-
What is P2V Migration?
-
Benefits of P2V Migration
-
P2V Use Cases
-
3 Ways to Achieve P2V Migration
-
Backup is Important Both Before and After P2V!
-
P2V Migration FAQs
-
Wrap Up
Gearing up for having a higher sense of agility in modern IT infrastructure, more and more IT owners has now shifted their traditional physical-server-based data center to virtualization-based one. This goal cannot be accomplished without passing the process namely P2V migration.
What is P2V Migration?
P2V (Physical-to-Virtual) is a data migration approach that helps physical server users shift to virtualization. The operating system and all upper-level applications in one physical server are the main objects of the migration, whose final destination would be the target virtual server managed by VMM (Virtual Machine Monitor). P2V can often be realized with the help of specific tools and software by mirroring the system status and data on the physical server to the virtual machine provided by VMM, and replacing the storage hardware and network card driver of the physical server in the virtual machine. As long as you correctly install the corresponding driver in the virtual server, and configure the same address as the original physical server (such as TCP/IP address), the virtual server can be able to replace the physical server to work once being rebooted.
Benefits of P2V Migration
Cost Efficiency: Virtualization reduces the need for physical hardware, leading to lower capital and operational expenditures. It consolidates multiple physical servers into a single host, minimizing power consumption, cooling requirements, and physical space.
Improved Resource Utilization: Virtualization allows for more efficient use of computing resources. By running multiple VMs on a single physical host, organizations can maximize CPU, memory, and storage usage, reducing wastage.
Enhanced Scalability and Flexibility: VMs can be easily scaled up or down to meet changing workload demands. This flexibility allows businesses to quickly adapt to growth or varying resource requirements without significant hardware investments.
Simplified Management and Maintenance: Centralized management tools enable easier monitoring, maintenance, and updating of virtualized environments, reducing administrative overhead and improves operational efficiency.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Virtualization facilitates more robust disaster recovery solutions. VMs can be easily backed up, replicated, and restored, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
P2V Use Cases
1. The utilization of physical servers is very low. Converting them into virtual machines can greatly help improve the resource utilization rate.
2. The software environment built upon physical servers is very complex. P2V does not require reconfiguration of the environment.
3. Higher reliability of the IT system is needed. Snapshots and high availability can be achieved at the hypervisor level after conversion.
3 Ways to Achieve P2V Migration
Method 1: Manual Migration
This method requires the migration operator to have a solid understanding of the physical system and the virtual environment.
1. Shut down the services and operating system on the original physical machine, and start a new system from another medium, such as booting a new CD system from LiveCD. Most distribution systems have LiveCD.
2. Convert the disk of the physical machine system into a virtual machine image file. If there are multiple disks, you need to make multiple images, and copy the image to the virtual host.
3. Create a virtual device for the virtual machine, load the image file to start the virtual machine, adjust the system settings, and start the service.
Method 2: Semi-Automatic Migration
Use professional tools that helps automate parts of the manual setting process to assist P2V migration. For example, converting the disk data of a physical machine into a virtual machine format has always been a time-consuming task. Here, you can then choose a professional tool to complete this step.
Commonly used P2V tools:
Virt-p2v: capable of converting a physical machine to run virtualized on KVM, managed by libvirt, OpenStack, oVirt, Red Hat Virtualisation (RHV), or one of the other targets supported by virt-v2v, another tool that reads Linux and Windows guests running on other hypervisors and converts them to KVM.
disk2vhd: a utility that creates VHD versions of physical disks for use in Microsoft Virtual PC or Microsoft Hyper-V VMs.
There are tons of other tools available in the market, it’s better to make up your mind by taking the desired virtual platform and usability into consideration.
Method 3: P2V Live Migration
Unlike most P2V tools that only support cold migration (during the migration process, the physical server should be unavailable), live migration refers to zero downtime when data is being migrated. With the development of P2V technology, VMware vCenter Converter and Microsoft Hyper-V have been able to perform live migration capabilities to avoid downtime. This is often used when business continuity is required but a physical server is in need of update or maintenance.
Backup is Important Both Before and After P2V!
After all your data has been settled down in the virtual machines, it’s time to think about making a VM backup plan to protect it from harm. But here may come the problem: the legacy backup solution you use for physical server backups may not be able to help you as before due to the difference between normal physical servers and virtualized servers. Backup software should also update with your IT infrastructure, and specialized software for virtual machine backup can be a wise choice.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery can be a useful tool to protect your critical VM data after P2V migration. With 10+ hypervisors including VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, XCP-ng, OLVM, etc., you can easily backup multiple types of VMs through a single pane of glass, centralizing protection of data in hybrid cloud environments.
It provides advanced features like agentless backup, forever incremental backup, V2V migration, instant restore, granular restore, backup encryption, compression, deduplication, and ransomware protection. These are critical factors in ensuring data security and optimizing storage resource utilization.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your VMs with Vinchin Backup & Recovery. Here taking Hyper-V VM as an example:
1.Select the backup object.
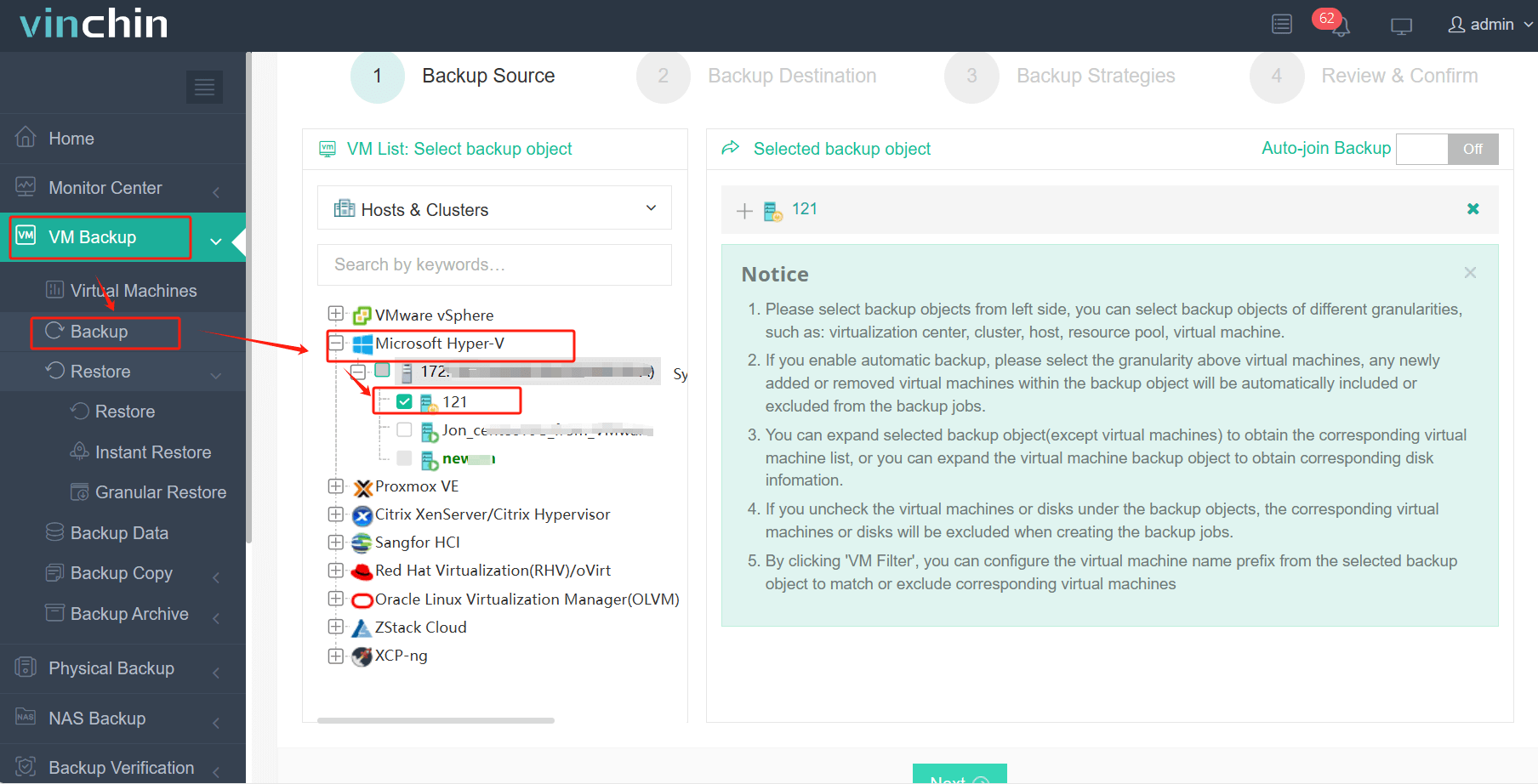
2.Select backup destination.
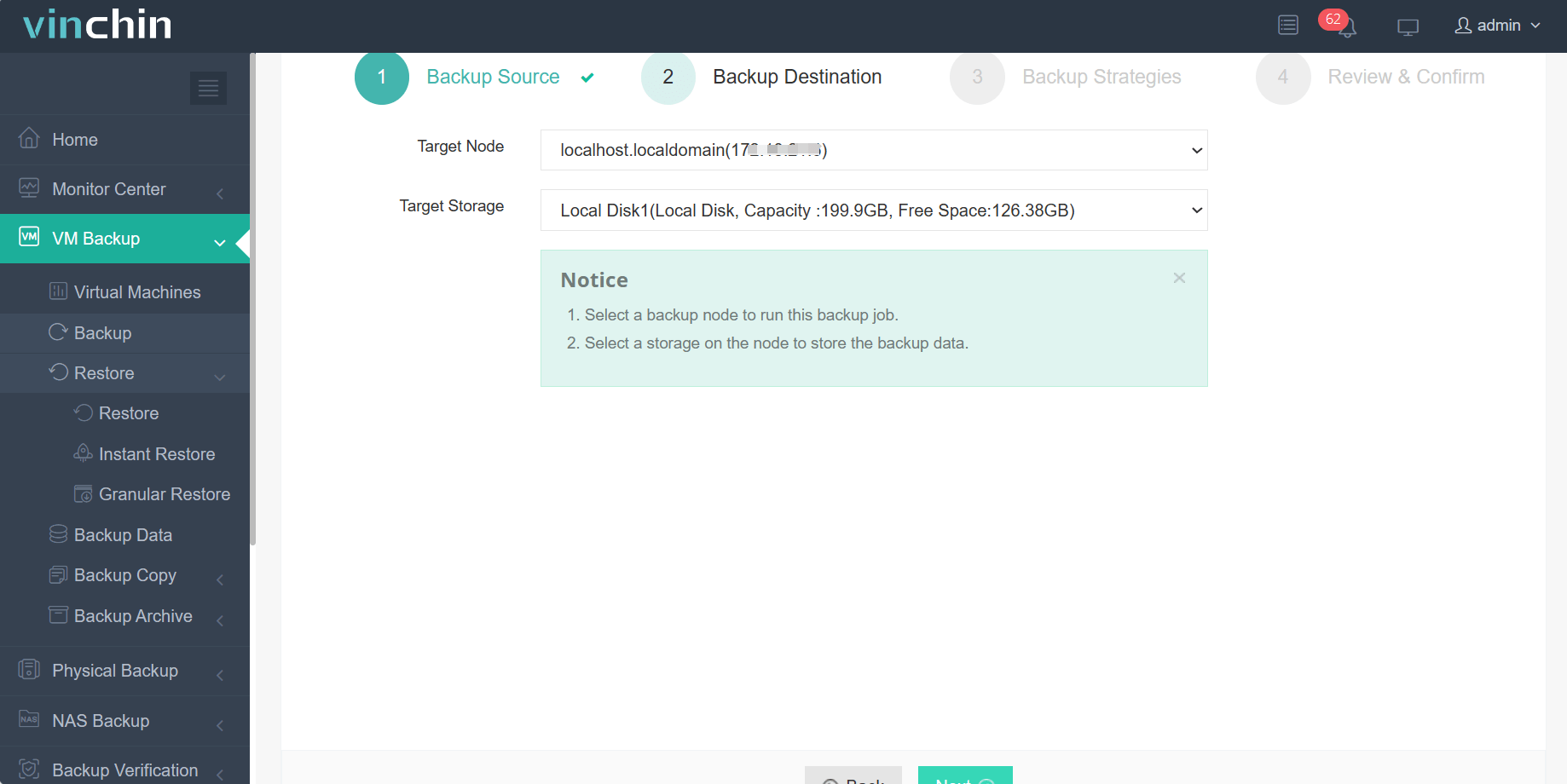
3.Select backup strategies.
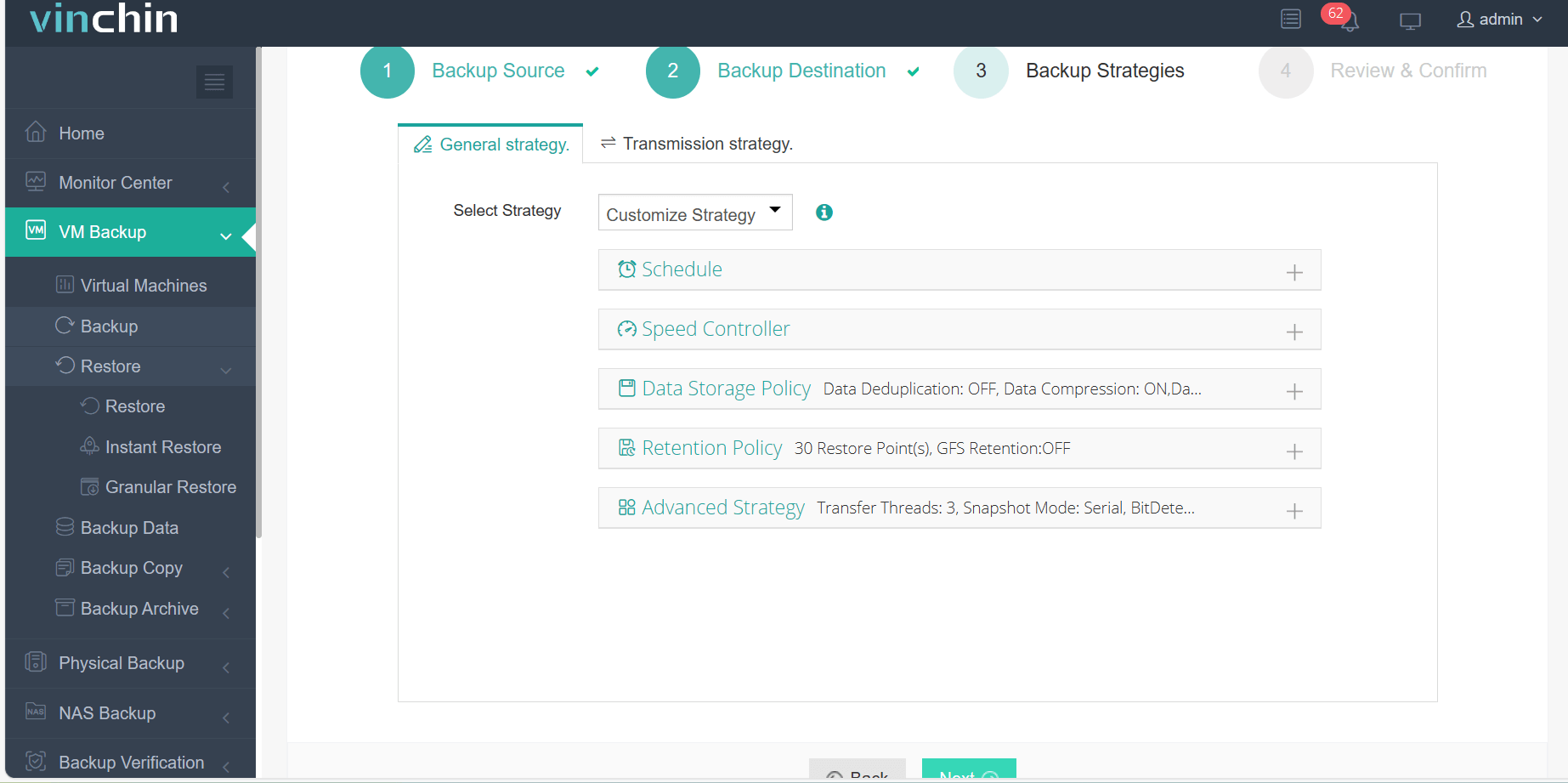
4.Review and submit the job.
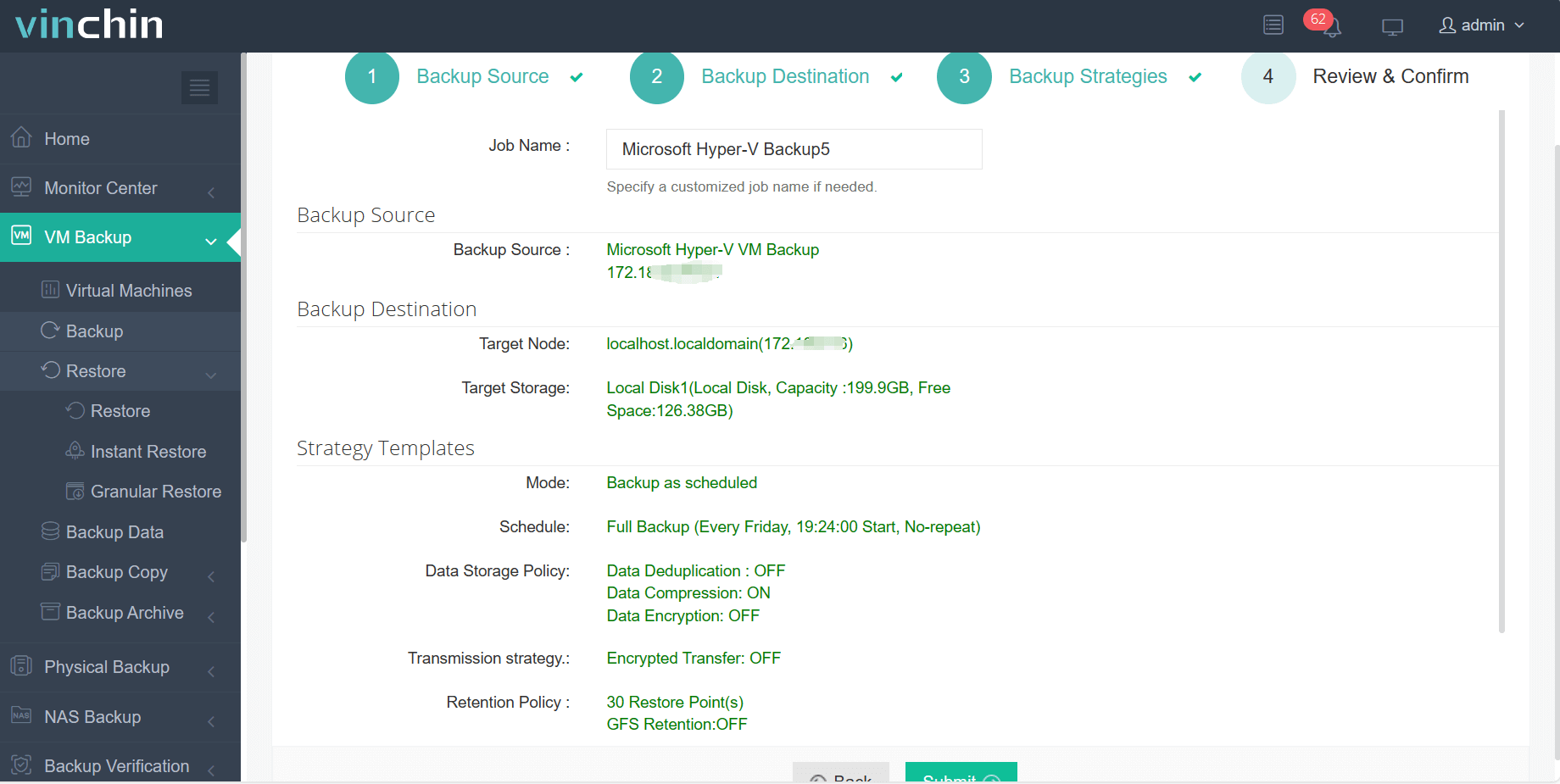
Along with many more advanced features waiting for you to explore. Free 60 days of full-featured trial available now, start your VM data protection journey in just a few minutes!
P2V Migration FAQs
1. Q: What challenges might be encountered during P2V migration?
A: Common challenges include:
Hardware compatibility issues
Driver and software compatibility problems
Network configuration adjustments
Performance tuning post-migration
2. Q: Is it possible to migrate a server that is still in use?
A: Yes, it is possible to migrate a server that is still in use, often referred to as "live migration." Techniques like incremental replication can be used to synchronize data while the server is running.
Wrap Up
This blog introduces 3 ways to realize the process of migrating data from physical servers to virtual machines. If you’re in need of updating your IT infrastructure, it’s important to choose a method that suits actual operation routine in the data center most, and remember to set up a complete backup plan in advance to secure your critical data.
Share on:







