-
The Trouble Caused by Duplicate Data
-
Categories of Duplicate Data in Backup
-
What is Deduplication?
-
How to Know if Deduplication is Effective for the Data?
-
Establishing a Reasonable Backup Strategy to Reduce Duplicate Data
-
Which Backup Software is the Best?
-
Backup Data Deduplication FAQs
-
Conclusion
Data backup ensures that in the event of data loss caused by hardware failure, natural disasters, human error, or malicious attacks, an enterprise can quickly resume operations, minimizing downtime and losses. One often overlooked but crucial issue in the data backup process is duplicate data. Duplicate data refers to identical or redundant data within the backup set. This problem may arise from repeatedly backing up the same data, failing to delete old versions after updates, or improper backup strategies.
The Trouble Caused by Duplicate Data
Duplicate data not only consumes valuable storage space and increases storage costs, but it can also make the backup and recovery process more complex and inefficient. When a backup set contains a large amount of duplicate data, each backup operation has to process and transmit this redundant content, wasting network resources and prolonging backup time. During data recovery, duplicate data also increases the difficulty and time required, as the system must sift through and identify the files that actually need to be restored.
Furthermore, duplicate data can complicate data management. A large amount of duplicate data makes data management more complex, increasing maintenance difficulty and costs. Additionally, duplicate data can obscure real changes in data, interfering with data analysis.
Therefore, addressing the issue of duplicate data in backups is critical. By employing effective deduplication techniques, the backup process can be optimized, improving storage and backup efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring data accuracy and manageability.
Categories of Duplicate Data in Backup
File-Level Duplication: The entire file is backed up multiple times, with each backup being a complete copy of the file. This is common in full backups of folders or entire systems.
Data Block-Level Duplication: Data blocks within a file are redundantly saved across multiple backups. This is more subtle but can lead to significant storage space waste. Block-level duplication usually requires specialized deduplication technology to detect and eliminate.
Version Duplication: Multiple versions of the same file are saved, with each version containing minor differences but largely the same data.
Metadata Duplication: During backup, file metadata (e.g., creation time, modification time) may also be redundantly saved. Although these data occupy relatively small space, in large-scale backups, they can accumulate significantly.
What is Deduplication?
Deduplication technology optimizes storage space utilization by identifying and eliminating duplicate data blocks. This process relies on creating unique digital signatures (fingerprints) for each data block and using hash storage to detect duplicates. Depending on when it is implemented, deduplication can be classified into two main types: inline (online) and post-process (offline). Inline deduplication is applied before data is written to storage, storing only unique data segments, while post-process deduplication optimizes data after it has been written. Additionally, based on the execution location, deduplication can be divided into source-based and target-based deduplication. Source-based deduplication processes data before it is transmitted, effectively reducing network transmission volume.
In the past, SIS (Single Instance Storage) was a form of deduplication technology that operated at the file level. Modern deduplication technology works at the data block level, offering better deduplication effects but with higher implementation complexity. Incremental backups can reduce duplicate backups to some extent, but since they operate at the file level, they have poor granularity, and long-term use of incremental backups is impractical due to the complexity of the restoration process.
Deduplication technology is not only suitable for backup and archival systems but can also be applied to online, nearline, and offline data storage systems, including file systems, volume managers, NAS, SAN, and other scenarios.
How to Know if Deduplication is Effective for the Data?
The effectiveness of deduplication depends on several factors:
A. Amount of Data Change: The less the data changes, the more effective deduplication will be.
B. Compressibility of Data: Compression technology is usually used alongside deduplication. Highly compressible data can significantly save bandwidth and storage even if the deduplication ratio is not high.
C. Data Retention Period: The longer the data retention period, the more advantageous deduplication becomes, as it can greatly reduce storage space requirements.
Establishing a Reasonable Backup Strategy to Reduce Duplicate Data
To establish a reasonable backup strategy to reduce duplicate data, the following measures can be taken:
1. Combine Full and Incremental Backups: Perform full backups initially or after critical data updates to create a complete snapshot of the data; use incremental backups daily to record new changes, reducing duplicate data and saving resources.
2. Implement Archiving and Cleanup Policies: Set up regular archiving plans to move infrequently accessed but necessary data to low-cost storage; identify and clean up redundant or outdated data, set data retention periods, and automate the cleanup process.
3. Optimize the Backup Process: Choose backup software that supports deduplication, which automatically removes duplicate data during backup; compress and encrypt archived data to further save space and enhance security.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Strategy Adjustment: Regularly verify the effectiveness of backup data, monitor storage usage, and adjust backup and archiving strategies as needed based on business changes to ensure efficient operation and compliance.
Which Backup Software is the Best?
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional virtual machine backup software that supports over 10 virtualization platforms, including VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, and oVirt, etc. It provides excellent virtual machine backup and recovery features and also enables cross-platform migration.
Of course, Vinchin Backup & Recovery also includes deduplication and compression functions. It offers a customizable block size deduplication feature, which is more advantageous than traditional fixed deduplication, effectively reducing backup storage space.
By adopting Vinchin's deduplication and compression technology, you can improve the backup speed during the backup storage process and reduce the storage resources occupied by backup data, while also eliminating the risk of global data corruption caused by global deduplication.
To enable deduplication during backup, simply follow these steps:
1. Select the virtual machine you want to back up.
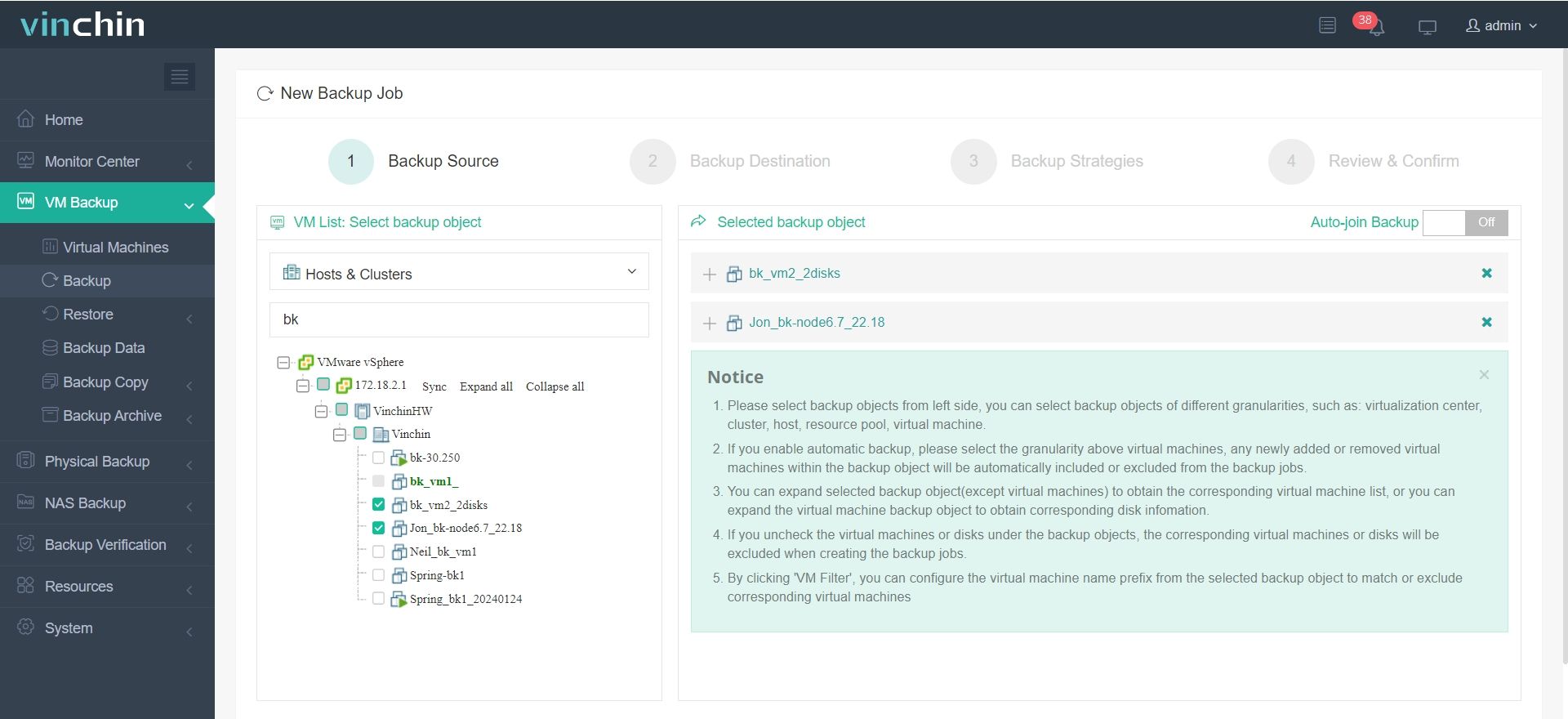
2. Choose the backup destination.
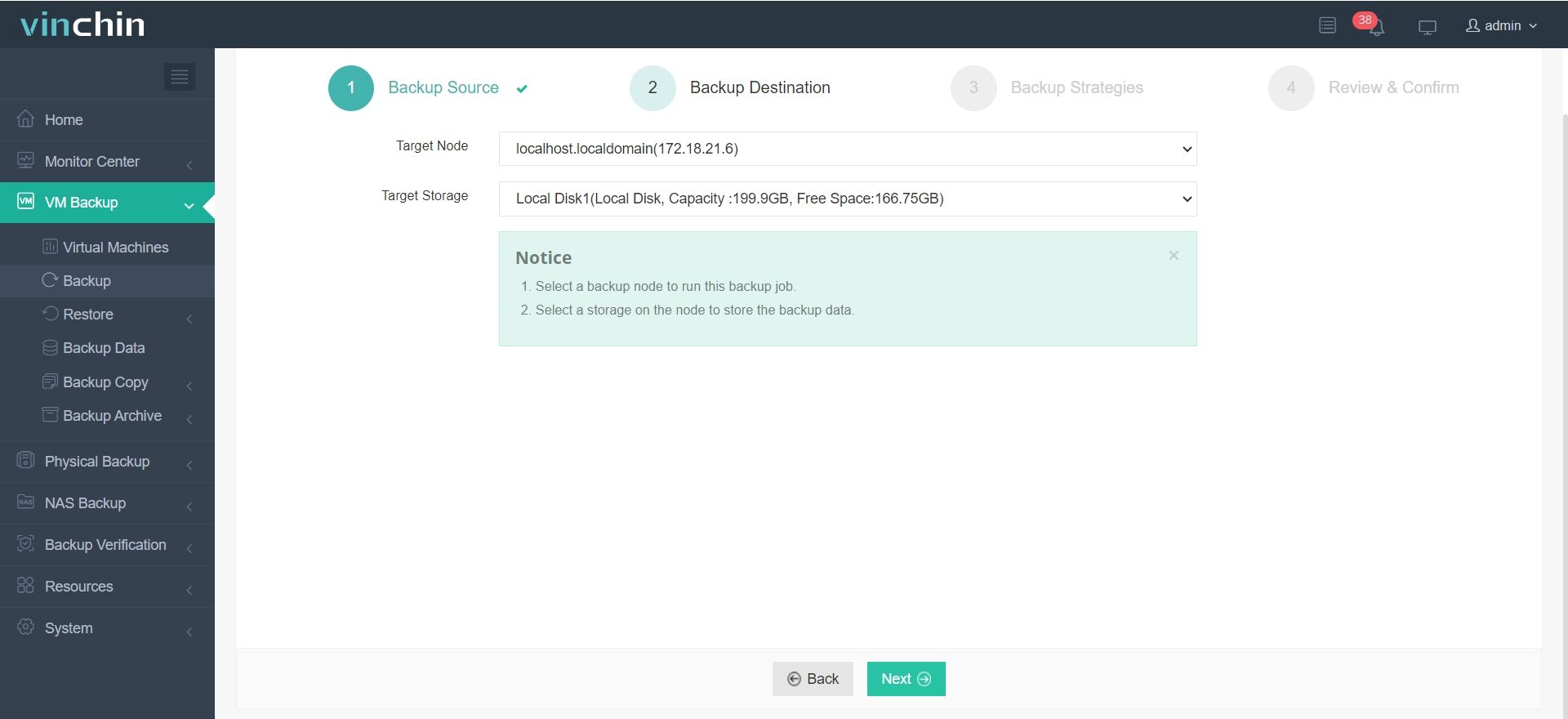
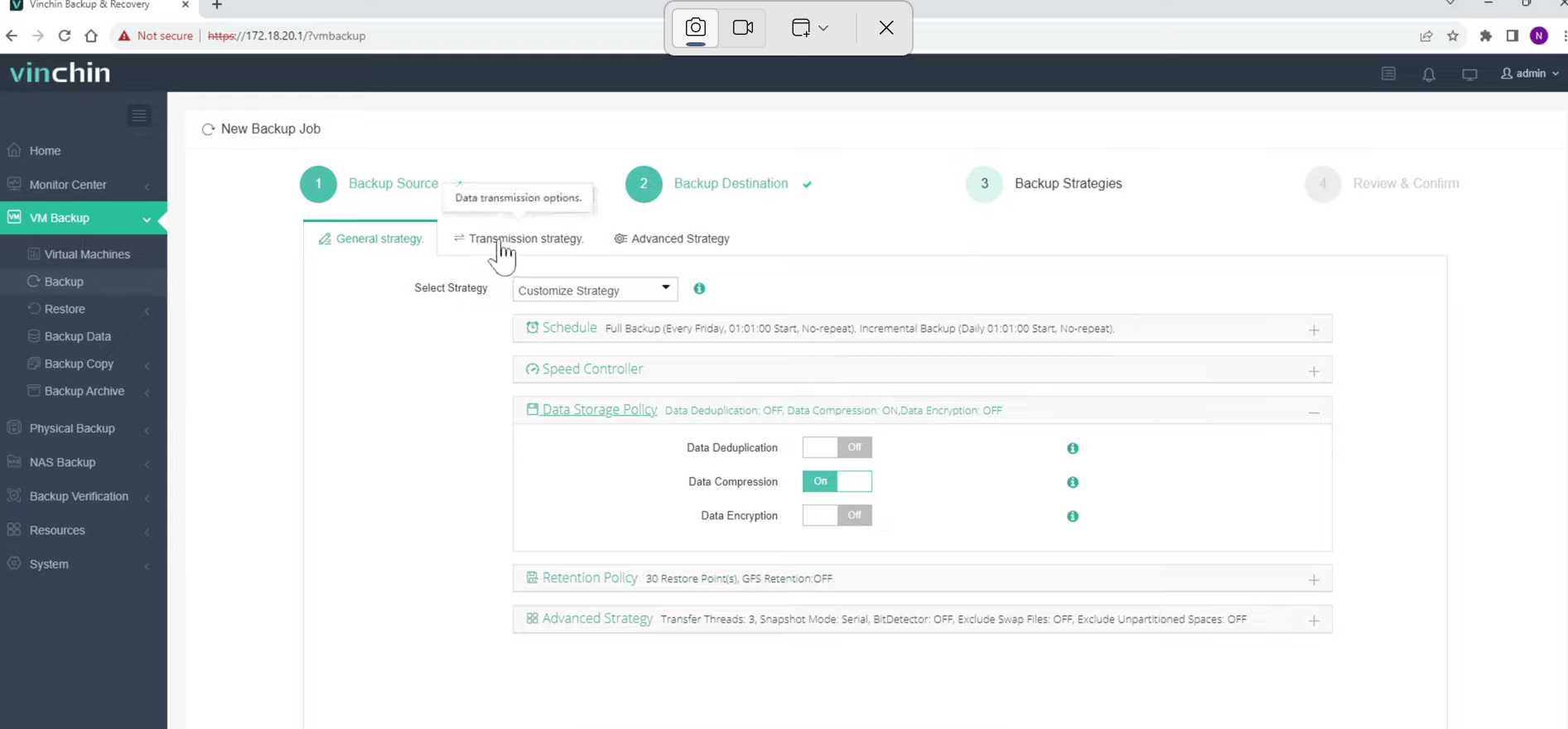
3. Configure the backup strategies.
In the "Data Storage Policy" section, you can choose whether to enable deduplication and compression.
4. Confirm the backup job.
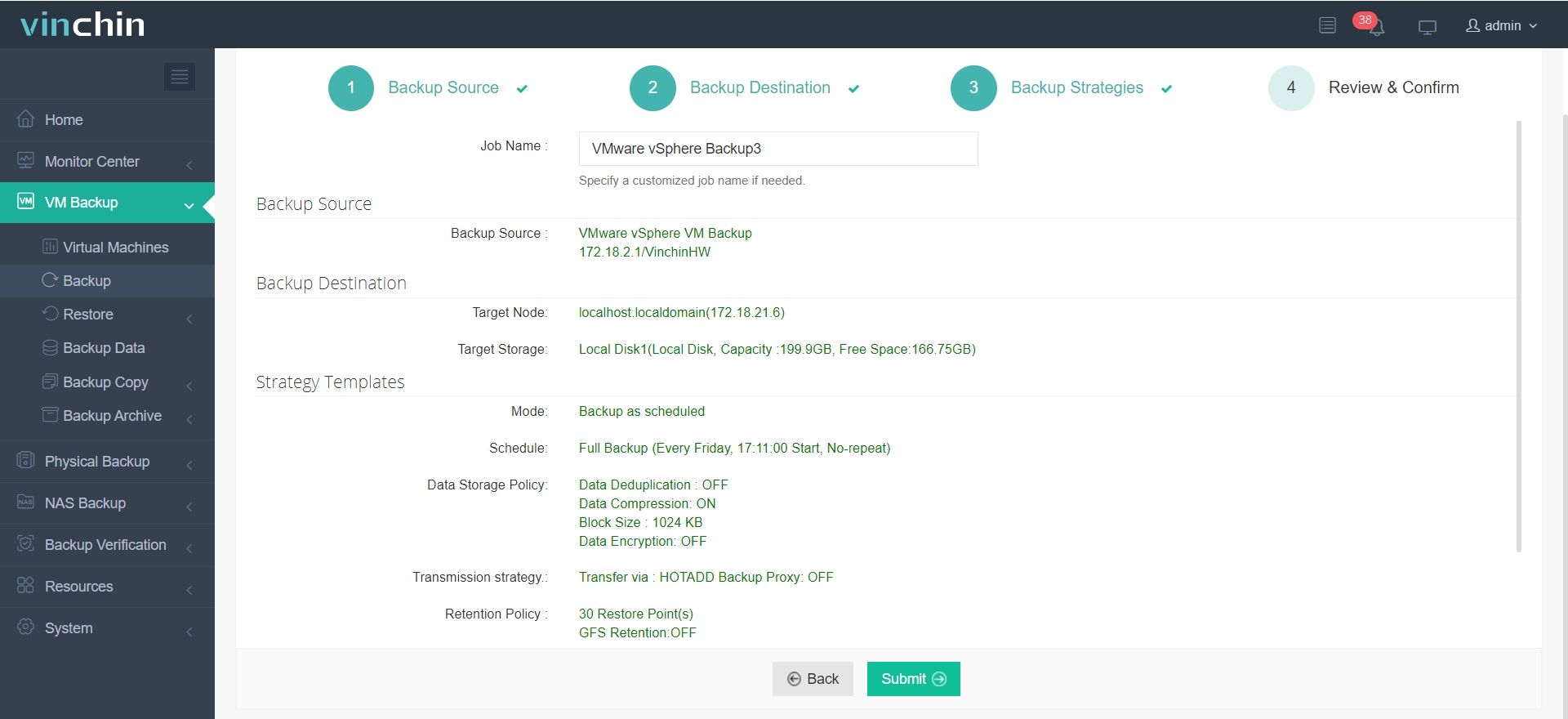
Besides the mentioned features, Vinchin offers many other advanced features waiting for you to discover. Click the button below to start a 60-day free trial with full functionality!
Backup Data Deduplication FAQs
1. Q: What types of data are suitable for deduplication and what types are not?
A: Deduplication is suitable for any type of data, including office documents, databases, multimedia files, and virtual machines. Although some data may not show significant deduplication effects during the first backup due to their nature, the advantages of deduplication become apparent in subsequent backups. The more frequently backups are performed and the shorter the intervals between them, the higher the deduplication ratio.
2. Q: What is fixed-length block deduplication and what is variable-length block deduplication?
A: Fixed-length block deduplication divides data into fixed-sized blocks and identifies duplicates by comparing each block's content. This method is simple but may miss opportunities to eliminate redundancies if identical data shifts slightly. Variable-length block deduplication, on the other hand, divides data into blocks of varying sizes based on content patterns, which allows for more precise detection of duplicates even if data shifts. This makes variable-length deduplication more efficient in reducing storage, though it's more complex to implement.
Conclusion
Duplicate data not only wastes storage space, increasing operational costs for enterprises, but can also affect the efficiency of data backup and recovery, complicating data management. Therefore, using effective deduplication technology to reduce duplicate data is crucial. Through deduplication, enterprises can optimize storage space usage, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency and accuracy of data management.
Share on:








