-
What is vSphere Command-Line Interface?
-
Install vSphere CLI on Linux
-
Install vSphere CLI on Windows
-
Backup and Manage ESXi VMs More Smartly
-
Conclusion
The command line interface enables immediate results from commands input for IT pros, software developers, and network administrators. But it can be complicated involving many commands in different tools. VMware provides serval command-line interface tools for the management of virtual machines and vSphere including PowerCLI, DCLI, and vSphere CLI.
What is vSphere Command-Line Interface?
vSphere Command-Line Interface (vCLI) is an administration tool for VMware virtual environments built on vSphere SDK for Perl. It comes as a standalone installer available on Linux and Windows. The most recent version is 6.7 in 2018.
You can run system administration commands against ESXi systems and automate routine processes like establishing and managing storage for ESXi hosts and configuring VM networks that you conduct when deploying and maintaining your virtual data center.
It contains a series of commands for host management such as ESXCLI, vicfg, DCLI, and others listed as follows:
| Command | Description |
| esxcli device | Descriptions for device commands. |
| esxcli esxcli | Descriptions for esxcli commands. |
| esxcli fcoe | FCOE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet) commands |
| esxcli graphics | Commands for Graphics |
| esxcli hardware | Namespace for hardware. used largely to extract data about the present system configuration. |
| esxcli iscsi | iSCSI namespace for controlling and watching over iSCSI-enabled hardware and software. |
| esxcli network | Network namespace for controlling virtual switches and VMkernel network interfaces. |
| esxcli nvme | NVMe devices management commands. |
| esxcli rdma | RDMA devices monitoring commands. |
| esxcli sched | Control the shared system-wide swap space. |
| esxcli software | Software namespace that contains commands for managing and installing image profiles and VIBs. |
| esxcli storage | Commands for managing storage and core storage commands. |
| esxcli system | Commands for monitoring and managing system. |
| esxcli vm | Namespace for listing virtual machines and turning them off forcefully. |
| esxcli vsan | Namespace for managing Virtual SAN commands. |
| svmotion | Migrates the configuration file and optionally disks for a running virtual machine in a vCenter Server system. |
| vicfg-advcfg | Enabling and disabling CIM providers. |
| vicfg-authconfig | Handles Active Directory authentication. |
| vicfg-cfgbackup | Backs up an ESXi system's configuration file and restores the previously saved data. |
| vicfg-dns | Specifies the DNS (Domain Name Server) setup for an ESX/ESXi host. vicfg-dumppart Manages diagnostic partitions. |
| vicfg-hostops | Enables you to command ESX/ESXi hosts to go into maintenance mode and come out of maintenance mode, as well as to start, stop, and analyze those hosts. |
| vicfg-ipsec | IPSec setup. |
| vicfg-iscsi | iSCSI storage management. |
| vicfg-module | Enables VMkernel options. |
| vicfg-mpath | Displays details about storage array pathways and gives you the option to modify a path's status. |
| vicfg-nas | NAS file systems management. |
| vicfg-nics | ESX/ESXi host's NICs (uplink adapters) management. |
| vicfg-ntp | Defines the NTP (Network Time Protocol) server. |
| vicfg-rescan | Rescans the storage setup. |
| vicfg-route | Lists or modifies the route entry (IP gateway) for ESX/ESXi hosts. |
vicfg-scsidevs | Locates available LUNs. |
| vicfg-snmp | The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent management. |
| vicfg-syslog | Defines the syslog server and the port for ESXi hosts to connect to that server. |
| vicfg-user | Enables the creation, modification, erasure, and listing of local direct access users and user groups. |
| vicfg-vmknic | Adds, removes, and changes virtual network adapters (VMkernel NICs). |
| vicfg-volume | Resignaturing, mounting, and unmounting of VMFS snapshot volumes. |
| vicfg-vswitch | Adds or removes virtual switches or vNetwork Distributed Switches, or changes switch settings. |
| vifs | Performs file system activities such as retrieving and uploading files on the remote server. |
| vihostupdate | ESX/ESXi hosts update management. Use vihostupdate35 for ESXi 3.5 hosts. |
| vmkfstools | Creates and manages virtual disks, file systems, logical volumes, and physical storage devices on ESX/ESXi hosts. |
vmware-cmd | Perform remote virtual machine activities. |
Install vSphere CLI on Linux
Applies to:
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 5.2 64/32 bit;
SUSE Enterprise Server 10 SP1 32 bit;
Ubuntu 8.04 32 bit.
1. Download the installer package from vmware.com.
2. Open a shell prompt and go to the directory where you download the package.
3. Unzip the package.
4. Launch the installer (vmware-install.pl).
5. Input yes at the prompt and hit Enter.
6. Define the installation directory or press Enter for the default (/usr/bin).
7. Run commands to verify the installation.
a. Launch the command prompt.
b. Change to the installation directory.
c. Run the command.
<command> <conn_options> <params>
Uninstall the package
1. Connect to the installation directory.
2. Run the vmware-uninstall-vSphere-CLI.pl script
Install vSphere CLI on Windows
Applies to:
Windows XP SP2 32/64 bit;
Windows Vista Enterprise SP1 32/64 bit.
1. Download the installer package from vmware.com.
2. Launch the installer.
3. Click Next on the Welcome page, and click Change to modify the installation directory, or stay with the default (s C:Program FilesVMwareVMware vSphere CLI). Click Next.
4. Click Install.
5. Run commands from the Windows command prompt.
a. Launch the command prompt.
b. Change to the installation directory.
c. Run the command.
<command>.pl <conn_options> <params>
Note: .pl is not required for esxcli.
Uninstall the package
1. Go to Start> Settings> Control Panel> Add or Remove Programs.
2. Choose vSphere CLI> Remove in the panel.
3. Click Yes.
Backup and Manage ESXi VMs More Smartly
vSphere CLI is a management utility to automate daily jobs, however, memorizing a huge amount of commands is a hard task, and you could copy the wrong commands and accidentally delete or move files to the wrong location even if you do copy-paste. Not to mention its termination since vSphere 7. You can use a GUI tool to take over CLI.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a backup solution certified by VMware Ready and centrally manages the backups of 12 virtualizations such as VMware, Hyper-V, XCP-ng, XenServer, Oracle OLVM, etc., 6 databases, NAS, and Linux & Windows Servers in one console.
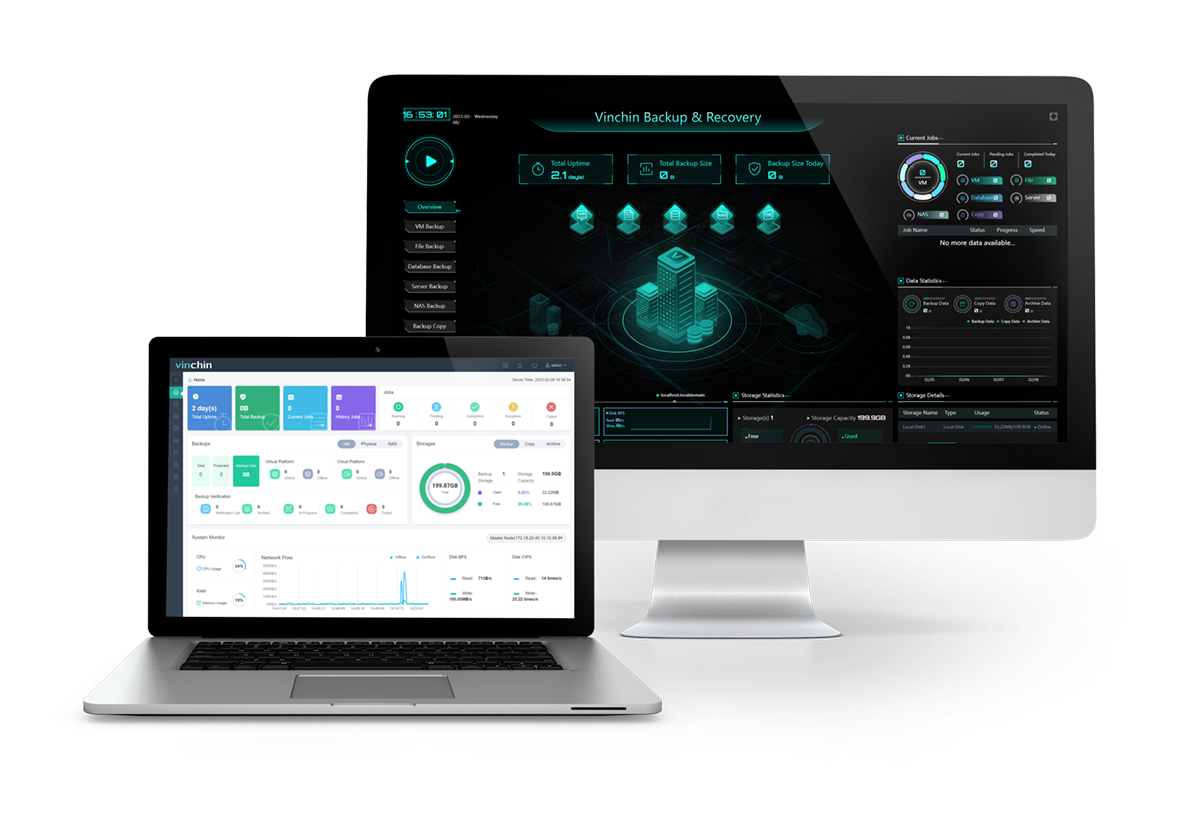
You can automate VM backup under schedule and perform instant recovery in seconds from the backup repository, while reassuring that storage and speed are both maximized due to data deduplication and compression, CBT incremental backup, HotAdd, and other techniques.
You can perform worry-free V2V migration to and from 10+ platforms without any migration tools or command lines.
You can get a 60-day full-featured free trial now to test other advanced features like anti-ransomware Backup Storage Protection or data archiving.
Conclusion
vSphere CLI is a command line tool to manage virtual machines in VMware environments and automate day-to-day tasks, but you should note that although it is still available on the VMware website, it has been terminated since vSphere 7, and its capabilities will be supported with API centric tools.
You can opt for Vinchin Backup & Recovery to backup automatically and manage backups of VMware and other platforms in a web pane.
Share on:








