-
What is OpenStack disaster recovery?
-
How to backup and restore OpenStack VM?
-
OpenStack Disaster Recovery FAQs
-
Sum Up
OpenStack is an open-source cloud computing platform, managing distributed computing, network, and storage, aggregating them into a resource pool, and allowing users to configure virtual resources through the self-service portal. Because of its highly efficient scalability, it becomes popular in the construction of public clouds, reducing maintenance fees for service providers and make it possible to build super large-scale infrastructures.
While OpenStack facilitates the service providers running a large-scale cloud platform, disaster recovery should never be overlooked.
What is OpenStack disaster recovery?
OpenStack VMs can be used to support production systems so they need to be carefully protected. There are some basic concepts about OpenStack disaster recovery:
Disaster: refers to a sudden event, caused by human or natural factors, which will result in severe failure or complete crashes to the information systems in the data center. It will then make the supported business systems slow or stopped and these influenced systems often need to be switched to a backup site.
Disaster Recovery: refers to the ability to recover applications or business systems of the influenced data center in a secondary data center.
Disaster Tolerance: means that except for the production data center, users also need to build another redundant data center. In the event of a disaster, the production data center could be damaged so the production systems can be switched to the redundant data center for business continuity. For better availability, many users have built more than one redundant data center.
RPO and RTO: refer to the two major factors of a disaster recovery system. RPO (Recovery Point Objective) means the acceptable data loss in the event of a disaster, while RTO (Recovery Time Objective). Shorter TPO and RTO means better ability for disaster recovery and of course, the investment will also be higher.
Disaster Recovery Level: Generally speaking, there are 3 levels, data level, application level, and business level. The data level requires building a remote DR center to store data backup so that the data in the primary data center can be recovered in the event of a disaster; the application level requires building the same application systems in the remote DR center and uses data replication technology to ensure the recovery of applications as soon as possible; business level requires building almost the same environment in the remote DR center to recover business in the event of a disaster as soon as possible.
For OpenStack environments, users often choose to backup and restore VMs. If certain VMs fail, users don’t have the restore the whole hosts because this will influence other working VMs. Just restoring the failed VMs on the working host will simply fix the problem. This only works for on-site disaster recovery, and for offsite disaster recovery, users still need to build a remote DR center for storing backup data or restarting business systems.
Disaster recovery often includes HA, High Availability, which will ensure business continuity by switching the VM from the problematic server to a working server. For OpenStack HA, node redundancy of Cloud Controller Node, Neutron Controller Node, Storage Controller Node, Compute node is the most basic requirement. According to the features and requirements of the software deployed on every node, different HA modes will be applied to these nodes.
How to backup and restore OpenStack VM?
To build a highly efficient disaster recovery system for OpenStack, the powerful software is essential. Vinchin is an official supporting organization of OpenStack and Vinchin Backup & Recovery can help backup and restore OpenStack VM agentlessly.
Except for basic data protection, Vinchin Backup & Recovery can also facilitate OpenStack disaster recovery. You don’t have to deploy another software for transmitting VM backup data between the primary site and the secondary site. After you have created the backup job of OpenStack VM in Vinchin Backup & Recovery, you can also create a job to copy the backup data to the secondary site regularly.
Except for the remote site, you can also send the copy of backup to the public cloud like Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, etc. When you need to recover the VM, just download the backup data from the cloud.
A user-friendly web console will help you create the backup backup job.
1. Select the VMs of OpenStack
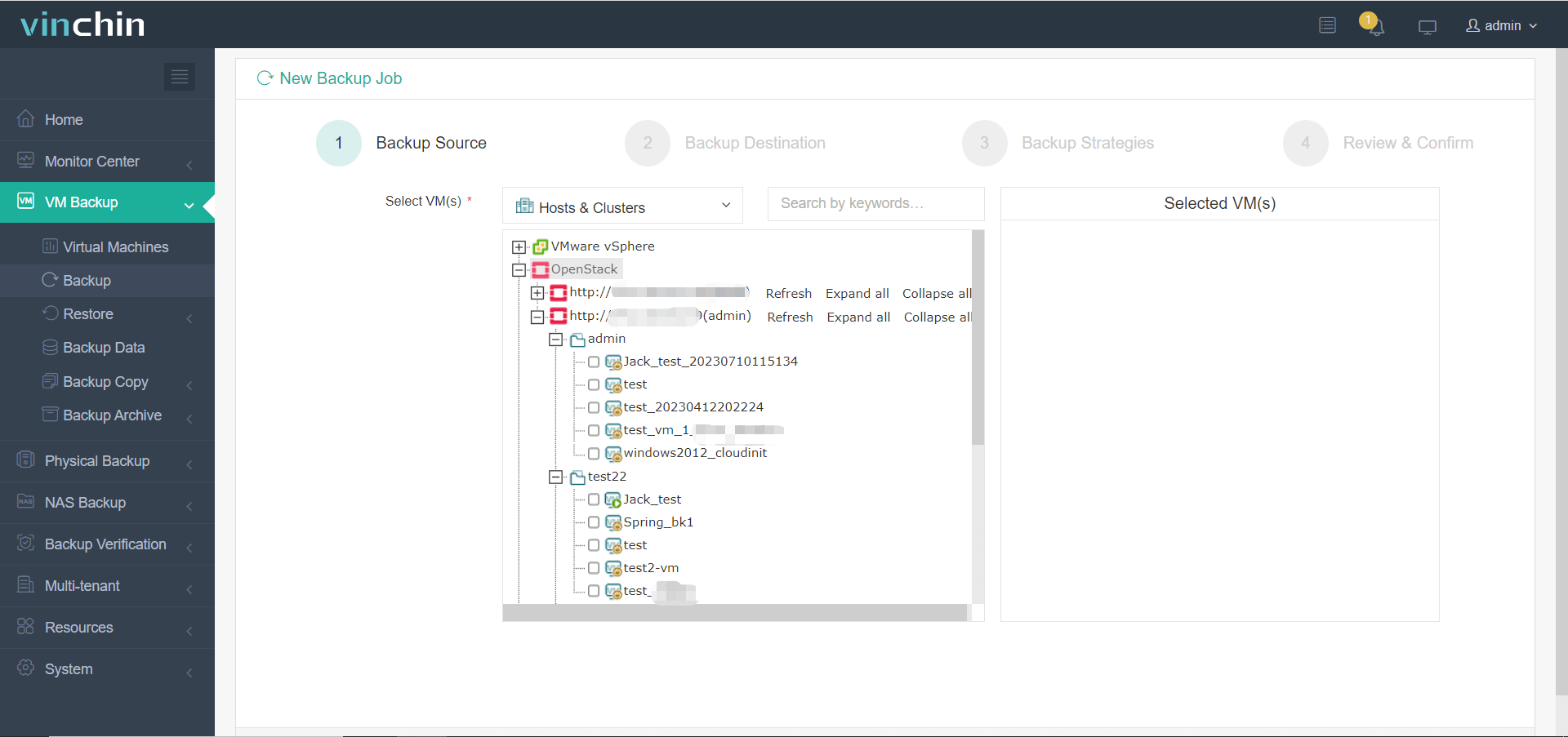
2. Select the storage to store the backup

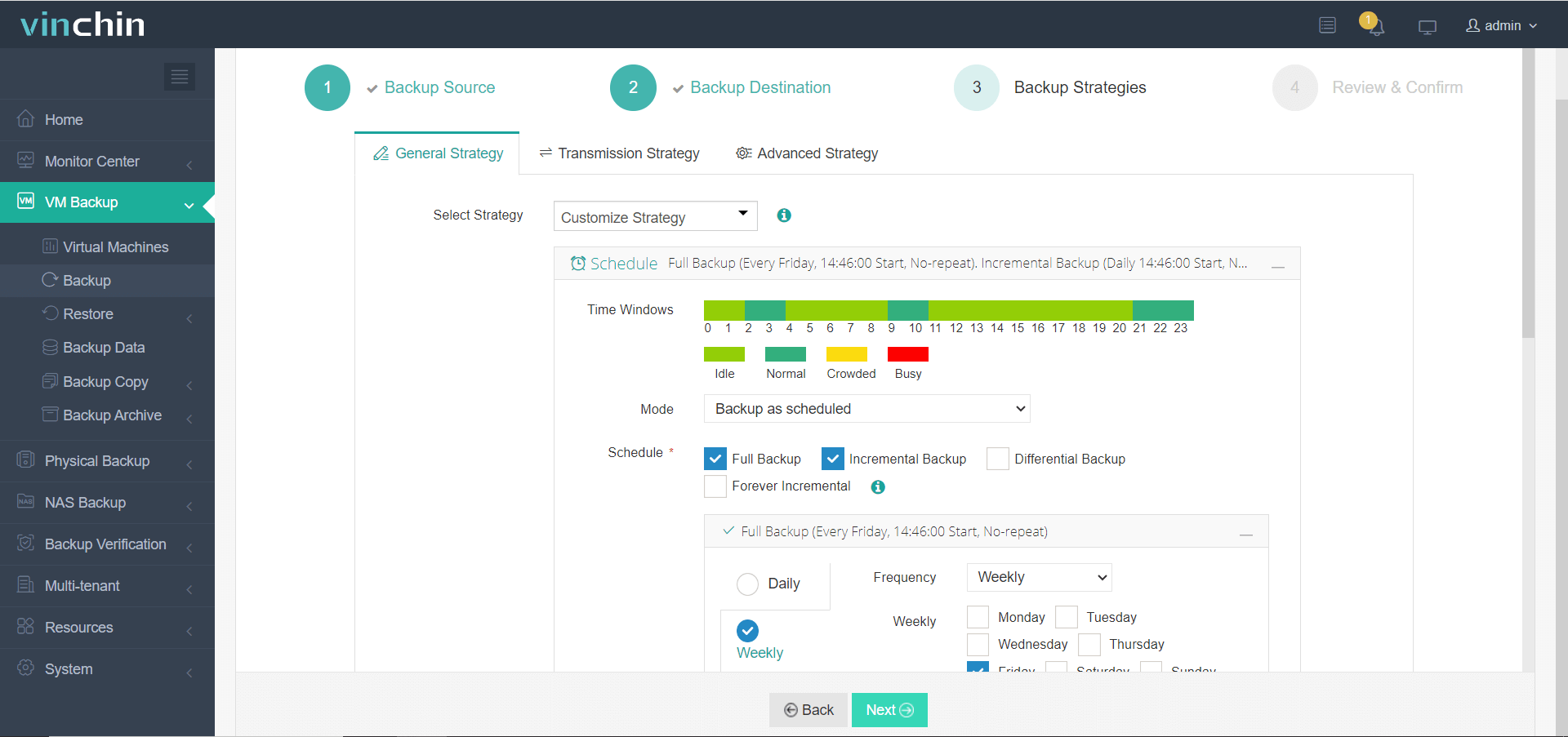
3. Select the backup strategies
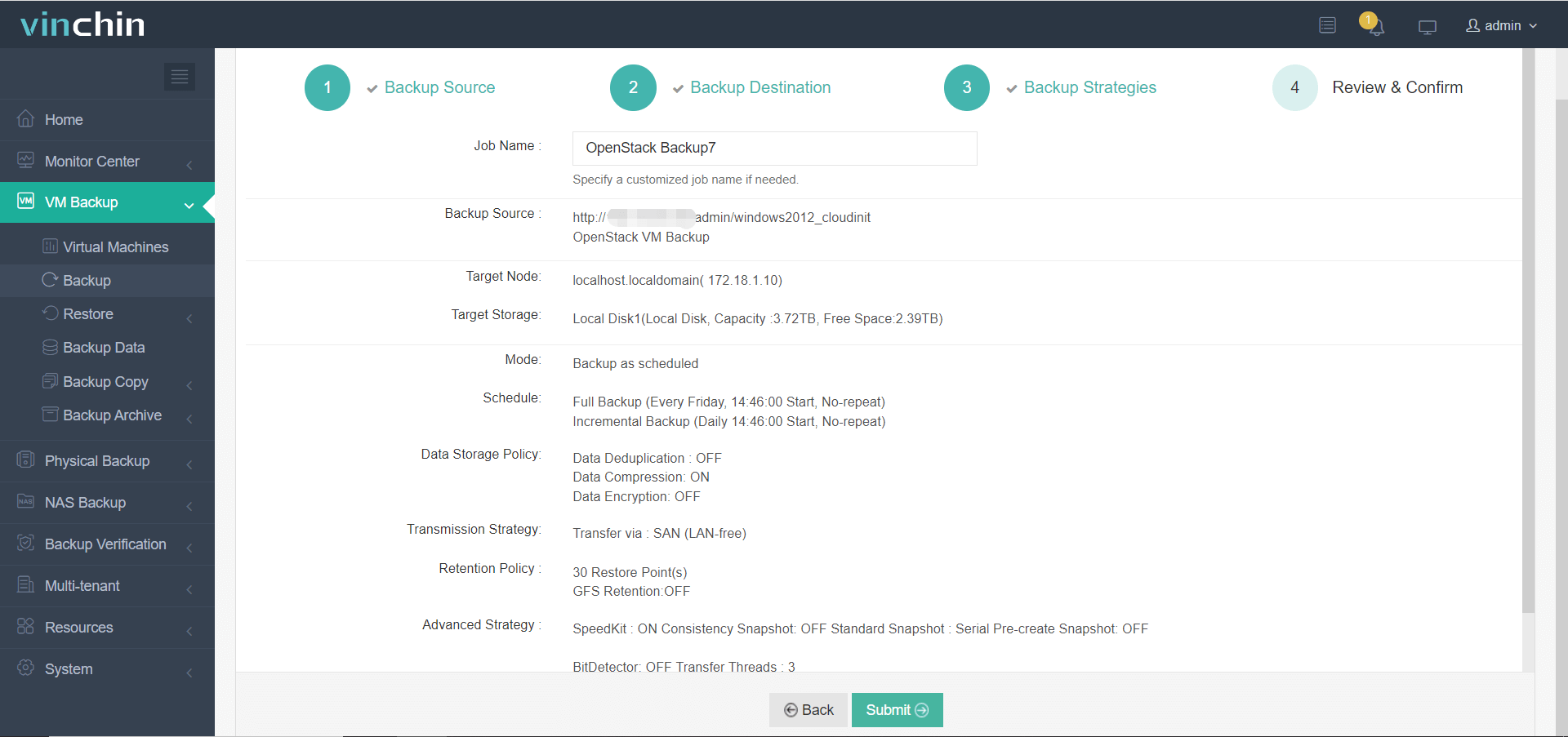
4. Submit the job
Vinchin Backup & Recovery has been selected by thousands of companies and you can also start a 60-day full-featured free trial here. Also, contact us, leave your requirements, and then you will receive your tailored solution. We have established partnerships with reputable companies all over the world so if you would like to do a local business, you can select a local partner here.
OpenStack Disaster Recovery FAQs
1. Why is disaster recovery important for OpenStack environments?
OpenStack is commonly used in the telecommunications industry to deploy large-scale virtual environments, ranging from hundreds to thousands of VMs. To avoid the poor experience for end users caused by downtime, planning for disaster recovery in advance can help enterprises and customers avoid significant losses.
2. Can you take just OpenStack VM snapshots for disaster recovery?
No. Although snapshots can restore VM data to a specific point in time, their disaster recovery capabilities are not as robust as backups. This is because snapshots rely on local data and are often stored in the same storage as the local data. If any of them is lost, the VM data cannot be recovered.
3. How do you plan a disaster recovery site for OpenStack?
It is recommended to have at least one off-site storage to save OpenStack backup data and a further disaster recovery measure is to deploy an identical OpenStack environment in a different location. If the local site is unable to operate due to a disaster, the offsite OpenStack environment can take over the relevant operations.
Sum Up
OpenStack is an open-source cloud computing infrastructure widely used for large-scale cloud computing like telecommunication and IT service. To protect the business systems supported by it, users should build a disaster recovery system in case of any disasters that destroy the local system and influence the business.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an officially verified disaster recovery solution for OpenStack and it will help easily build a highly efficient disaster recovery system. Don’t miss the free trial.
Share on:








