-
How important is disaster recovery?
-
Challenges of traditional disaster recovery solutions
-
What is Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)?
-
How does DRaaS work?
-
Is DRaaS right for you?
-
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
-
DR as a service FAQs
-
Conclusion
How to protect an enterprise’s critical digital assets and improve disaster recovery capabilities after disruptive events such as natural disasters, power outages, technical failures, or cyberattacks is one of the key concerns for companies in the security field. With the continuous advancement of disaster recovery technologies, many companies today offer products, technologies, or services that can meet the needs of modern businesses and their clients. Among these, a representative solution for ensuring business continuity is Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS).
How important is disaster recovery?
How important is disaster recovery? Statistics show that 93% of businesses that experience a data center outage lasting 10 days or more typically go bankrupt within a year. Disasters often strike unexpectedly, and when major disasters occur, the control measures established during normal operations may no longer be effective. How can an organization protect its core operations from being disrupted and minimize the risks caused by disasters? That’s exactly what disaster recovery is intended to address.
Disasters affecting data centers can occur in various forms, such as power failures, hardware malfunctions, human error, or natural disasters. Numerous cases have demonstrated that business interruptions are not a matter of “if” but “when.” Therefore, any organization with IT systems must be prepared for potential disruptions at any time. Ensuring business continuity means ensuring operations keep running under any circumstances—critical systems and networks must remain continuously available.
Challenges of traditional disaster recovery solutions
Traditional disaster recovery plans rely on very complex processes and infrastructure: replicating data centers, duplicating server infrastructures, transferring data to recovery sites, restarting servers, reinstalling operating systems, and so on. Because disaster recovery can be extremely complex and costly, many enterprises find themselves only able to provide proper protection for a few critical workloads, while other workloads remain unprotected or insufficiently protected.
As data center modernization has advanced significantly, IT systems are becoming increasingly complex, with growing demands for availability and ever-increasing volumes of data. Therefore, protecting IT resources, ensuring availability, and being able to recover operations quickly according to plan in the event of unexpected disasters has become a top priority for today’s IT leaders. In traditional IT architectures, companies must build their own disaster recovery systems to mitigate risks—this involves heavy investments in software and hardware, coordination between recovery systems, and detailed recovery planning. However, self-built recovery systems are not only costly but also face barriers such as low resource utilization, difficulty conducting drills, and a lack of professional support teams.
What is Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)?
VMware defines DRaaS as a new cloud computing service model that allows enterprise organizations to back up their data and critical IT infrastructure information in a third-party cloud environment, and provides corresponding disaster recovery orchestration services.After a disaster, access to IT infrastructure, software functionality, and data can be quickly restored through a SaaS business model.
Essentially, DRaaS delivers disaster recovery as a service. Professional third parties provide either the tools, services, or both, allowing organizations to replicate their workloads to data centers managed by the providers. Compared with traditional disaster recovery technologies, this cloud-based model—DRaaS—can easily provide higher agility, enabling businesses to operate remotely in near-normal fashion while the original site is being restored.
Advantages of DRaaS:
Multi-site: Since DRaaS is 100% cloud-based, resources are replicated across many different sites to ensure continuous backup in case one or more sites become unavailable.
Array-agnostic: DRaaS can replicate any environment without favoring a particular vendor or platform.
Granular or full protection: Depending on customer needs, organizations can reduce costs by protecting only the data that truly needs to be backed up.
How does DRaaS work?
DRaaS works by replicating and hosting servers at a third-party vendor’s facility instead of at the physical location of the organization that owns the workloads. If a disaster causes the client site to shut down, the disaster recovery plan is executed at the third-party provider’s facility. Organizations can purchase DRaaS plans via a traditional subscription model or a pay-as-you-go model, which allows them to pay only when a disaster occurs. The scope and cost of such “as-a-service” solutions vary—organizations should evaluate potential DRaaS providers based on their unique needs and budget.
DRaaS eliminates the need for organizations to set up and maintain their own off-site disaster recovery environments, thus saving money. However, organizations should carefully review and understand the service level agreements. For example, what happens to recovery times if both the provider and the client are affected by the same natural disaster (e.g., a major hurricane or earthquake)? Different DRaaS providers have different strategies for prioritizing which clients receive assistance first during large-scale regional disasters or for allowing clients to perform their own disaster recovery tests.
Is DRaaS right for you?
Organizations can choose to hand over all or part of their disaster recovery plans to a DRaaS provider. There are several DRaaS models available, mainly including the following three:
Managed DRaaS: In this model, the third party takes full responsibility for disaster recovery. Choosing this option requires close communication between the organization and its DRaaS provider to ensure the provider is up to date on all changes to infrastructure, applications, and services. If your organization lacks the expertise or time to manage its own disaster recovery, this may be the best option.
Assisted DRaaS: If you want to retain responsibility for some aspects of the disaster recovery plan, or if you have unique or customized applications that may be difficult for a third party to take over, assisted DRaaS may be a better option. In this model, the provider offers expertise to optimize disaster recovery processes, but the customer is responsible for implementing part or all of the plan.
Self-service DRaaS: The cheapest option is self-service DRaaS, where the customer is responsible for planning, testing, and managing the disaster recovery process. The customer hosts backups of their infrastructure on virtual machines at remote locations. This option requires careful planning and testing to ensure that systems can be immediately failed over to virtual servers in the event of a disaster. It’s best suited for organizations with experienced disaster recovery professionals on staff.
For example, VMware offers different solutions. If you want to drive your own DRaaS solution to your own target DR site, you might consider solutions like Site Recovery Manager and VMware vSphere Replication. If you prefer to use VMware Cloud on AWS, you might consider VMware Cloud Disaster Recovery and VMware Site Recovery.
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional solution designed to provide data protection and disaster recovery for virtualized environments. It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc. Tailored for virtual environments, Vinchin offers automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. With data encryption and ransomware protection.
With agentless backup feature, it enables quick integration of VMs into the backup system. It offers disaster recovery features such as Instant Restore to reboot VMs from backups in seconds, offsite copy for remote backup storage, and automatic backup verification for integrity checks. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
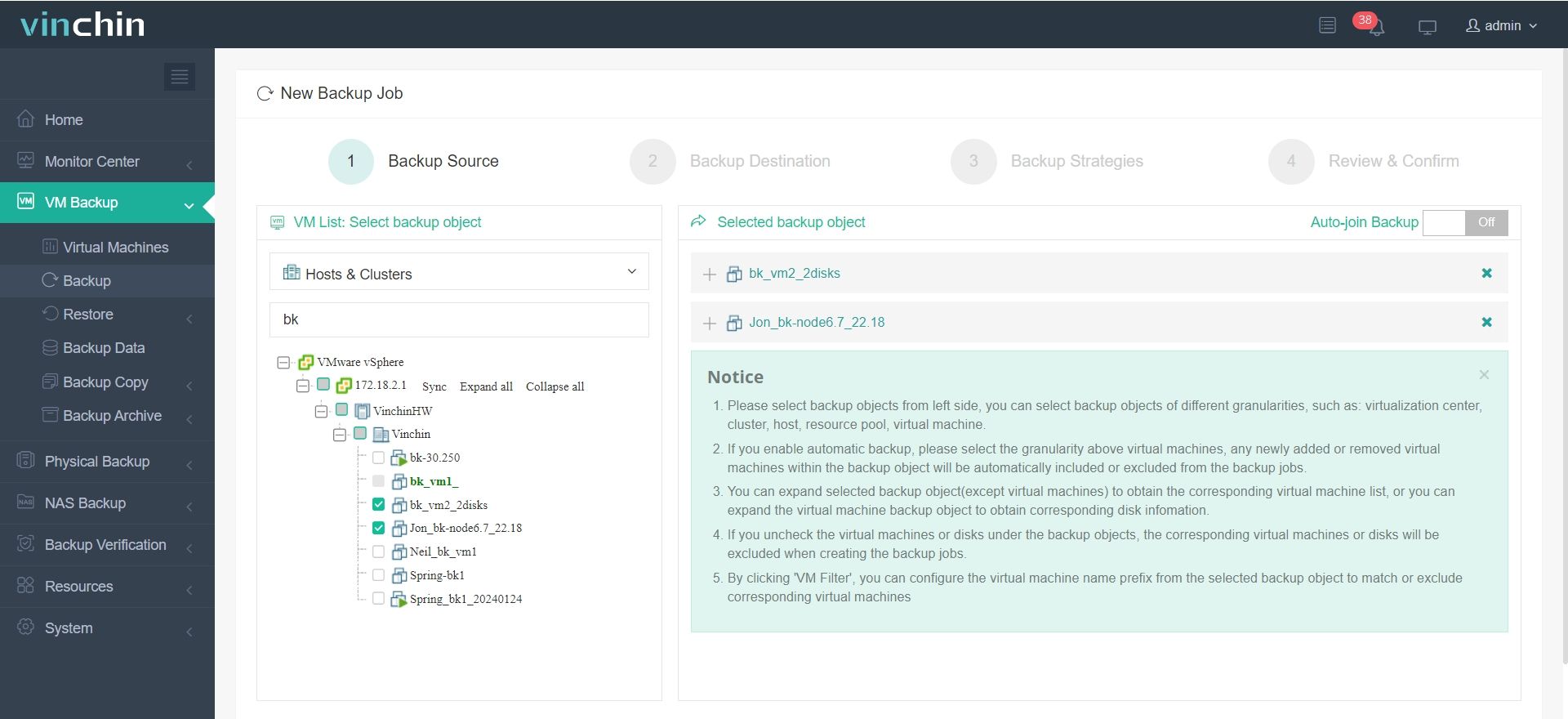
2.Select backup destination.
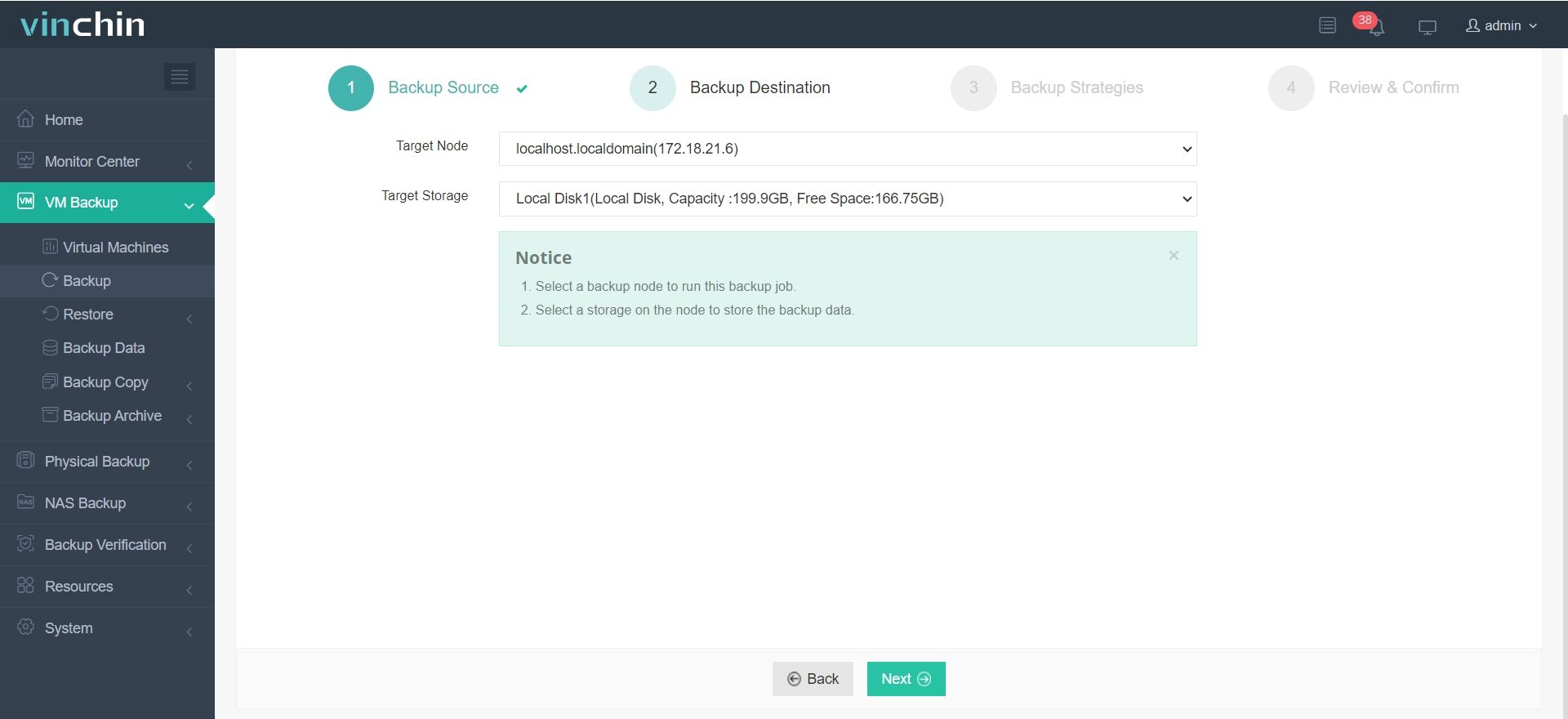
3.Configure backup strategies.
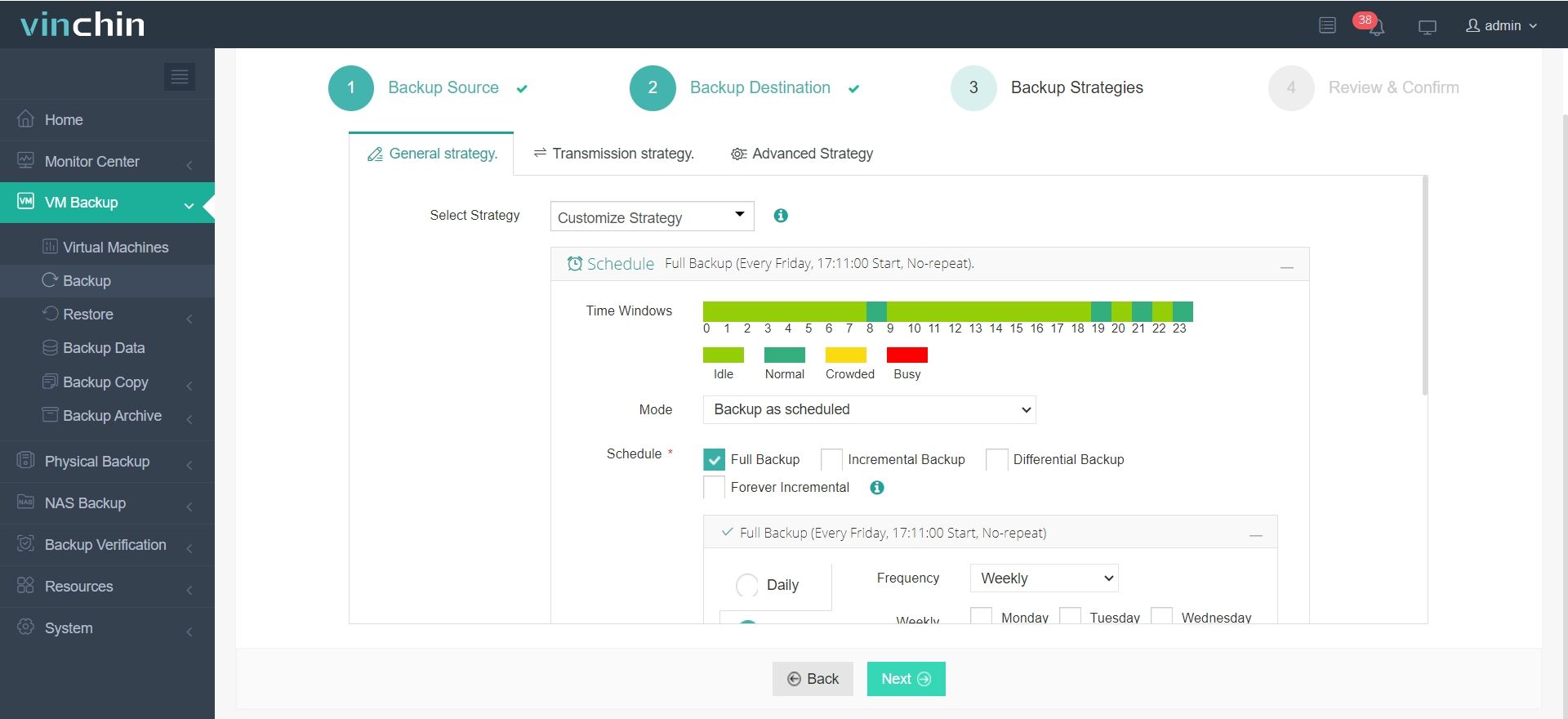
4.Review and submit the job.
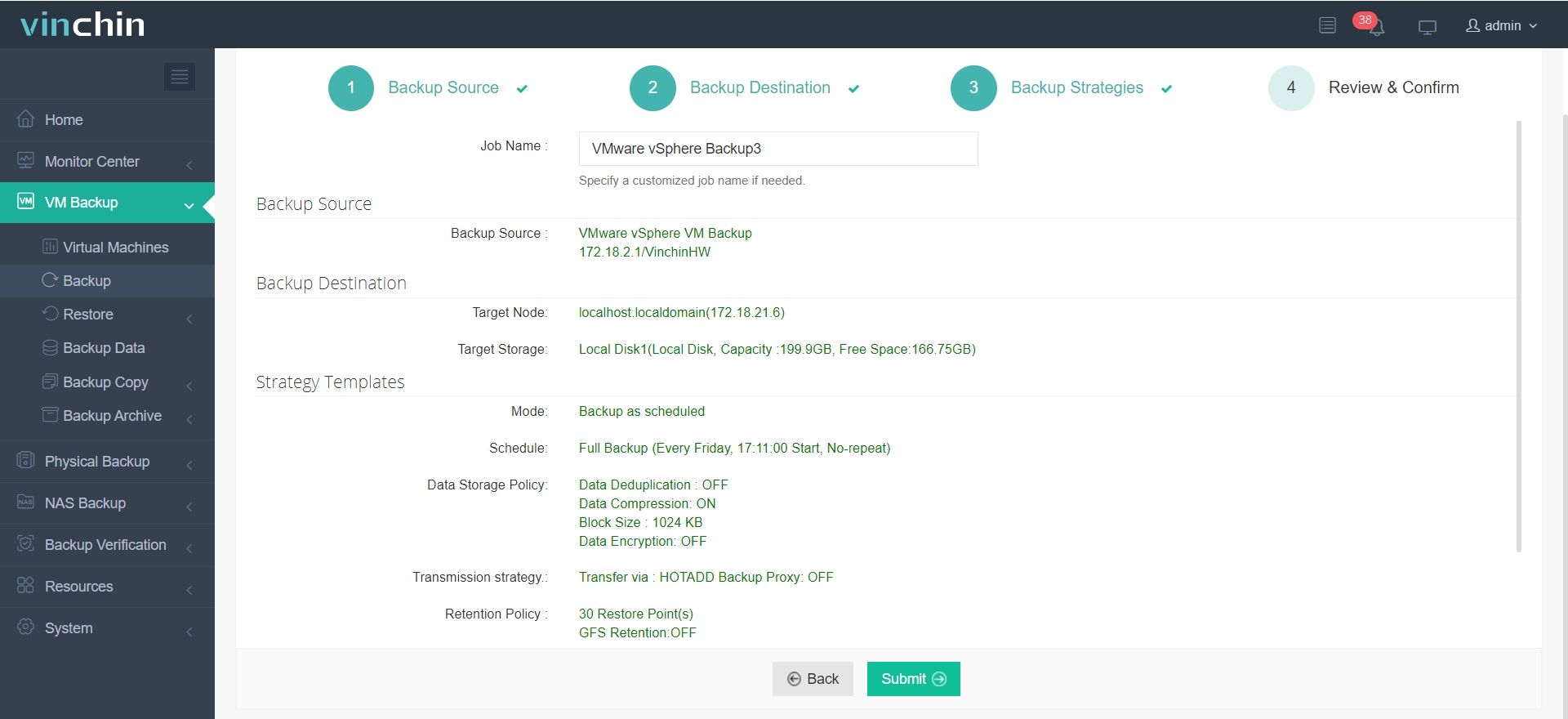
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
DR as a service FAQs
1. How is DRaaS different from Backup as a Service (BaaS)?
The difference between Disaster Recovery as a Service and Backup as a Service is that BaaS focuses solely on data backup, whereas DRaaS offers a complete backup—including servers, data, software functionality, and IT infrastructure. Therefore, DRaaS is relatively more expensive.
2. What is the difference between DR and DRaaS?
DR is a self-managed disaster recovery plan using your own infrastructure. DRaaS is a cloud-based, provider-managed service that handles disaster recovery for you.
Conclusion
DRaaS is becoming one of the most popular approaches in data centers, not only strengthening their disaster recovery strategies but also serving as a method for general data protection. It enables quick, efficient, and frequent backups of applications, helping organizations meet the needs of application owners. The same efficiency also allows IT teams to provide solid protection for end-user desktops and laptops.
Share on:








