-
Introduction to Cinder
-
Key Features of Cinder
-
How Cinder Backup Works
-
Enhanced OpenStack Protection
-
Cinder backup FAQs
-
Conclusion
Cinder is a component in OpenStack that provides block storage services, primarily serving to manage virtual disks for virtual machines. Cinder's predecessor was the "nova-volume", which was separated from Nova and became an independent OpenStack component starting with OpenStack version F. Currently, Cinder already supports snapshot, replication, and backup functions for data volumes.
Introduction to Cinder
Operating systems and applications typically use storage space in two ways: block storage and file system storage.
In OpenStack, Cinder provides block storage services for virtual machines. From the virtual machine's perspective, each mounted volume appears as a hard drive. Cinder manages the entire lifecycle of a volume from creation to deletion, with the following specific features:
Provides a RESTful API to query and manage resources such as volumes, snapshots, and backups;
Uses a scheduler to dispatch volume creation requests, optimizing the allocation of storage resources;
Supports multiple storage backends through a driver architecture, including open-source storage solutions like LVM and Ceph, as well as commercial storage products from NetApp, EMC, IBM, etc.
Cinder consists of four main functional modules: cinder-api, cinder-scheduler, cinder-volume, and cinder-backup, each of which is an independent service process.
cinder-api exposes Cinder services to external clients (such as the Cinder command line, other OpenStack service components, etc.) via a RESTful interface, responsible for converting client HTTP requests into RPC calls between internal components;
cinder-scheduler handles the scheduling of volume creation requests, sending RPC calls to the selected cinder-volume process;
cinder-volume handles specific volume requests (such as creating and deleting volumes);
cinder-backup handles requests related to volume backups (such as creating and restoring backups).
Key Features of Cinder
1. Volume Management: Cinder can create, delete, expand, and shrink volumes. Administrators can create volumes through the API or command line interface, specifying information such as volume size, type, name, and description. When needing to expand or shrink a volume, administrators can perform the operation via API or command line interface.
2. Volume Migration and Replication: Cinder supports volume migration and replication, allowing volumes to be migrated from one storage backend to another or copied within the same storage backend. Administrators can perform these operations via API or command line interface.
3. Backup and Restore: Cinder supports volume backup and restore, enabling volume data to be backed up to other locations for protection. Administrators can create, delete, and restore volume backups and snapshots through the API or command line interface.
4. Storage Backend Support: Cinder supports multiple storage backends, including local storage, iSCSI, NFS, Ceph, GlusterFS, etc. Administrators can select and configure different storage backends based on their needs.
5. Multi-Tenancy Support: Cinder supports multi-tenancy, providing independent block storage services for different tenants, with the ability to limit quotas and permissions for different tenants.
6. High Availability and Fault Tolerance: Cinder is designed with high availability and fault tolerance in mind, ensuring the availability of storage services and the security of data. Cinder supports multiple copies and data redundancy, as well as failover and automatic recovery.
7. Network Interoperability: Cinder can interact with other OpenStack components, such as Nova and Glance, and also supports API and command line interfaces for easy integration with other systems.
How Cinder Backup Works
Backup Creation:
When a user initiates a backup, Cinder reads the data from the source volume and writes it to the configured backup backend.
If incremental backup is enabled, only the differences since the last backup are copied, reducing time and storage usage.
Backup Storage:
Backups are stored in a defined backup backend, which could be Swift, Ceph, or NFS. The backend is configured based on the organization’s storage policies and infrastructure.
Backup Restore:
Users can restore backups to a new or existing Cinder volume. The restore operation fetches the backup data from the storage backend and writes it to the target volume.
The command lines related to Cinder backup are as follows:
backup-create Creates a volume backup.
backup-delete Removes one or more backups.
backup-export Export backup metadata record.
backup-import Import backup metadata record.
backup-list Lists all backups.
backup-reset-state Explicitly updates the backup state.
backup-restore Restores a backup.
backup-show Shows backup details.
Enhanced OpenStack Protection
Although Cinder supports backup functionality, backup and restore operations can be resource-intensive, especially when dealing with large volumes or performing full backups. In addition, the speed of backup and restore depends on the performance of the underlying storage system.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a robust OpenStack backup solution offering agentless, efficient backups with features like data deduplication, compression, incremental backups, file-level recovery and cloud archive, etc. It ensures quick recovery, seamless integration with OpenStack, and strong data security, making it an ideal choice for managing and protecting cloud environments.
Besides, data encryption and ransomware protection offer you dual insurance to protect your OpenStack VM backups. You can also simply migrate data from an OpenStack host to another virtual platform (like VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, oVirt, AWS EC2...) and vice versa.
Backing up OpenStack VM with Vinchin Backup & Recovery only requires the following 4 steps:
1. Select the backup object.
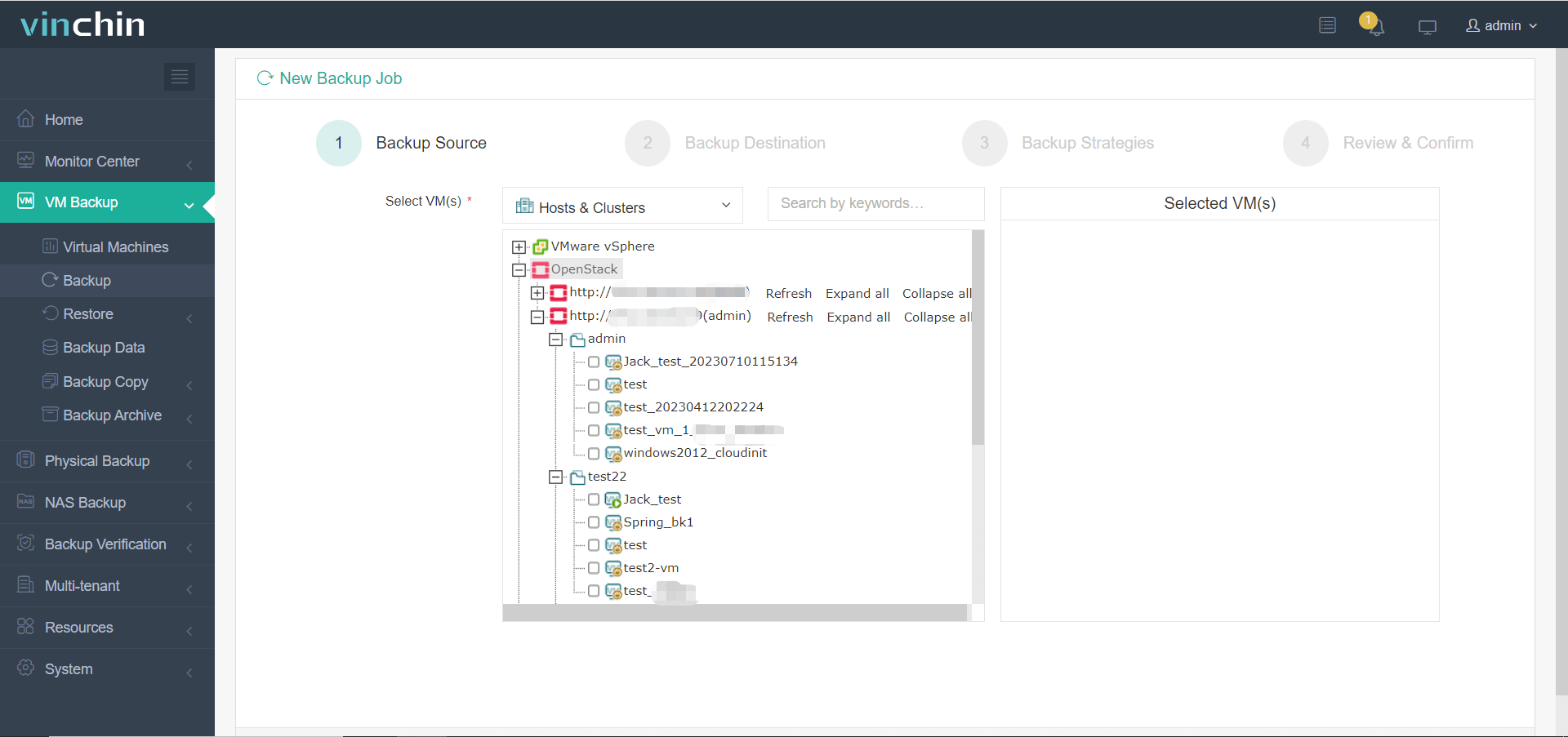
2. Select backup destination.

3. Configure backup strategies.
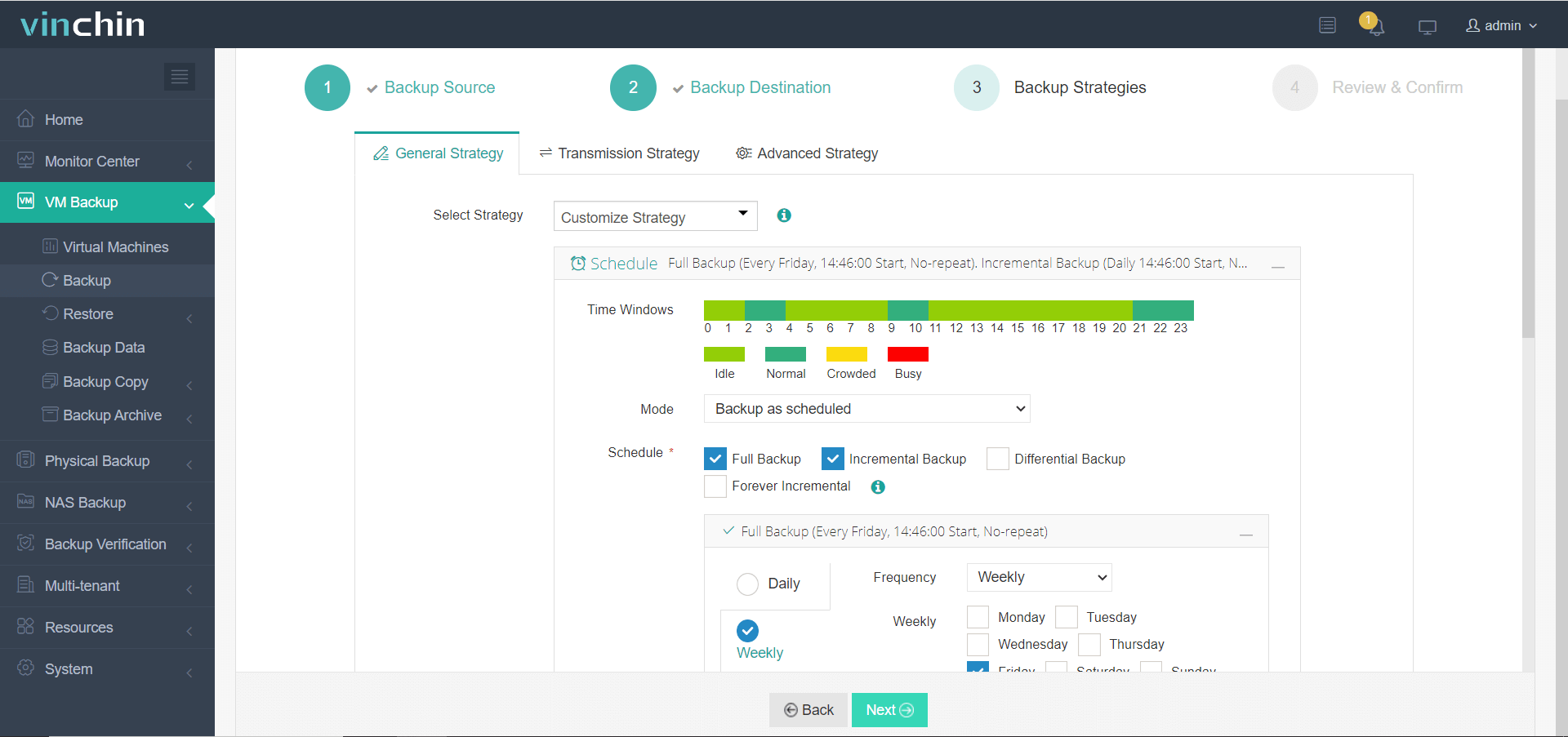
4. Review and submit the job.
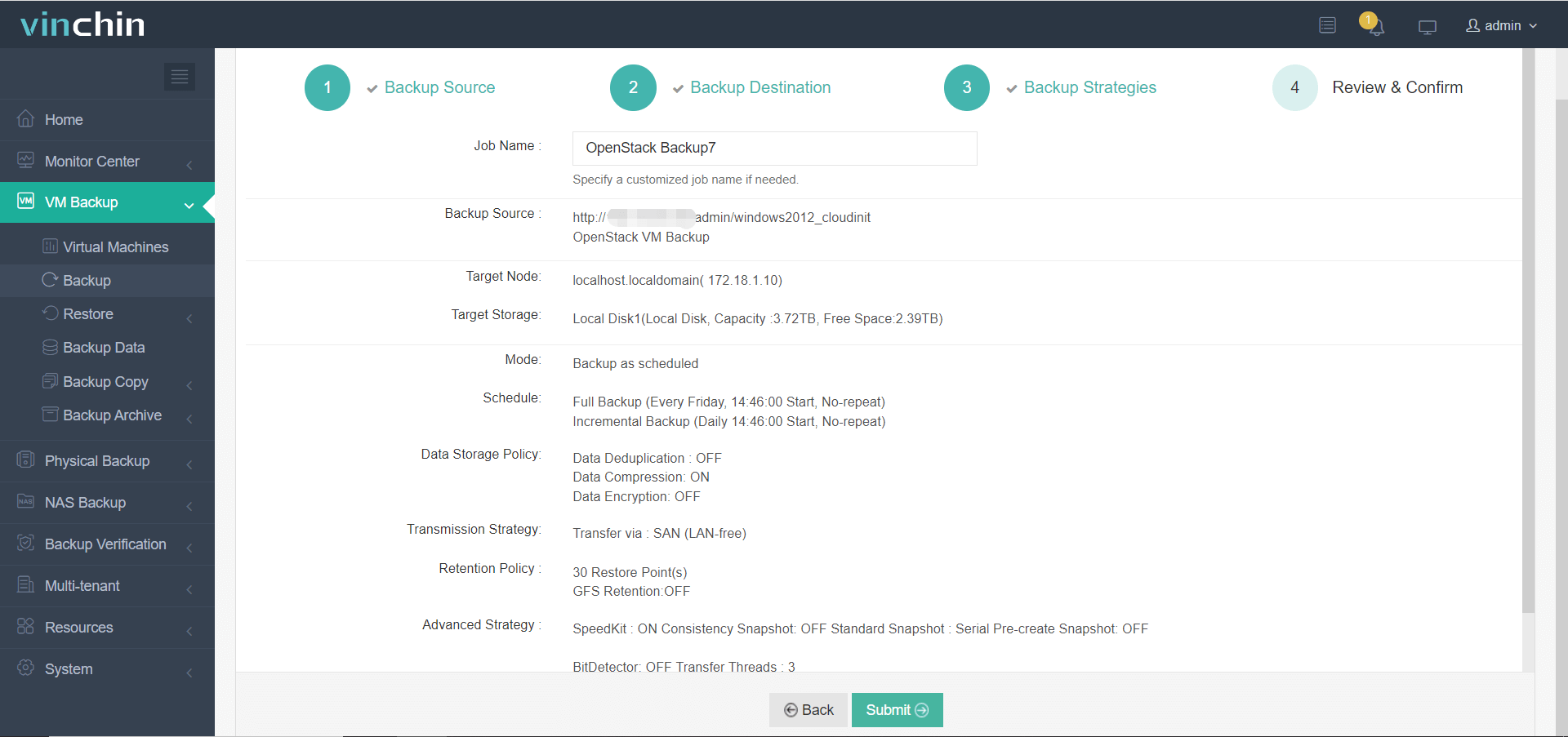
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is trusted by thousands of companies. Start your 60-day full-featured trial today!
Cinder backup FAQs
1. Q: What are the available storage backends for Cinder backups?
A: Cinder supports several storage backends for backups, including: OpenStack Swift, Ceph RADOS Gateway (RGW), NFS (Network File System), GlusterFS, Google Cloud Storage, Amazon S3 (via S3 API).
2. Q: What is the difference between snapshot and backup in Cinder?
A: A snapshot is a point-in-time copy of a volume that is stored within the same storage backend as the volume, while a backup is a copy of the volume data that can be stored on a different storage backend, often used for long-term storage and disaster recovery.
Conclusion
Cinder is an important component of the OpenStack platform. It provides persistent block storage services for virtual machines in cloud computing environments. It supports multiple storage backends and multi-tenancy, and has high availability and fault tolerance. The main advantages of Cinder are its scalability and flexibility. Different storage backends can be selected as needed, and it can be operated and managed through APIs and command line interfaces. As a block storage service framework, Cinder already has basic support for data protection.
Share on:








