-
1. Access control and user management
-
2. Data encryption and privacy protection
-
3. Database auditing and security monitoring
-
4. Network security and access control
-
5. Backup and Disaster Recovery
-
Cyber Security Oracle FAQs
-
Conclusion
As organizations increase their reliance on data, the security of Oracle database, as an enterprise-class database management system, is critical. Network attacks, data leakage and internal threats are increasing, how to protect the Oracle database has become the focus of enterprise security management. In this article, the key security measures of Oracle database will be introduced to help enterprises build a solid network security defense.
1. Access control and user management
The Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) is one of the core principles of database security. Organizations should ensure that each user has only the minimum privileges needed to perform their tasks to reduce the potential attack surface.
Strong Password Policy: Use complex passwords, change them regularly, and enable password expiration mechanisms.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): add additional layers of security such as SMS verification codes or hardware tokens.
Role and Privilege Management: Use Oracle's Roles feature to manage user privileges and avoid granting too many privileges directly.
Database Auditing: Monitor user activity with Oracle Audit Vault to detect abnormal behavior in a timely manner.
2. Data encryption and privacy protection
Data encryption is an important means of preventing data leakage. Oracle provides several encryption methods to ensure that data remains secure during storage and transmission.
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE): Encrypts stored data to prevent unauthorized access to database files.
Oracle Data Redaction: Dynamic masking of sensitive information (e.g. credit card numbers, social security numbers) to prevent unauthorized access.
Network Encryption: Encrypts communications between the database and the client using TLS/SSL to prevent traffic from being eavesdropped or tampered with.
3. Database auditing and security monitoring
Continuous monitoring of database activities helps to detect abnormal behavior and take timely action.
Oracle Database Audit: Tracks user actions, such as login failures, data modifications, and so on.
Oracle Database Firewall (ODF): Provides SQL-level attack protection to identify and block SQL injection attacks.
Security Event Response: Configures SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) system to centrally store and analyze logs to discover potential security threats.
4. Network security and access control
Network security for databases is critical, and a number of measures should be taken to minimize risk.
Network Segmentation: Segregate database servers into separate VLANs or subnets to restrict access to the database.
Firewall Rules: Allow only trusted IPs to access the database server.
Database Access Agent (Oracle Connection Manager): Provides connection control and traffic filtering to enhance access security.
Periodic Security Scans: Use the Oracle Database Security Assessment Tool (DBSAT) to check the security configuration of the database and fix potential vulnerabilities.
5. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data security is not only about preventing external attacks but also ensuring data availability and integrity.
Regular Backups: Use Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) to perform scheduled backups and ensure data recoverability.
Offsite Backups: Utilize Oracle Data Guard to synchronize data across multiple locations to prevent data loss due to local disasters.
Disaster Recovery Drills: Regularly test recovery procedures to ensure quick database restoration in case of security incidents.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery for Oracle database protection
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an advanced solution for Oracle database protection, significantly improving backup efficiency and storage utilization:
Efficient Backup Compression: Reduces the size of database backups by up to 70% without consuming the CPU resources of the production environment.
Centralized Management: Provides an intuitive web console for simplified database protection across complex IT infrastructures.
Optimized Backup Process: Unlike traditional database backup tools that duplicate data before transferring it to backup media, Vinchin integrates seamlessly with Oracle RMAN+SBT, ensuring efficient data transfer directly to the backup system while minimizing production resource consumption.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery's operation is very simple, just a few simple steps.
1.Just select database on the host
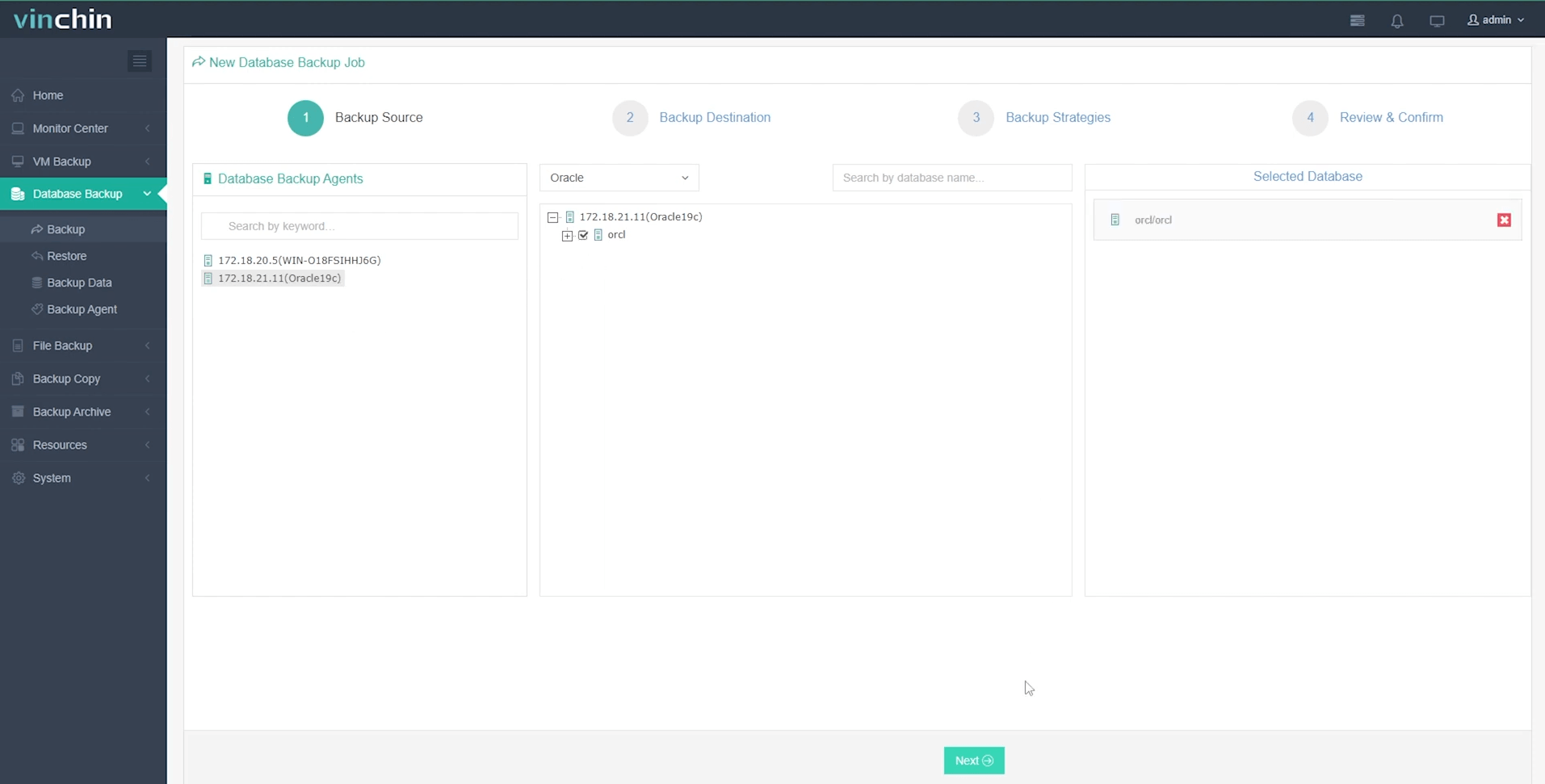
2.Then select backup destination

3.Select strategies
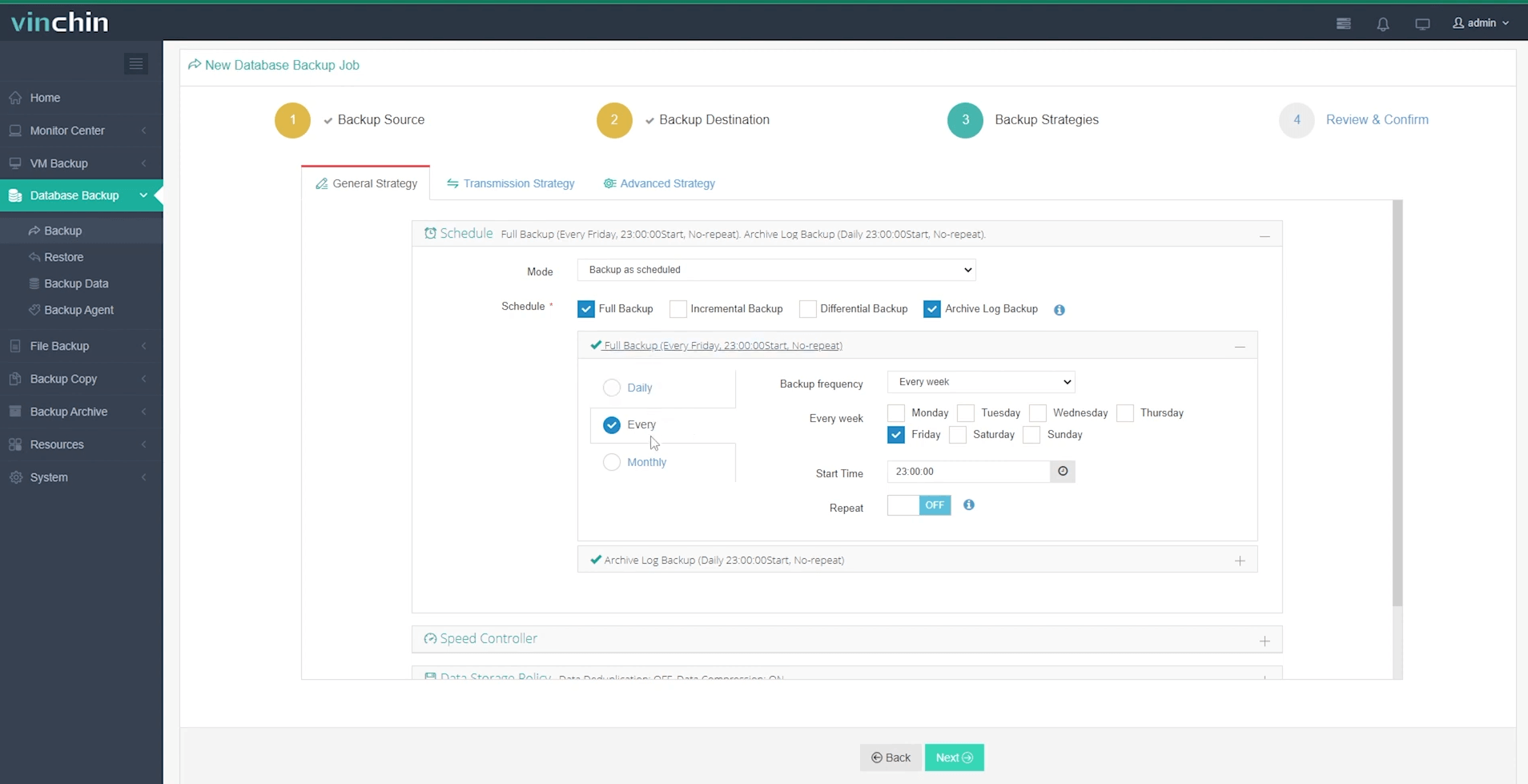
4.Finally submit the job
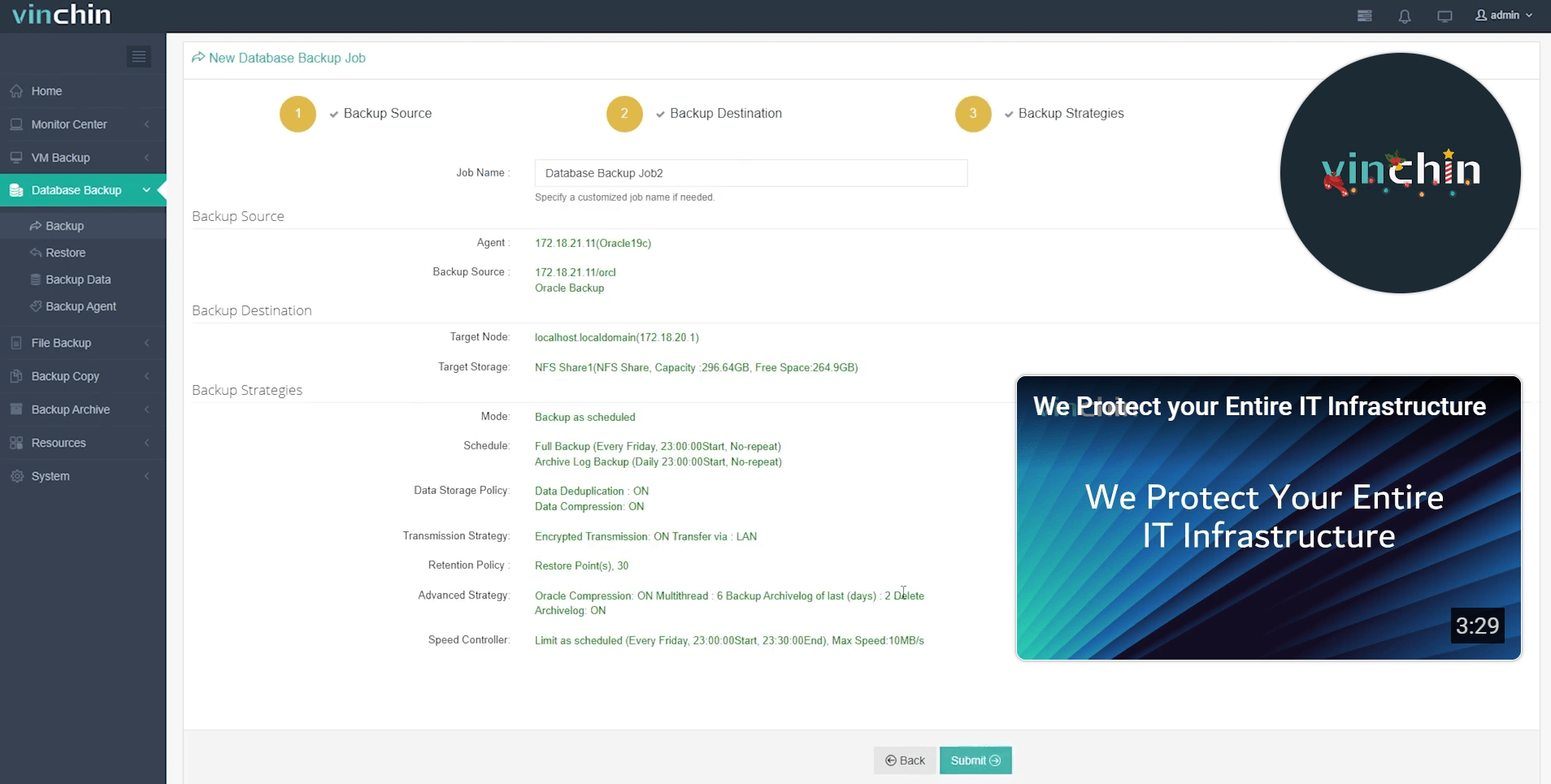
By implementing these security measures and leveraging solutions like Vinchin Backup & Recovery, enterprises can enhance the resilience of their Oracle databases against cyber threats while ensuring business continuity. Vinchin offers a free 60-day trial for users to experience the functionality in a real-world environment. For more information, please contact Vinchin directly.
Cyber Security Oracle FAQs
Q1: What types of encryption does Oracle Database support?
A1: Oracle supports transport layer encryption (e.g. SSL/TLS) and storage layer encryption (e.g. Transparent Data Encryption TDE) for securing data in transit and at rest.
Q2: How do I manage Oracle database user permissions?
A2: By using Oracle's role and privilege management system, DBAs can assign specific operational privileges to users or roles and can revoke these privileges as needed.
Conclusion
Implementing robust security measures is essential to protect Oracle databases from cyber threats. Access control, encryption, auditing, network security, and backup strategies help safeguard data integrity and availability. Vinchin Backup & Recovery further enhances Oracle database protection with efficient, streamlined backup solutions.
Share on:






