-
What is ESXCLI?
-
How to Open ESXCLI?
-
ESXi Backup and Recovery
-
Conclusion
One of the most significant changes since vSphere 7 is the deprecation of vSphere CLI, a command line interface package that enables VMware users to run management commands against ESXi systems from any machine with a network connection. But from then on, all its capabilities are supported with API-centric tools like esxcli.
What is ESXCLI?
ESXCLI is a Python-written script to manage and fix issues of ESXi with a command set. It is located in the /sbin/directory. As a part of ESXi Shell, ESXCLI commands must be run in the ESXi Shell or the console. You can also run ESXCLI commands in the SSH session, vCLI, and even PowerCLI. A host's setup determines which ESXCLI commands are available on that host, to get the detailed command list information on your host, run esxcli --server <MyESXi> --help.

ESXCLI Syntax
esxcli [dispatcher options] <namespace> [<namespace> ...] <cmd> [cmd options]
Dispatcher options: target host, user name, and other connection-related variables that are predefined. When you execute the command in the ESXi Shell, it is not necessary.
Namespace: ESXCLI commands are grouped.
Command: reports on or changes the system's state.
ESXCLI 7.0 Command-List
| Command | Description |
| esxcli device | Device commands descriptions. |
| esxcli esxcli | Esxcli commands descriptions. |
| esxcli fcoe | Commands for FCOE (Fibre Channel over Ethernet). |
| esxcli graphics | Commands for Graphics. |
| esxcli hardware | Namespace for hardware that is used largely to extract data about the present system configuration. |
| esxcli iscsi | Monitor and manage hardware and software iSCSI. |
| esxcli network | Manage virtual networking such as virtual switches and VMkernel network interfaces. |
| esxcli nvme | NVMe devices management commands. |
| esxcli rdma | RDMA devices monitoring commands. |
esxcli sched | Manage the shared system-wide swap space. |
| esxcli software | Manage and install image profiles and VIBs. |
| esxcli storage | Fundamental storage commands and other storage management commands. |
| esxcli system | Monitor and manage systems. |
esxcli vm | List VMs and shut them down forcefully. |
| esxcli vsan | vSAN management commands. |
| esxcli list | List the available objects for the specified namespace |
| esxcli get | Get the specified setting or property's value |
esxcli set | Manually set the required parameter. |
| esxcli load/unload | Load/unload system configurations. |
Note: type the command to see all namespaces available if you cannot remember a particular command, for instance, run esxcli network to see all commands for the network namespace.
Necessary ESXCLI Commands
Hardware:
See the complete information on installed devices:
esxcli hardware pci list | more
View the memory of the ESXi server:
esxcli hardware memory get
Installed processors details:
esxcli hardware cpu list
System configurations:
See the ESXi version and build number:
esxcli system version get
Get the hostname of ESXi server:
esxcli system hostname get
See the installation time:
esxcli system stats installtime get
Get the SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) setup:
esxcli system snmp get
List local users on the ESXi host:
esxcli system account list
Put ESXi host into the maintenance mode:
esxcli system maintenanceMode set --enable yes
Exit the mode:
esxcli system maintenanceMode set --enable no
Power off the ESXi:
esxcli system shutdown poweroff
Reboot:
esxcli system shutdown reboot
Network:
List active network connections:
esxcli network ip connection list
List installed network adapters:
esxcli network nic list
Show network interfaces details:
esxcli network ip interface list
Show all of ESXi's active interfaces' IPv4 configuration:
esxcli network ip interface ipv4 get
Show the VMs’ network details:
esxcli network vm list
See the domain search setup:
esxcli network ip dns search list
See the DNS (Domain Name System) servers configured in the network settings:
esxcli network ip dns server list
See the virtual switches and port groups:
esxcli network vswitch standard list
Show vmnic0 network interface data:
esxcli network nic stats get -n vmnic0
View the firewall status:
esxcli network firewall get
View the firewall rule list:
esxcli network firewall ruleset list
Disable the firewall:
esxcli network firewall set --enabled false
Enable it:
esxcli network firewall set --enabled true
Storage:
See mounted VMFS (vSphere Virtual Machine File System) volumes info:
esxcli storage vmfs extent list
See VMFS file system to disk device mappings:
esxcli storage filesystem list
View all iSCSI paths:
esxcli storage core path list
List the mounted NFS shares:
esxcli storage nfs list
iSCSI:
List iSCSI adapters:
esxcli iscsi adapter list
Rediscover iSCSI adapters:
esxcli iscsi adapter discovery rediscover -A adapter_name (/--all: list all options)
Re-scan iSCSI adapters:
esxcli storage core adapter rescan -A adapter_name (/--all: list all options)
Software:
List VIB (vSphere Installation Bundle) packages installed on the host:
esxcli software vib list
Install a VIB with a host in the maintenance mode required:
esxcli software vib install -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore/patches/patch_name.zip
Uninstall a VIB:
esxcli software vib remove -n scsi-arcmsr
VM:
List running VMs and their World IDs:
esxcli vm process list
Shut down the unresponsive VM when it cannot be done via a GUI:
esxcli vm process kill -w WorldID -t soft (-t hard: use hard mode to shut down immediately if the soft is not useful; -t force: force the VM to be powered off if the previous two don’t work)
How to Open ESXCLI?
In the ESXi default interface:
1. In the ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI), navigate to Troubleshooting Options> hit Enter to Enable ESXi Shell and press Enter to Enable SSH strings.
2. Press Alt+F1 to start the console.
3. Input the user credentials.
4. Press Alt+F2 to go back to the ESXi DCUI.
In the VMware Host Client:
1. Log in to the ESXi host and go to Host> Actions> Services> Enable Secure Shell (SSH).
2. Or enable the ESXi shell in the Services menu.
In the vSphere Client:
Prerequisite: the ESXi host is managed by vCenter Server.
1. In the vSphere Client, navigate to Hosts and Clusters> choose the host> Configure tab> System> Services> SSH.
2. Press Start to launch the SSH server once. Or press Edit Startup Policy and choose Start and Stop with host for a longer time.
3. Enable the ESXi Shell in the Services menu.
Install Software via ESXCLI in the SSH/ESXi Shell
1. Download a driver in a zip format.
2. Copy the driver to the host via WinSCP or upload it to a datastore.
3. List the VIBs.
esxcli software vib list
4. Install the driver with a depot file.
esxcli software vib install -d /tmp/arcmsr- offline_bundle.zip
5. Or install the driver with a VIB file.
esxcli software vib install -v /tmp/scsi-arcmsr- offline_bundle.vib
6. Reboot.
7. Uninstall a VIB if you need.
esxcli software vib remove -n scsi-arcmsr
Or esxcli software vib remove –vibname=scsi-arcmsr
Install Software via ESXCLI in the PowerCLI
1. Use Get-ESXCLI cmdlet to start ESXCLI in PowerCLI.
2. Install the driver with a depot file.
get-esxcli -VMHost “IPaddress” -V2).software.vib.install.invoke(@{depot=”/tmp/arcmsr-offline_bundle.zip“}
3. Or install the driver with a VIB file.
get-esxcli -VMHost “IPaddress” -V2).software.vib.install.invoke(@{viburl=”/tmp/scsi-arcmsr-offline_bundle.vib“}
4. Remove the package.
get-esxcli -VMHost “IPaddress” -V2).software.vib.remove.invoke(@{viburl=” scsi-arcmsr“} “}
Upgrade to ESXi 8 Using ESXCLI
1. Download the offline bundle.
2. In the VMware Host Client, browse and upload the bundle.
3. Connect the ESXi host via SSH.
4. Run the following commands.
# List the depot image
esxcli software sources baseimage list -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore/VMware-ESXi-8.0-xxxxxx-depot.zip
# Run the installation and reboot when asked.
esxcli software vib install -d /vmfs/volumes/datastore/VMware-ESXi-8.0-xxxxxxx-depot.zip
5. Wait for the reboot, and the upgrade is completed after that.
ESXi Backup and Recovery
ESXCLI is a command-line interface framework and administration tool for vSphere environments. You can get some details or modify some configurations about the VM or the network other than the GUI tools for efficiency. But it doesn’t contain backup and recovery capabilities, which are extremely essential for data protection.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an agentless and image-based backup solution certified by VMware Ready for 12 virtualizations including VMware, Hyper-V, Citrix hypervisor (XenServer), XCP-ng, oVirt, Oracle OLVM, Red Hat Virtualization, etc., and 6 databases (Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, PostgreSQL PRO, and Maria DB).
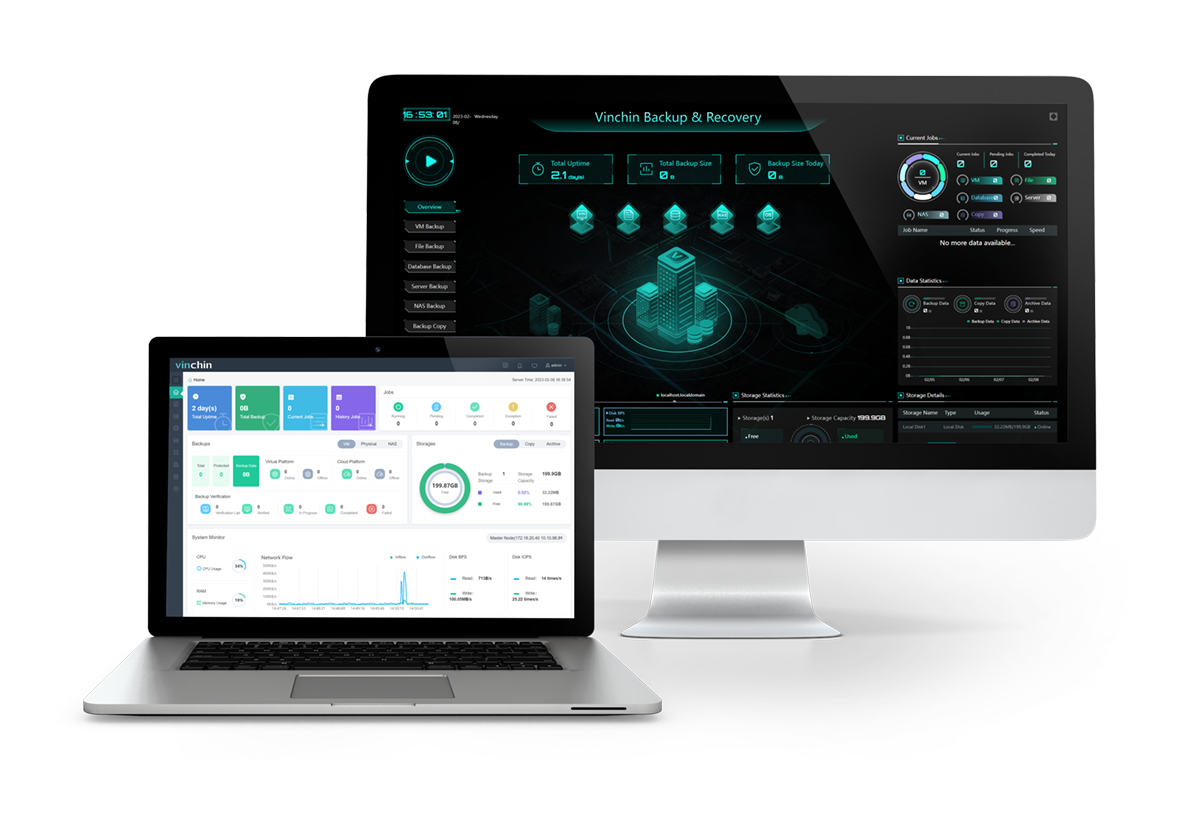
It has the following features:
Automatic ESXi backup: schedule VM backup with various backup types including CBT-enable incremental backup and monitor the process with an email alert reminder.
Speed and efficiency: transfer the reduced data after deduplication and compression via SAN/HotAdd/LAN, multithread, and other techniques.
Enhanced security: provide Backup Storage Protection to protect data from external threats with AES-256 encryption, and data transmission encryption to secure data while transferring. Allow users to archive data to public clouds for retention and send an offsite backup copy to another location.
Instant recovery: enable instant recovery directly from the backup repository in seconds for seamless business continuity and minimum RTO.
You can also migrate ESXi VMs from and to 10+ platforms without any agents, conversion tools, or command lines. Download the 60-day free trial of the newly released Vinchin Backup & Recovery 7.0 now for more advanced functions.
Conclusion
ESXCLI offers a suite of subcommands typically called namespaces and included options that allow admins to manage a virtual infrastructure except for the GUI tools. You can use them to view and change configurations, install a driver, and even upgrade the ESXi version.
Also do not forget to back up ESXi VMs and restore them in emergencies with a cost-effective and trustful backup solution certified by VMware.
Share on:








