-
What is Business Continuity?
-
Metrics for Business Continuity Planning
-
Why is Business Continuity Management Critical?
-
Key Components of Business Continuity Management
-
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
-
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
-
Business Continuity FAQs
-
Conclusion
In the global wave of digital transformation, virtualization technology has become the cornerstone of enterprise IT architecture. According to Gartner’s forecast, by 2026, over 90% of global organizations will adopt some form of virtualization technology. The widespread application of virtualization environments has not only enhanced resource utilization and reduced costs but also significantly improved business flexibility and responsiveness. However, the full realization of these advantages depends on one crucial premise: virtual machine business continuity.
What is Business Continuity?
Business continuity refers to the ability of an organization to ensure the uninterrupted operation of critical business services and the integrity of data in the face of hardware failures, system crashes, network interruptions, human errors, or catastrophic events. According to IDC research, the average economic loss due to each IT system downtime for large enterprises is as much as $9,000 per minute. In modern enterprises highly dependent on virtualization environments, any factor causing virtual machine interruption can quickly evolve into a "digital storm," severely impacting business operations. Therefore, ensuring virtual machine business continuity is not only a necessary condition for maintaining an enterprise’s reputation and meeting customer expectations but also an essential strategic consideration for the survival and growth of the organization.
Business continuity management refers to the strategies, plans, and measures that an organization implements to mitigate these risks and ensure a swift and effective recovery of business operations in the event of an emergency. These measures may include formulating disaster recovery plans, backing up critical data and equipment, establishing backup workplaces, and training employees to respond to emergencies.
Through effective business continuity management, organizations can minimize the impact of business disruptions on their operations and reputation, enhancing resilience and sustainability.
Metrics for Business Continuity Planning
IT infrastructure is the foundation of most business-critical functions. Therefore, when developing a BC plan, the first thing IT should do is map the relationship between technological resources and business functions. One of the most important outputs of BIA (Business Impact Analysis) is identifying the IT resources that support critical mission functions because it generates two key metrics: Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO).
RTO (Recovery Time Objective): Defines the maximum amount of time required to disable a specific business function before the organization suffers a loss. For IT, this means the maximum time before disabling specific systems and resources to prevent business harm. A general rule of thumb for RTO and RPO is: the shorter the time frame, the greater the potential investment required to achieve the metric.
RPO (Recovery Point Objective): Refers to the time of the last backup for current data, databases, and other resources. For example, customer personal data may be critical to an organization’s business and should be backed up more frequently than other resources. Achieving a low RPO (i.e., less than 1 hour or 5 minutes) requires investment in more complex data mirroring or replication technologies, as well as increased data storage capacity.
Why is Business Continuity Management Critical?
In today’s complex and ever-changing business environment, the importance of BCM is increasingly apparent. Imagine a scenario where a company suddenly faces an unexpected natural disaster, such as a flood or earthquake, or suffers a severe cyberattack that paralyzes key business systems and halts operations. This can result in not only direct economic losses but also customer churn, damage to reputation, and a series of cascading effects.
Take, for example, the large-scale service outage faced by Canadian telecom giant Rogers in 2022, which caused a disruption in voice calls, text messaging, and wireless data services for a large number of users. Affected users could not book vaccination appointments, students could not attend online classes, and citizens could not order takeout. This incident not only caused significant inconvenience to users but also placed Rogers under immense public pressure, severely damaging its brand image.
According to relevant data, the losses caused by business interruptions can be enormous. An hour of business disruption can result in losses amounting to tens of thousands or even millions of dollars, excluding additional recovery costs. If a company lacks an effective BCM strategy, it may fall into chaos when faced with these unexpected situations and even face the risk of closure. BCM acts as a "lifeline" for businesses, helping them maintain the operation of critical business functions during a crisis, reduce losses, quickly recover, and ensure that the company can continue to move forward after the storm.
Key Components of Business Continuity Management
Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA):
Risk Assessment: Identifies various threats that could impact organizational operations, including natural disasters, technical failures, human errors, etc.
Business Impact Analysis: Assesses the impact of these threats on critical business functions, determining which functions are most important and the maximum allowable downtime (Maximum Tolerable Downtime, MTPD) and data loss (RPO) they can tolerate.
Business Continuity Strategy:
Based on the results of the BIA, develop specific response strategies, including recovery priorities, backup facilities, and data backup plans. Define RTO, i.e., the time required to restore normal operations after a disaster.
Emergency Response Plan:
Develop a detailed emergency response process, including personnel evacuation, emergency contact lists, communication plans, etc. Ensure that all employees understand their roles and responsibilities in an emergency.
Business Continuity Plan (BCP):
Detailed documentation of how to restore critical business functions after an interruption event. It includes resource allocation, task assignments, recovery steps, and timelines.
IT Disaster Recovery Plan (IT DRP):
Focuses on the recovery of information systems, ensuring data and application availability. Includes measures such as data backups, system recovery, and network restoration.
Training and Awareness:
Regular training for employees to ensure they are familiar with the BCP and emergency response plans, enhancing their security awareness and emergency response capabilities.
Exercises and Testing:
Regular tabletop exercises, simulation drills, and live exercises to validate the effectiveness of the plan and employees' preparedness. Use tests to identify and correct shortcomings in the plan.
Maintenance and Updates:
Regularly review and update the BCP to reflect organizational changes and technological advancements. Ensure the plan is aligned with current risk environments and business needs.
Documentation and Communication:
Maintain detailed documentation to ensure all stakeholders have access to the latest BCP. Establish effective communication channels to ensure the rapid transmission of critical information during an interruption event.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Business Continuity Management is a comprehensive management process that pre-defines the potential impacts that could disrupt an organization’s ability to operate, enabling the organization to tolerate the loss of part or all of its business capabilities.
Disaster Recovery refers to the process of reactivating information systems, data, hardware, and software after a natural or human-made disaster to restore normal business operations. DR is part of BCM, with its core focus on assessing and mitigating disaster risks to key business data and processes through timely recording, backup, and protection.
Differences and Connections Between BCM and DR
| Feature/Standard | Business Continuity Management (BCM) | Disaster Recovery (DR) |
| Main Focus | Entire business processes and functions | IT systems and data |
| Objective | Ensure rapid recovery of critical business functions after an interruption | Rapid recovery of data and applications after an IT system failure |
| Method | Risk assessment, business impact analysis, recovery strategies | Data backup, system recovery, backup sites |
| Scope | All critical business processes in the organization | Primarily IT systems and data |
| Implementation Time | Before, during, and after an interruption event | After an interruption event |
| Relationship with Other Standards/Concepts | BCM usually includes DR as part of its framework | DR is a subset of BCM |
| Applicable Scenarios | Any organization facing business interruption risks | Organizations reliant on critical IT systems and data |
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional solution designed to provide data protection and disaster recovery for virtualized environments. It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc. Tailored for virtual environments, Vinchin offers automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. With data encryption and ransomware protection.
With agentless backup feature, it enables quick integration of VMs into the backup system. It offers disaster recovery features such as Instant Restore to reboot VMs from backups in seconds, offsite copy for remote backup storage, and automatic backup verification for integrity checks. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
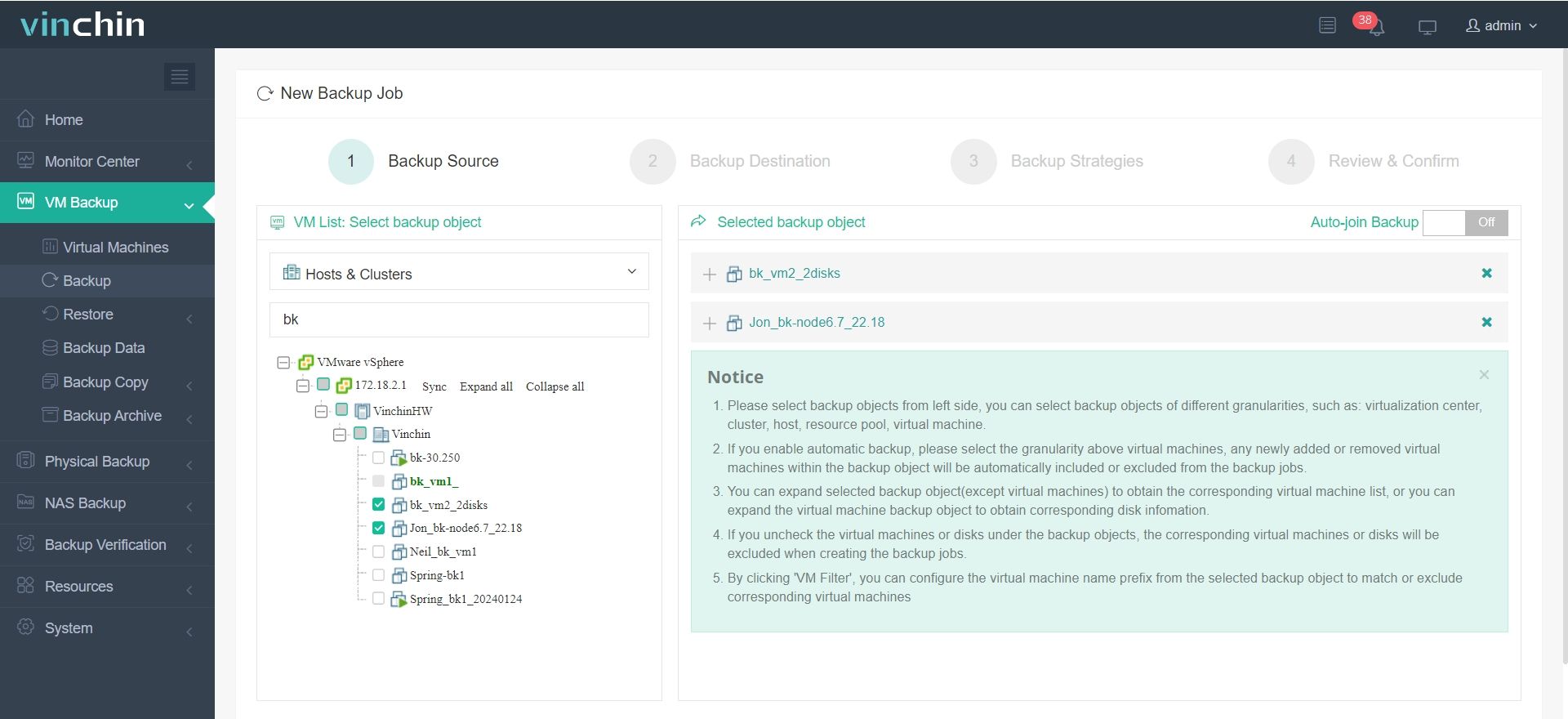
2.Select backup destination.
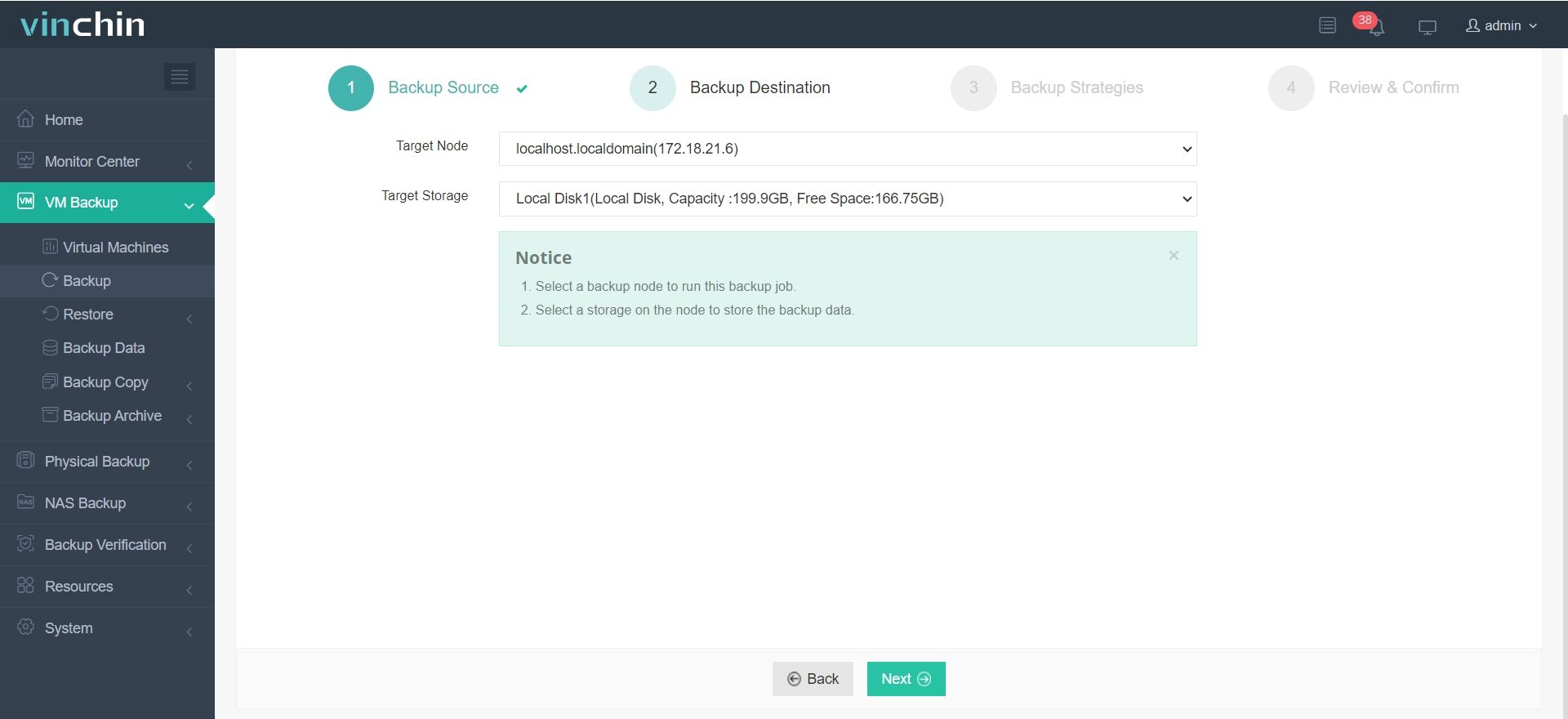
3.Configure backup strategies.
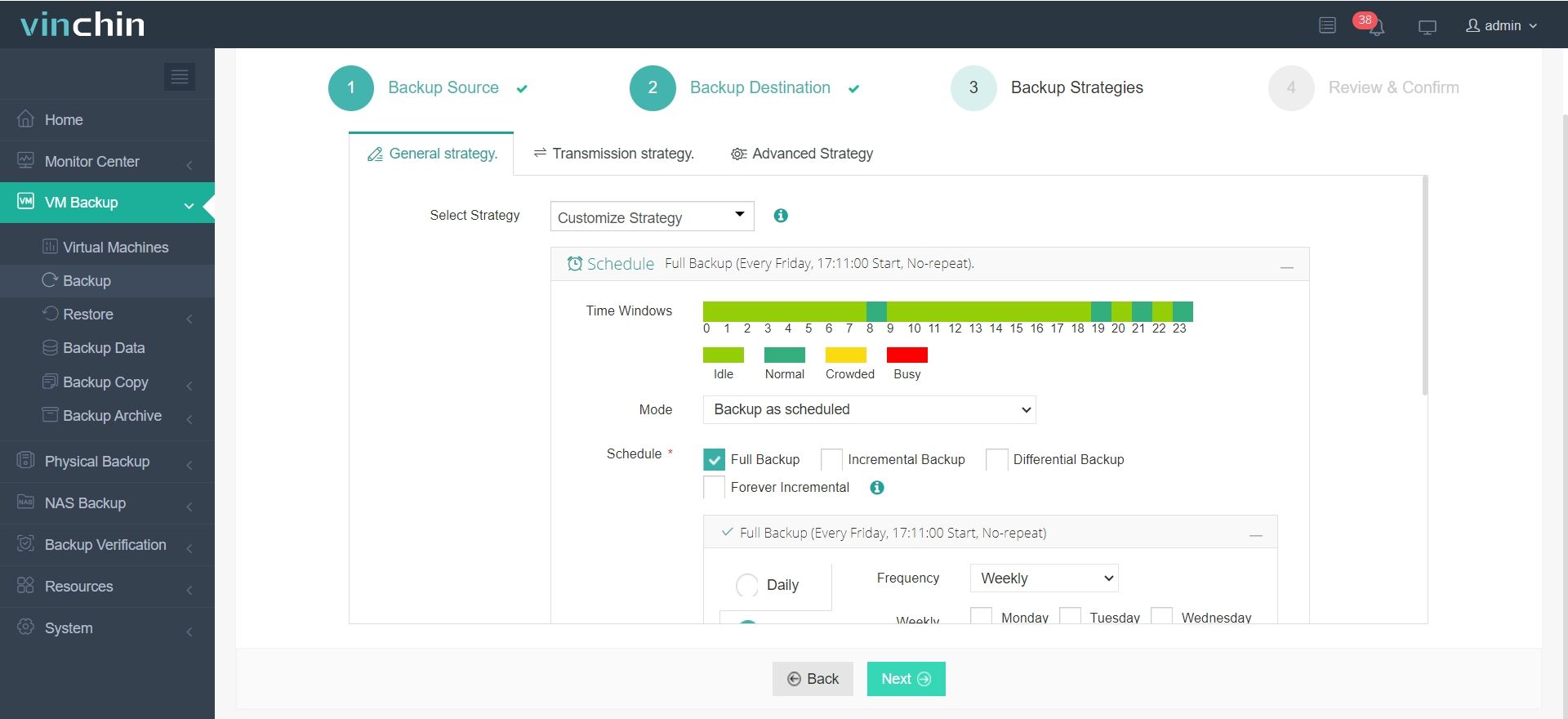
4.Review and submit the job.
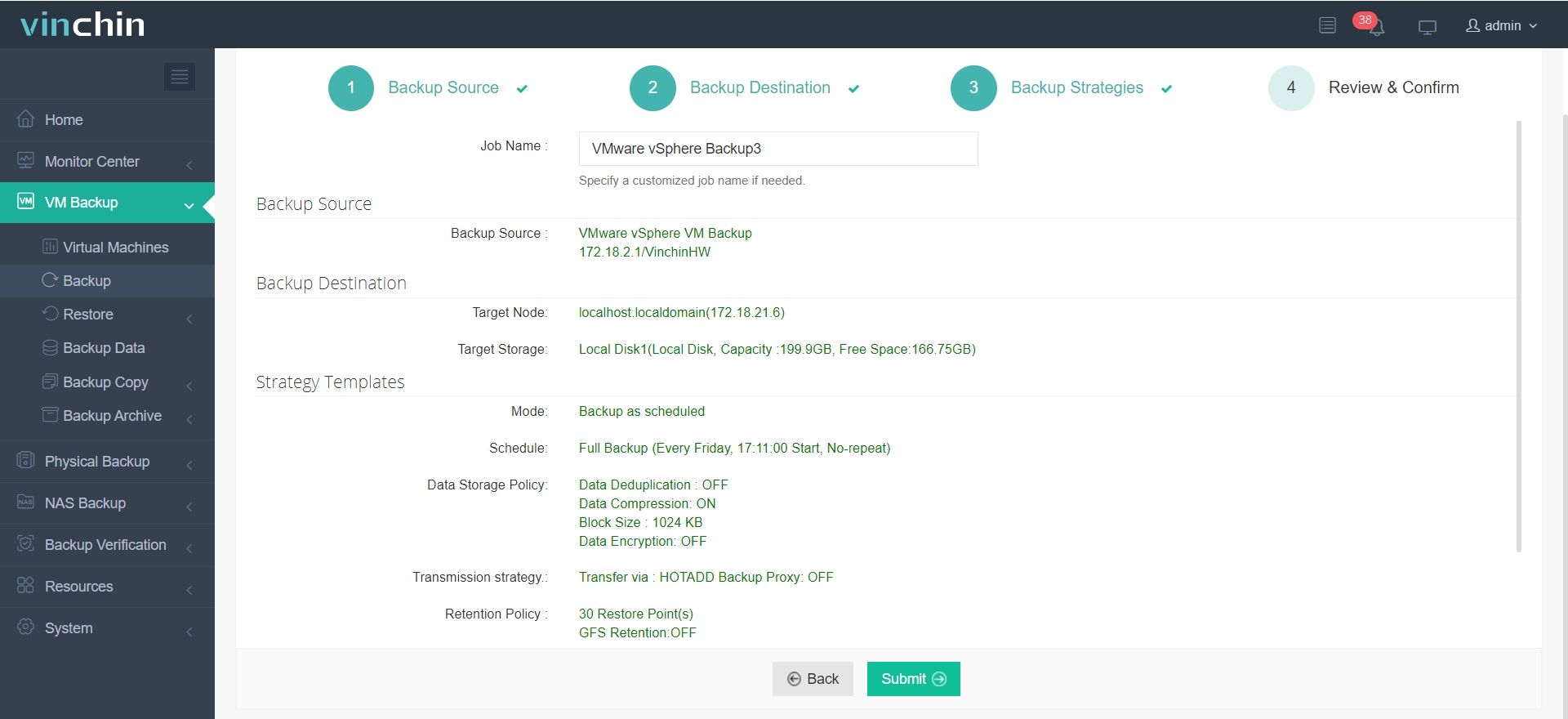
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
Business Continuity FAQs
1. What is business resilience?
Business resilience refers to a company's ability to adapt to and recover from disruptions, such as economic downturns, natural disasters, or technological failures. It involves proactive planning, risk management, and the ability to maintain operations, safeguard assets, and continue delivering value to customers even in the face of adversity.
2. What is the role of cloud computing in business continuity?
Cloud computing plays a significant role in business continuity by providing flexible, scalable, and secure resources for data storage, computing power, and disaster recovery. Cloud services can ensure that data and applications are accessible from anywhere, even in the event of a physical office disruption.
Conclusion
In this uncertain era, business continuity management has become an essential skill for corporate survival and development. It helps enterprises effectively respond to various unexpected challenges, ensure the continuous operation of critical business functions, reduce losses, and maintain reputation and customer trust.
Enterprises should fully recognize the importance of BCM and actively take action to establish a comprehensive BCM system. From strategic planning and building a sound organizational structure to developing comprehensive contingency plans and ensuring resource security, and continuously improving employees' emergency response capabilities through training and exercises, every step is crucial.
Share on:








