourDatabaseName SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL = 150;
Replace YourDatabaseName with yours; adjust 150 as needed for other versions.
Supported values include 160 (2022), 150 (2019), 140 (2017), 130 (2016), etc.[^1]
After making changes, confirm them with:
SELECT name, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases WHERE name = 'YourDatabaseName';
Introducing Vinchin Backup & Recovery: Enterprise-Level Protection for Your Databases
Before adjusting important settings such as database compatibility levels on platforms like Microsoft SQL Server—or any mainstream enterprise DB—you need reliable backup protection tailored for modern IT environments. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an enterprise-grade solution supporting today’s leading databases including Oracle, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL/PostgresPro,MongoDB,and especially Microsoft SQL Server.With robust capabilities such as incremental backup,sophisticated batch backup scheduling,data retention policies,GFS retention policy,and advanced source-side compression,Vinchin Backup & Recovery delivers both flexibility and efficiency across diverse infrastructures.These core features help minimize storage costs,maximize recovery speed,and ensure compliance—all while simplifying daily operations through automation.The intuitive web console makes protecting your data straightforward:
1. Select source SQL Server database(s),
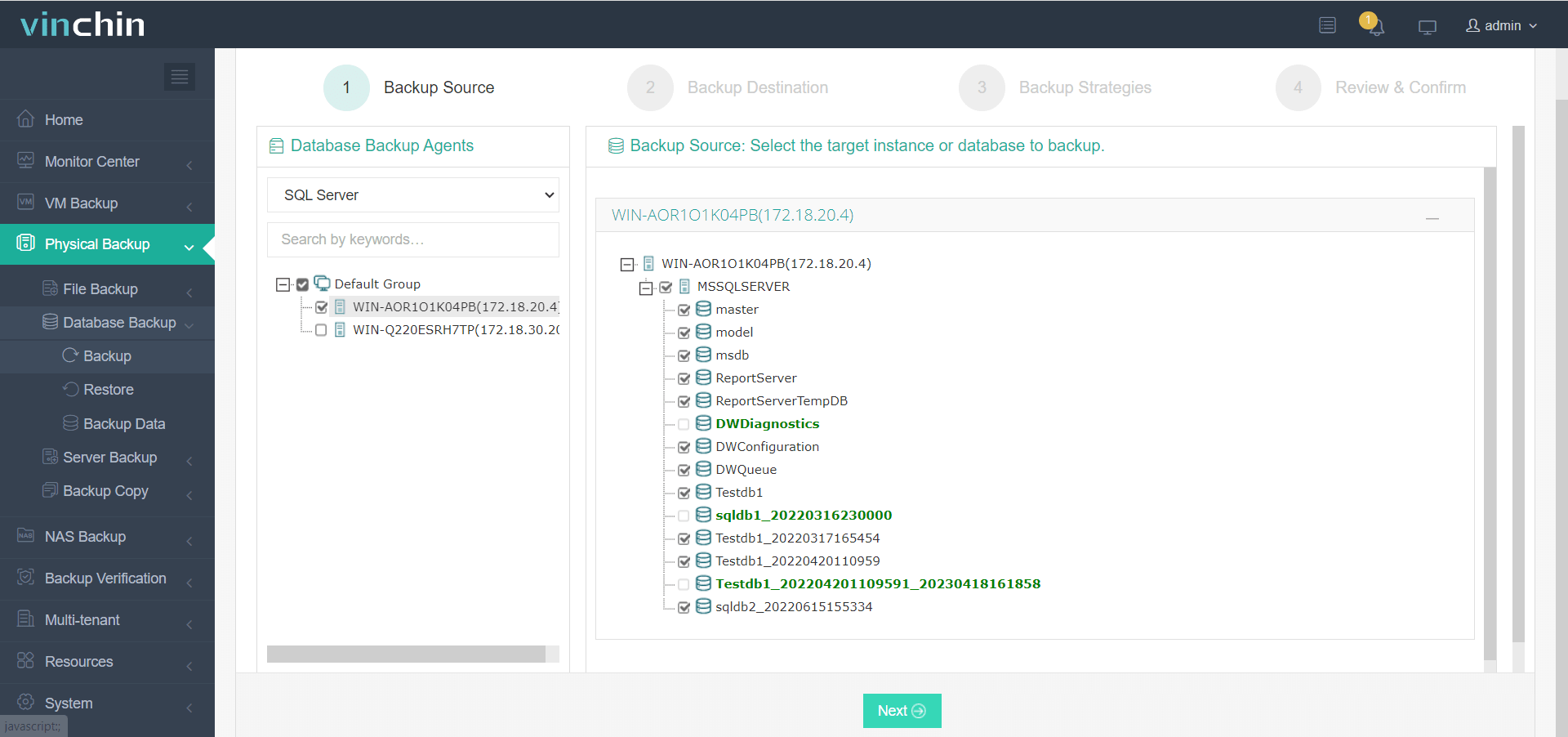
2. Choose target storage location(s),
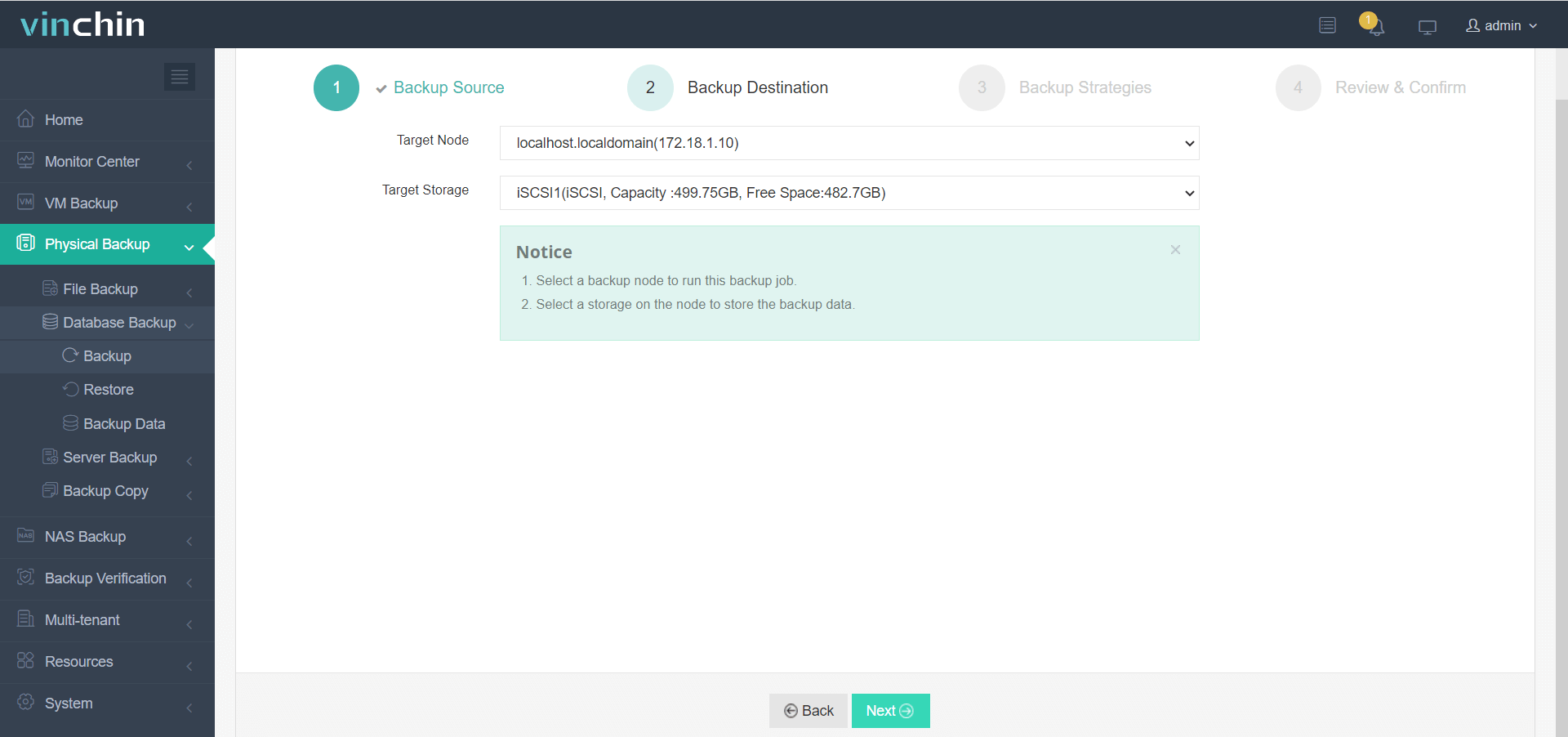
3. Configure backup strategies,

4. Submit the job.
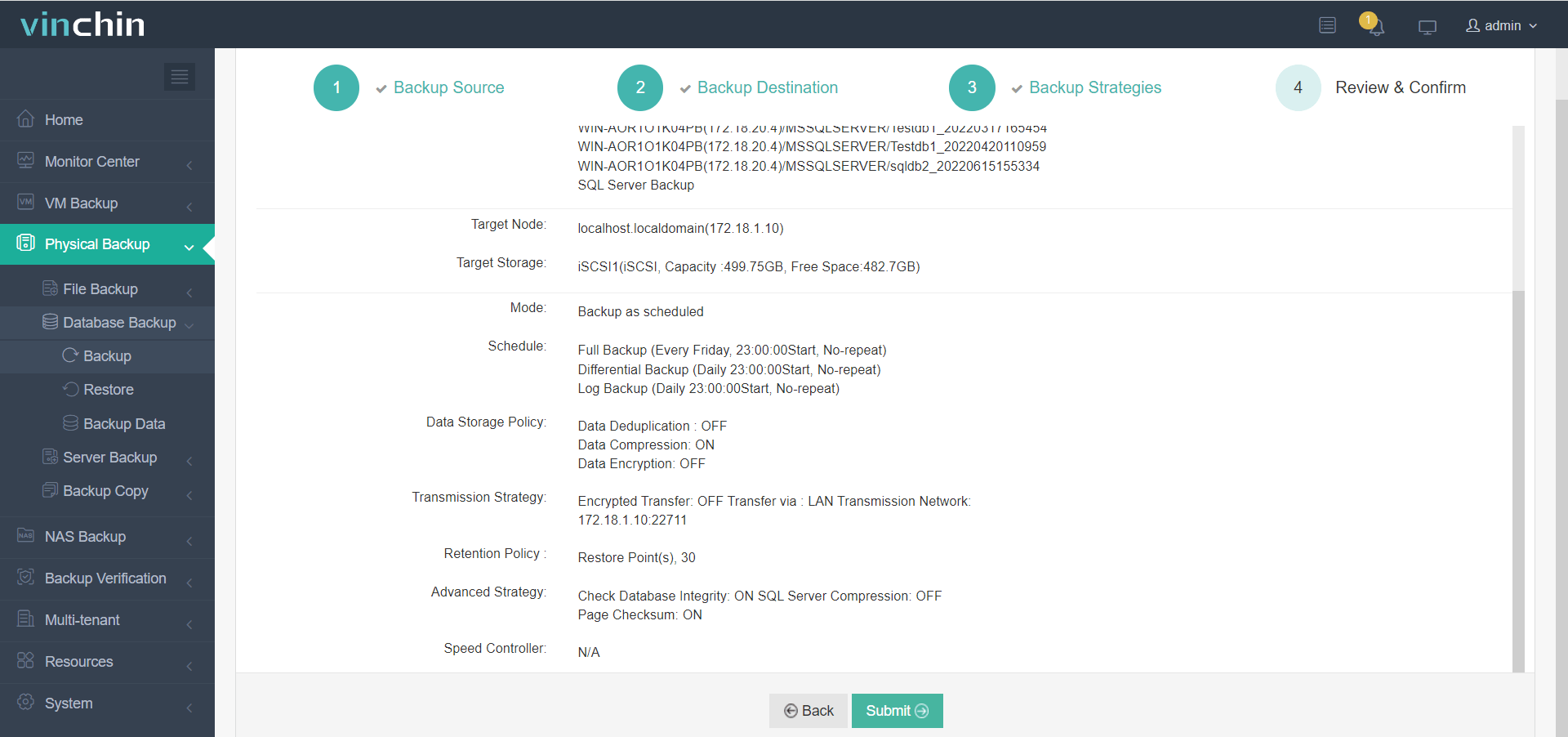
With global recognition,a strong customer base,and top industry ratings,Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers trusted enterprise data protection.Try its full-featured platform free for 60 days—click below to download.
SQL Server Database Compatibility Level FAQs
Q1: Can I script bulk updates of multiple databases’ compatibility levels?
A1: Yes—use T-SQL loops or PowerShell scripts with ALTER DATABASE commands targeting each desired database name.
Q2: What should I do if my application breaks after raising the compatibility level?
A2: Restore from backup if needed; then test code against both old/new settings until issues are resolved before retrying migration.
Q3: Does changing only one database’s compatibility affect others?
A3: No—each database has its own independent setting; changing one does not impact others unless they share linked objects requiring cross-database queries.
Conclusion
SQL Server’s database compatibility level helps balance legacy support with modern features through careful management of settings per-database basis—not just per-server version alone! Always back up data using solutions like Vinchin before making changes so you’re ready for anything that comes next.
Share on:







