-
What is Tape Vaulting?
-
The Importance of Tape Vaulting
-
Two Types of Tape Vaulting
-
The Tape Vaulting Process
-
Tape Vaulting vs. Modern Cloud Solutions
-
How to Choose an Offline Tape Vaulting Service?
-
Protect Your Data with Vinchin
-
Conclusion
In the era of digital transformation, organizations generate vast amounts of data daily. While cloud-based storage solutions are popular, tape vaulting remains a critical component of long-term data preservation strategies for many enterprises.
What is Tape Vaulting?
Tape vaulting is the practice of securely storing backup tapes in offsite locations to ensure data protection and disaster recovery. Unlike traditional on-premises storage, tape vaulting involves transferring physical tape cartridges to a secure, remote facility to protect them from local risks such as fire, flooding, theft, and cyberattacks. These facilities, often referred to as tape vaults, are designed with advanced security measures and environmental controls to preserve the integrity of the data stored on tapes.
The Importance of Tape Vaulting
Tape vaulting offers several critical advantages for businesses that need to ensure long-term data retention and regulatory compliance:
Disaster Recovery: In the event of a catastrophic event, having offsite tape backups ensures that an organization can recover its essential data and resume operations.
Data Security: Storing tapes in a secure, monitored facility reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Compliance and Legal Requirements: Many industries have strict regulations regarding data retention. Tape vaulting helps organizations meet these requirements by providing a reliable and auditable storage solution.
Cost-Effective Long-Term Storage: Tapes offer a cost-effective solution for archiving large volumes of data for extended periods compared to other storage mediums.
Two Types of Tape Vaulting
1. Onsite Vaulting (Local Storage)
Backup tapes are stored at the company’s local facility, such as in fireproof safes or dedicated tape storage rooms. This method allows for quick access to the tapes. However, if the local facility is affected by a natural disaster or attack, the tapes could also be damaged.
2. Offsite Vaulting (Remote Storage)
Backup tapes are transferred to a remote, offsite storage facility. This is the more commonly used method, as it effectively reduces the risk of damage from natural disasters, fires, or cyberattacks.
The Tape Vaulting Process
The tape vaulting process involves several key steps to ensure secure data storage and retrieval:
Backup and Tape Creation: Data is backed up from production systems and written to tape cartridges using backup software.
Cataloging: Each tape is cataloged with metadata, including its contents, backup date, and retention period, to facilitate easy tracking and retrieval.
Transport: The tapes are securely transported to the offsite vault using secure courier services that follow chain-of-custody protocols.
Storage: Tapes are stored in a secure, climate-controlled vault with advanced fire suppression systems, access controls, and monitoring.
Retrieval and Rotation: Tapes may be retrieved for data restoration or rotated back to the primary site for reuse. Rotation policies ensure that tapes are regularly refreshed to prevent degradation.
Tape Vaulting vs. Modern Cloud Solutions
While cloud-based solutions have gained popularity, tape vaulting remains relevant for several reasons:
Cost-Effectiveness: For long-term, large-volume data archiving, tape storage is more cost-effective than cloud storage.
Data Sovereignty: Tapes stored in a physical vault ensure organizations maintain complete control over their data.
Offline Storage: Unlike cloud storage, offline tape storage is immune to cyberattacks and ransomware.
Longevity: Tapes have a longer lifespan compared to many digital storage solutions, making them suitable for long-term archival.
How to Choose an Offline Tape Vaulting Service?
Many users who rely on tape systems for backups often hand over their tapes to professional tape vaulting service providers for offsite offline storage. This approach ensures that backup data remains intact even if a disaster such as a fire or hurricane damages the user’s data center. When selecting an offline tape vaulting service, the following factors should be considered:
1. Cost of Offsite Tape Vaulting Services
The cost of tape vaulting services can vary due to hidden fees. Pricing differences may arise from different storage methods, and some providers also charge fuel surcharges. Costs related to tape collection and transportation can fluctuate significantly. For example, frequent onsite tape pickups by technicians or urgent tape retrieval after a disaster will increase expenses. Therefore, users should carefully review the details of service contracts to avoid unexpected charges.
2. Disaster Recovery
Offsite tape storage aims to prevent data loss in case of disasters. An ideal tape vaulting service should store tapes in an environment with magnetic shielding to prevent data erasure due to exposure to magnetic objects or electromagnetic interference. The fire protection measures of the storage facility are also critical. Users should ensure that the storage site is at least NFPA 232 certified, a fire safety standard issued by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) in the U.S., to guarantee the safety of the facility.
3. Physical Security
Tape vaulting services must ensure the physical security of their storage facilities. Since data is taken offsite, it is essential to prevent any damage to tapes caused by physical security issues at the facility. Users should also ensure that all backup tapes are encrypted to protect against potential internal threats from the service provider’s staff.
4. Importance of Service Level Agreements (SLA)
Reputable service providers will sign a Service Level Agreement (SLA) with their clients, detailing service commitments, including the speed of tape retrieval in the event of a disaster. It is not only important to review the SLA terms, but also to verify whether the provider can fulfill their promises. Users should not adjust their disaster recovery process to accommodate the service provider’s limitations. The SLA should include at least a 24/7 tape retrieval service to ensure timely access to tapes regardless of when a disaster occurs.
5. Tracking and Regulatory Compliance
In addition to tape collection, transportation, and storage services, the provider should offer comprehensive tape tracking and audit capabilities. For example, a web-based tape inventory system can allow users to track and verify the status of their tapes to ensure none are lost. Users should carefully select their service provider after thorough preliminary research to reduce long-term costs.
Protect Your Data with Vinchin
Vinchin Backup & Recovery supports both physical and virtual tape libraries as backup storage options, allowing you to store backups on a reliable, long-lasting medium. It supports several types of tape libraries and standlone drives including LTO6 - LTO9, IBM, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, DELL and Quantum.
Vinchin focuses on virtual machine backup, recovery and migration, and supports more than 10 popular virtualization platforms, such as VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, oVirt, XCP-ng, etc. With Vinchin, you can easily copy and archive important backup data to tape libraries for long-term retention.
It takes you 4 steps to back up virtual machines to tape storage using Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the virtual machine to be backed up.
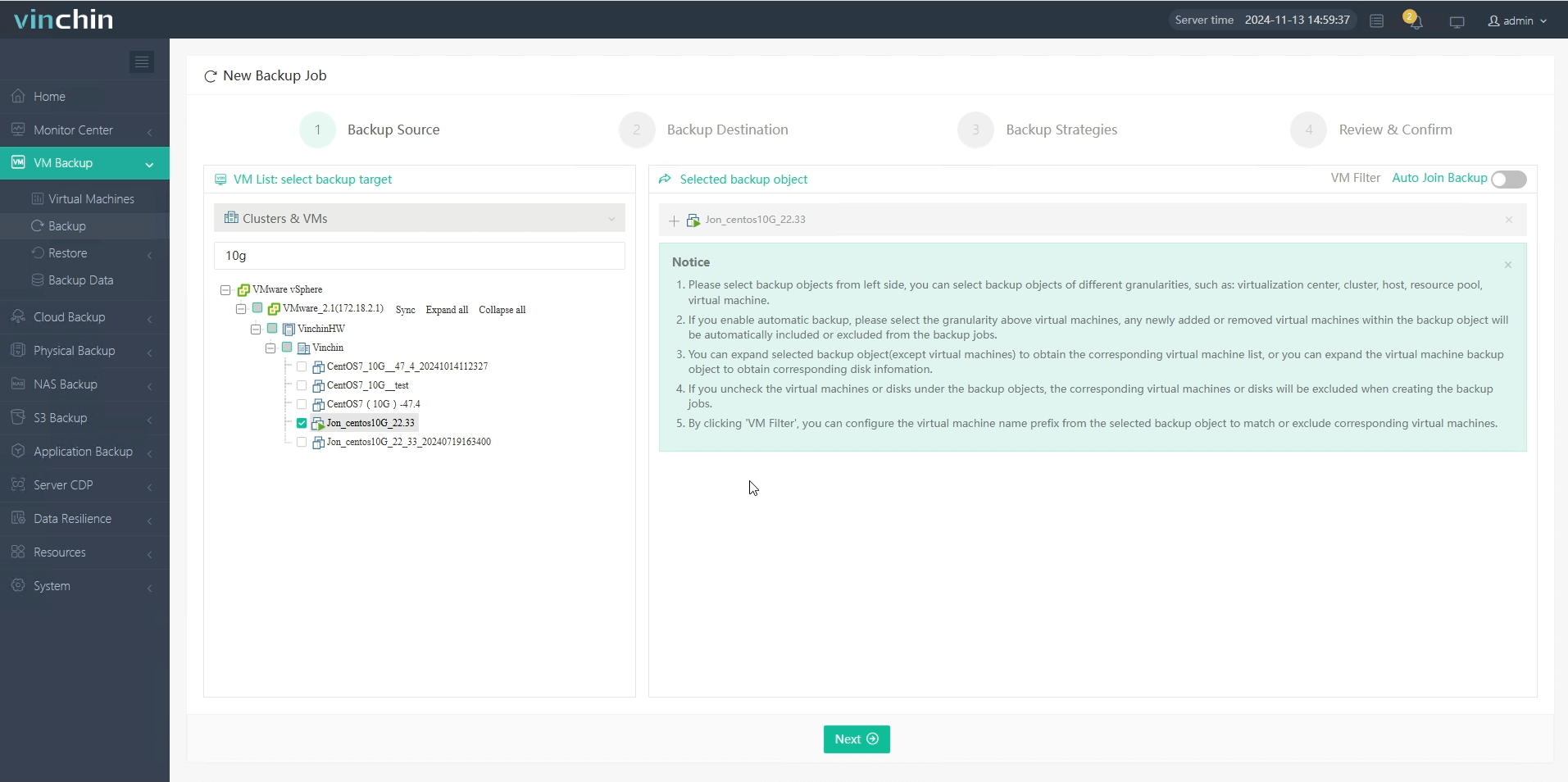
2.Select the backup storage for it.
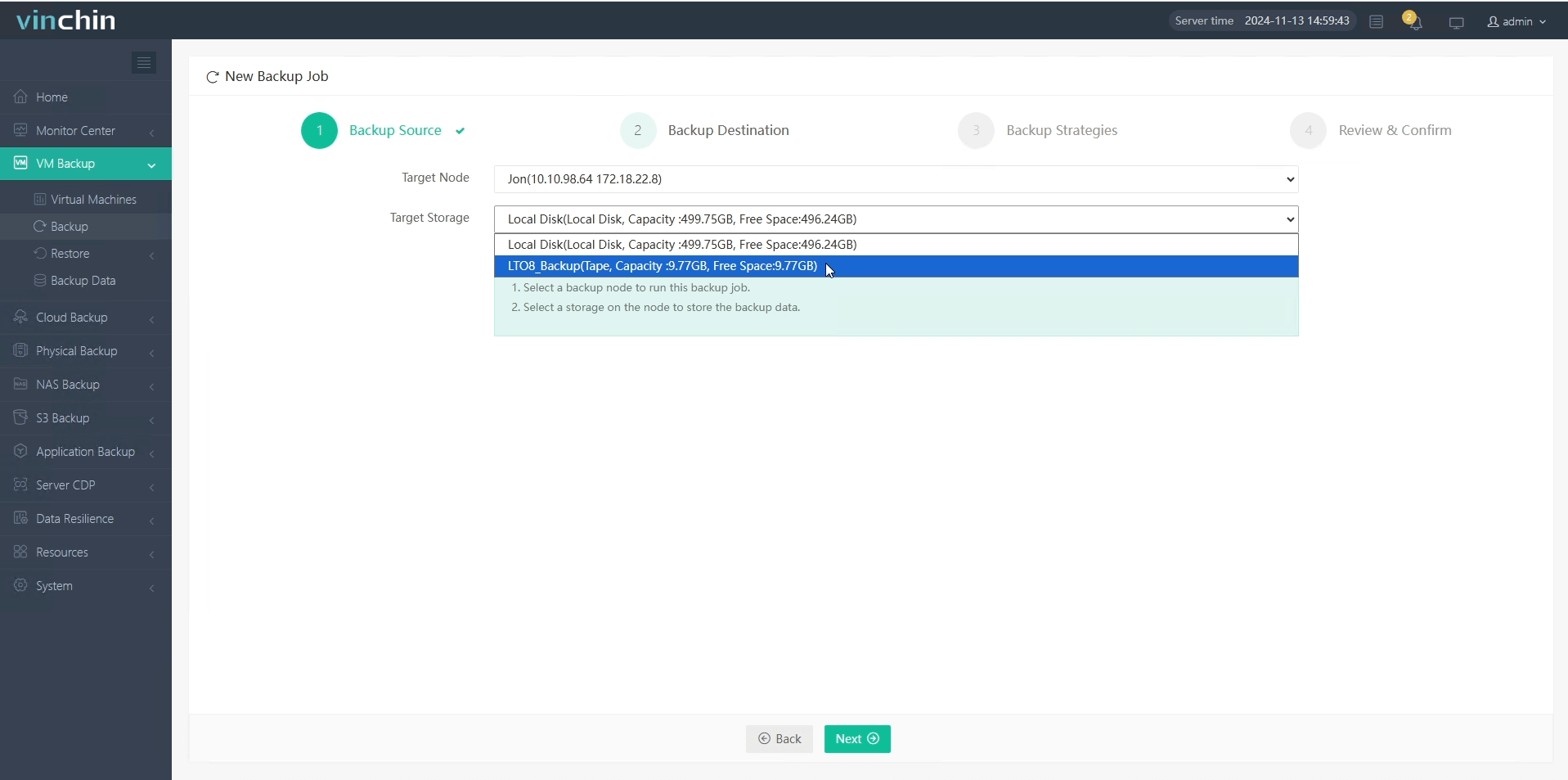
3.Configure the backup strategies.
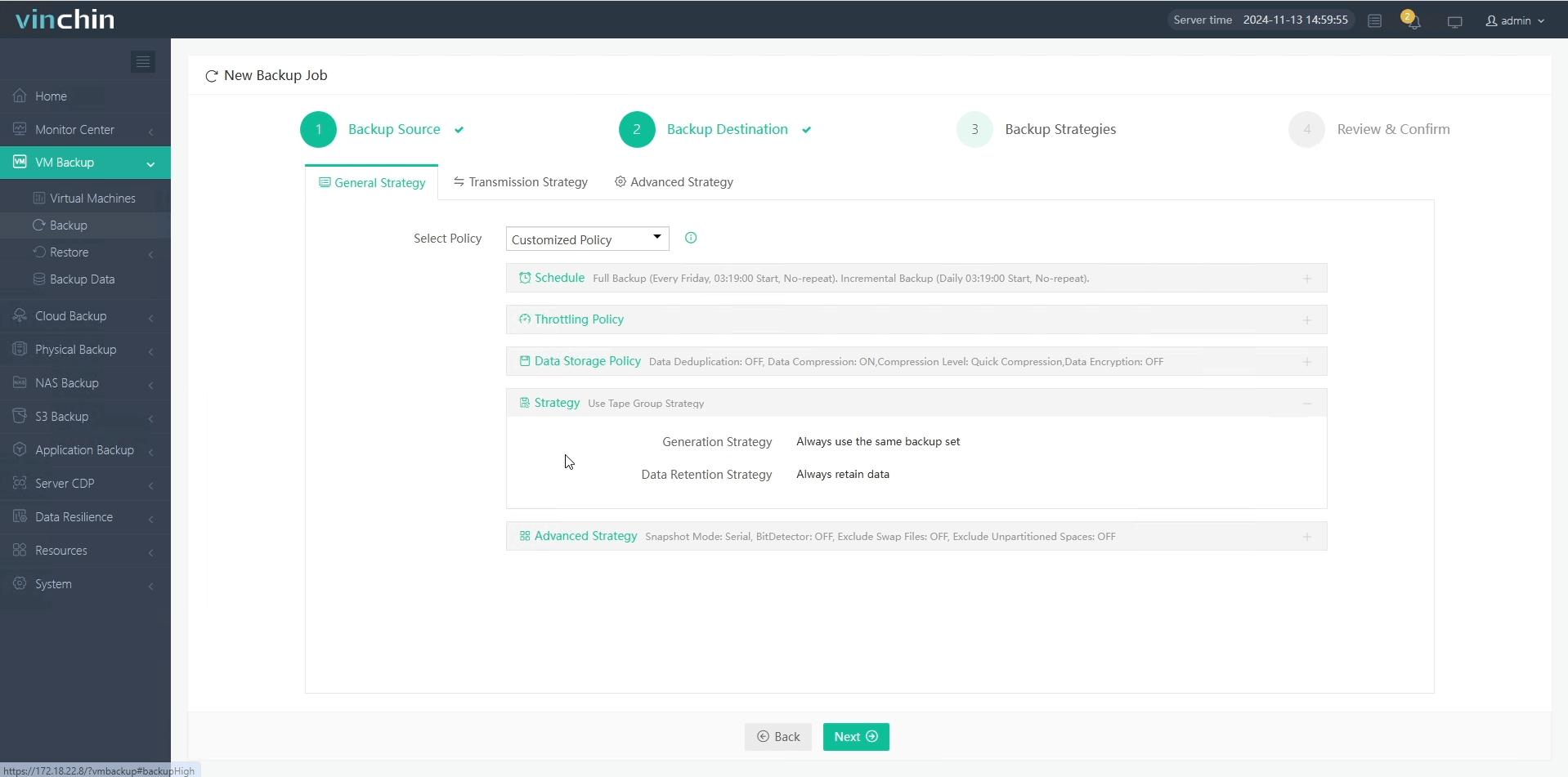
4.Submit the job.
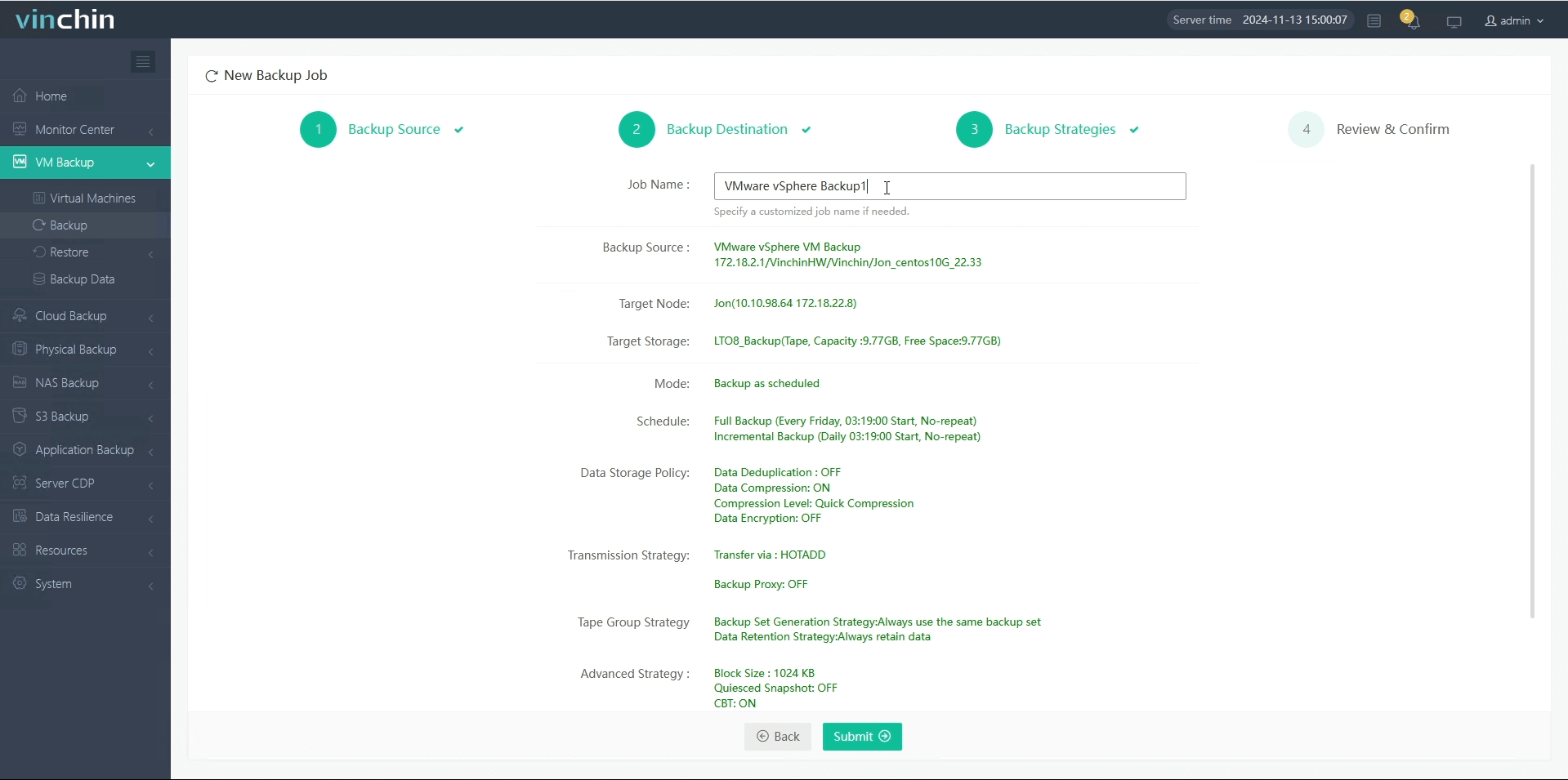
You can click the download button below to try it for 60 days for free and experience more features.
Conclusion
Tape vaulting remains a vital component of comprehensive data protection strategies, especially for organizations with long-term data retention requirements. Its cost-effectiveness, security, and offline nature make it an attractive option for mitigating risks associated with digital-only storage solutions. As technology evolves, tape vaulting continues to adapt, ensuring its relevance in modern IT infrastructures.
Share on:







