-
What is Business Continuity?
-
What is Disaster Recovery?
-
Why Do Businesses Need Both Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery?
-
Key Components of a BCDR Plan
-
Case of an Integrated Solution
-
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
-
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery FAQs
-
Conclusion
In our daily work, we often confuse the concepts of Business Continuity Management (BCM) and Disaster Recovery (DR). While they are intrinsically linked, they are also different. Business continuity management is broader, focusing on the enterprise strategy with the goal of ensuring business operations and addressing issues throughout the entire lifecycle. In contrast, disaster recovery focuses more on specific operations, with the system as the target, concentrating on resolving immediate issues and simultaneously dealing with post-incident issues. Generally speaking, disaster recovery can be considered a part of business continuity, but not the whole.
What is Business Continuity?
Business continuity is a method to address business interruptions before solving the underlying issues. For example, during the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses faced tremendous operational pressures and needed to adopt temporary measures to continue operations as much as possible. In such cases, business continuity often involves providing employees with the tools necessary to work from home.
Business continuity involves a planning process that results in a business continuity plan. This usually begins with risk assessments and business impact analyses. These measures help stakeholders determine the scope of the business continuity plan while considering any regulatory or legal impacts. Many business continuity plans primarily focus on IT and communication systems, as they play a core role in most businesses.
A business continuity plan must consider all potential risks a company may face, such as natural disasters, cyber-attacks, and service disruptions. The goal of business continuity is not to solve these problems but to keep critical operations running as smoothly as possible during an interruption. Business continuity plans also involve proactively reducing risks, such as maintaining redundant computing systems and real-time copies of data.
What is Disaster Recovery?
Business continuity deals with how to respond to interruption events, while disaster recovery planning focuses on solving the underlying problems, whether it's data breaches, system failures, or other unforeseen events. Therefore, it is more focused on the immediacy of unforeseen events, often occurring simultaneously with business continuity. The disaster recovery process includes several stages: from identifying the source of the event to applying various methods for recovery. To this end, it involves not only data recovery but also the restoration of damaged or failed hardware and software applications.
Deadlines play a core role in disaster recovery plans, as any business can only tolerate a limited amount of time or data loss. RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) are two critical parameters that relate to the operational availability of key business functions and the availability of fundamental data. RTO refers to the maximum time allowed to resolve an issue, while RPO refers to the maximum amount of data loss a company can tolerate.
Like business continuity plans, prioritization is crucial in disaster recovery plans. This is why different RTO and RPO values must be assigned to different applications and systems. For example, a business may tolerate being unable to access non-essential marketing systems or data for a few days or weeks but cannot tolerate not accessing payroll systems and data. All data assets must be categorized based on their importance to the business and then prioritized accordingly.
Why Do Businesses Need Both Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery?
The main difference between business continuity and disaster recovery is when each action plan takes effect. Business continuity is about maintaining functional operations, while disaster recovery plans focus on restoring normalcy within a given timeframe. For this reason, it is also accurate to view disaster recovery plans as a subset of the broader continuum (i.e., business continuity plans).
Although the two plans are closely related, they do not necessarily have to be used simultaneously. For example, in the case of minor disruptions, a business continuity plan may not even need to be activated. If a company has automatic failover and real-time data backups, disaster recovery plans might be sufficient. However, for more persistent and complex disruptions, a business continuity plan must be activated.
Things can also be viewed from another perspective, such as what was done for businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic. For instance, if a business faces a long-term interruption, such as a public relations crisis or long-term employee shortages, the business continuity plan should be activated to minimize the impact on operations. In contrast, disaster recovery plans focus mainly on the immediacy of unforeseen disruptions, such as data breaches or network outages.
In many cases, these two plans will overlap. For example, in the case of natural disasters such as floods, if a company's office is submerged, it may immediately damage or destroy the company's data and systems. In such cases, recovery must happen as quickly as possible. That said, the company's office may take weeks or even months to be restored, requiring business continuity to help the company through this challenging period.
Key Components of a BCDR Plan
1. Risk Assessment and Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
A risk assessment identifies potential threats to an organization, including natural disasters, cyberattacks, equipment failures, and human errors. BIA evaluates the potential consequences of these risks on critical business functions. By understanding the impact of different scenarios, organizations can prioritize their recovery efforts.
2. Data Backup and Recovery
Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. Regular and reliable data backups are essential to ensure quick recovery in case of data loss. Organizations should also consider offsite backups, cloud storage solutions, and backup verification processes.
3. Redundancy and High Availability
Redundancy involves duplicating critical components, such as servers, network devices, and storage systems, to prevent single points of failure. High availability ensures that essential services remain operational with minimal downtime. This can be achieved through failover clusters and load balancing.
4. Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines the steps to take immediately after a disruption. It includes communication protocols, incident assessment, containment and mitigation.
5. Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO)
Case of an Integrated Solution
The close relationship between business continuity and disaster recovery plans means that both can be more effective if managed in a unified and consistent environment. An integrated approach provides a way to enhance and protect critical operations and offers a detailed understanding of the various risks faced. Of course, these risks and their mitigation measures must be regularly reviewed and updated as necessary.
Integrated management systems offer broader coverage by storing all essential business data in a centrally managed location. For example, integrating with human resources and task management systems can make it easier to assign and schedule personnel and assets for recovery and continuity operations. Similarly, integration with governance, risk management, and compliance solutions helps ensure that business continuity and disaster recovery plans comply with regulations and align with the broader enterprise risk management needs.
The most effective way to achieve business continuity and disaster recovery is through seamless integration into the corporate culture and broader technological environment. With a complete end-to-end solution, companies can have a comprehensive understanding of their business processes, develop and maintain plans, and implement them smoothly.
Enhance Data Protection with Vinchin Solution
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a professional solution designed to provide data protection and disaster recovery for virtualized environments. It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc. Tailored for virtual environments, Vinchin offers automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. With data encryption and ransomware protection.
With agentless backup feature, it enables quick integration of VMs into the backup system. It offers disaster recovery features such as Instant Restore to reboot VMs from backups in seconds, offsite copy for remote backup storage, and automatic backup verification for integrity checks. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
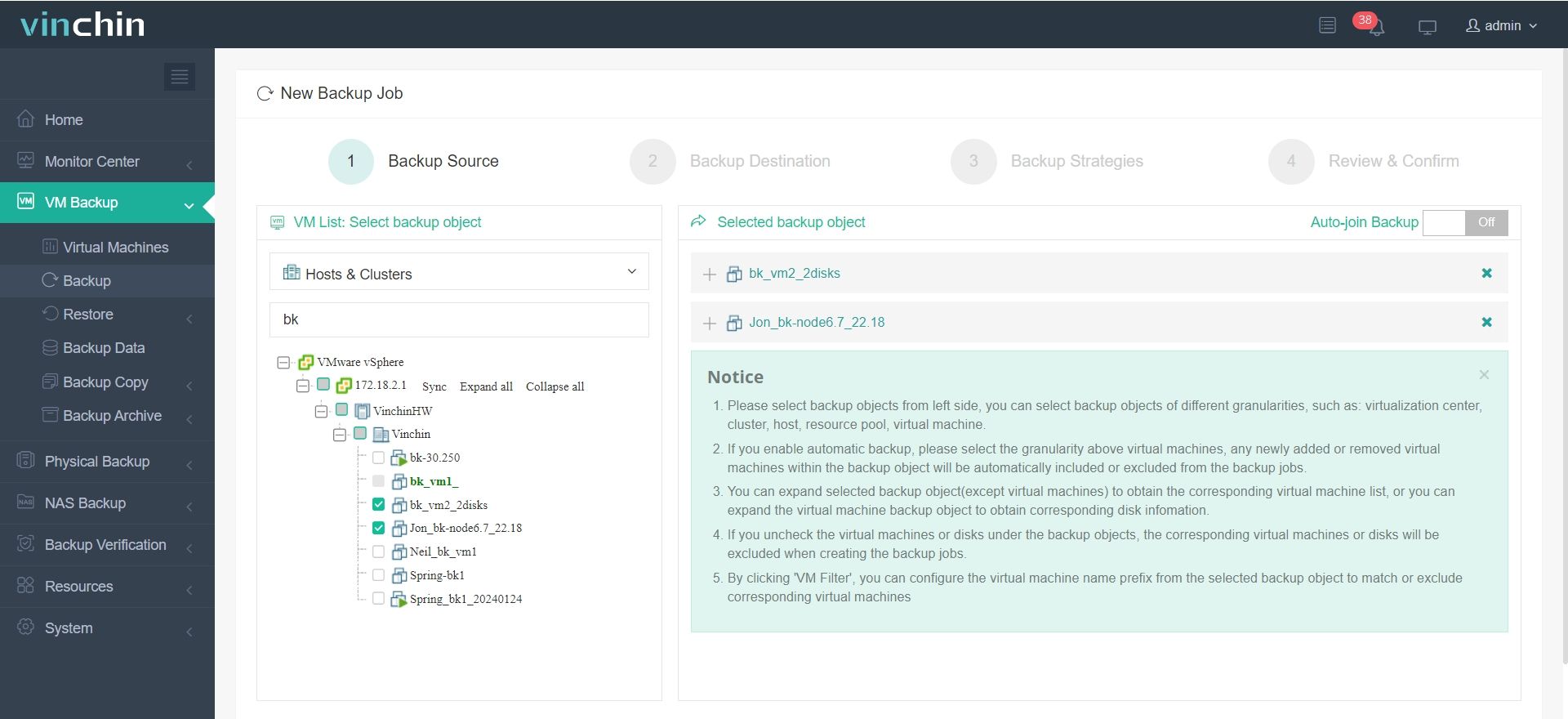
2.Select backup destination.
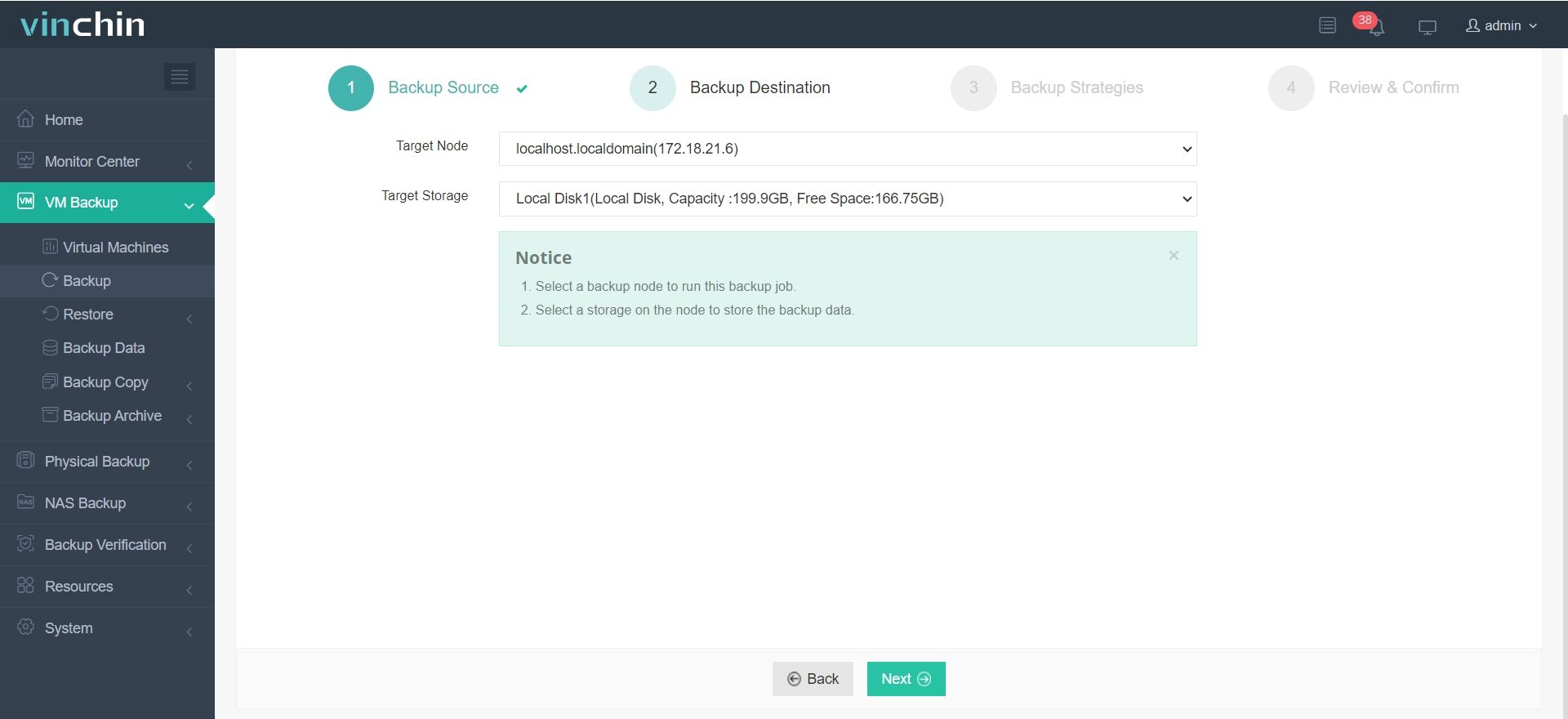
3.Configure backup strategies.
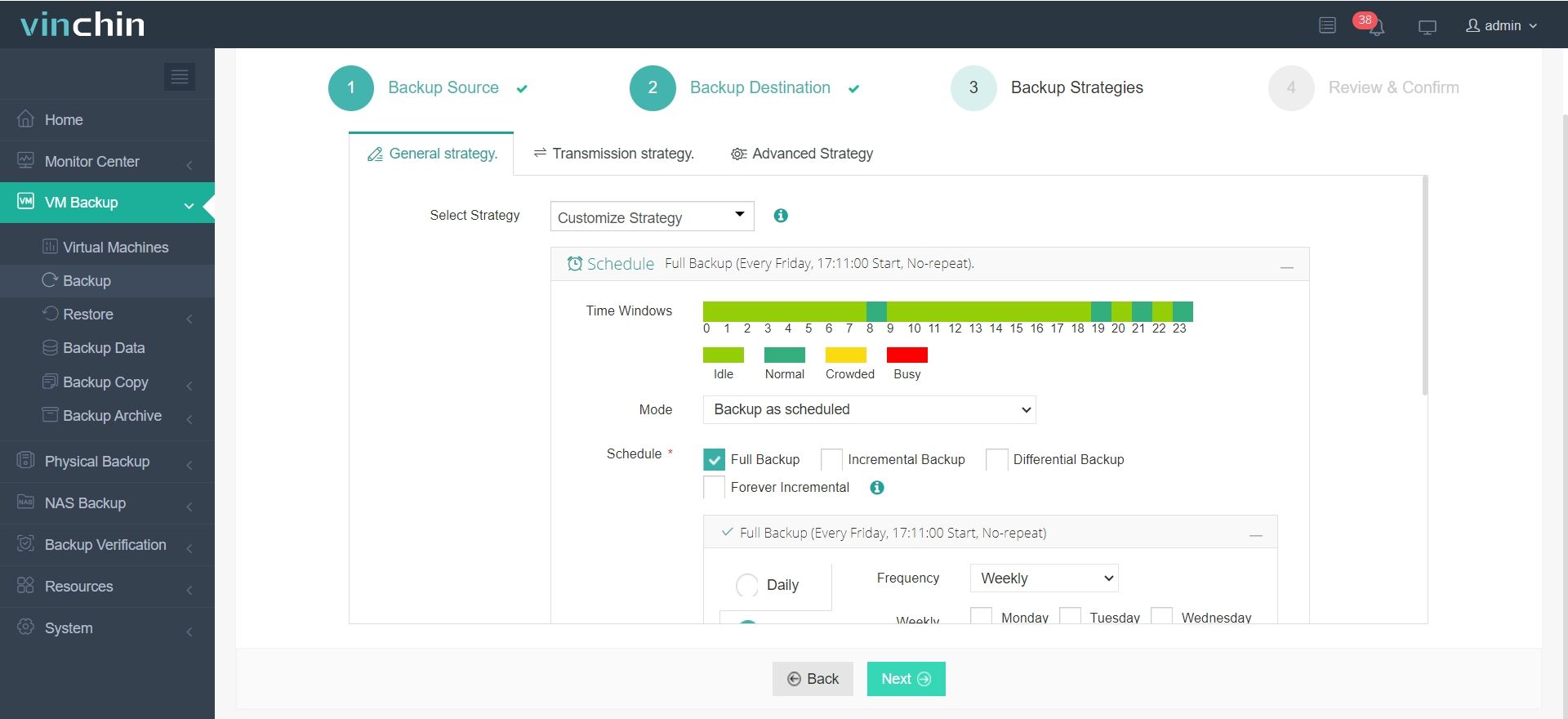
4.Review and submit the job.
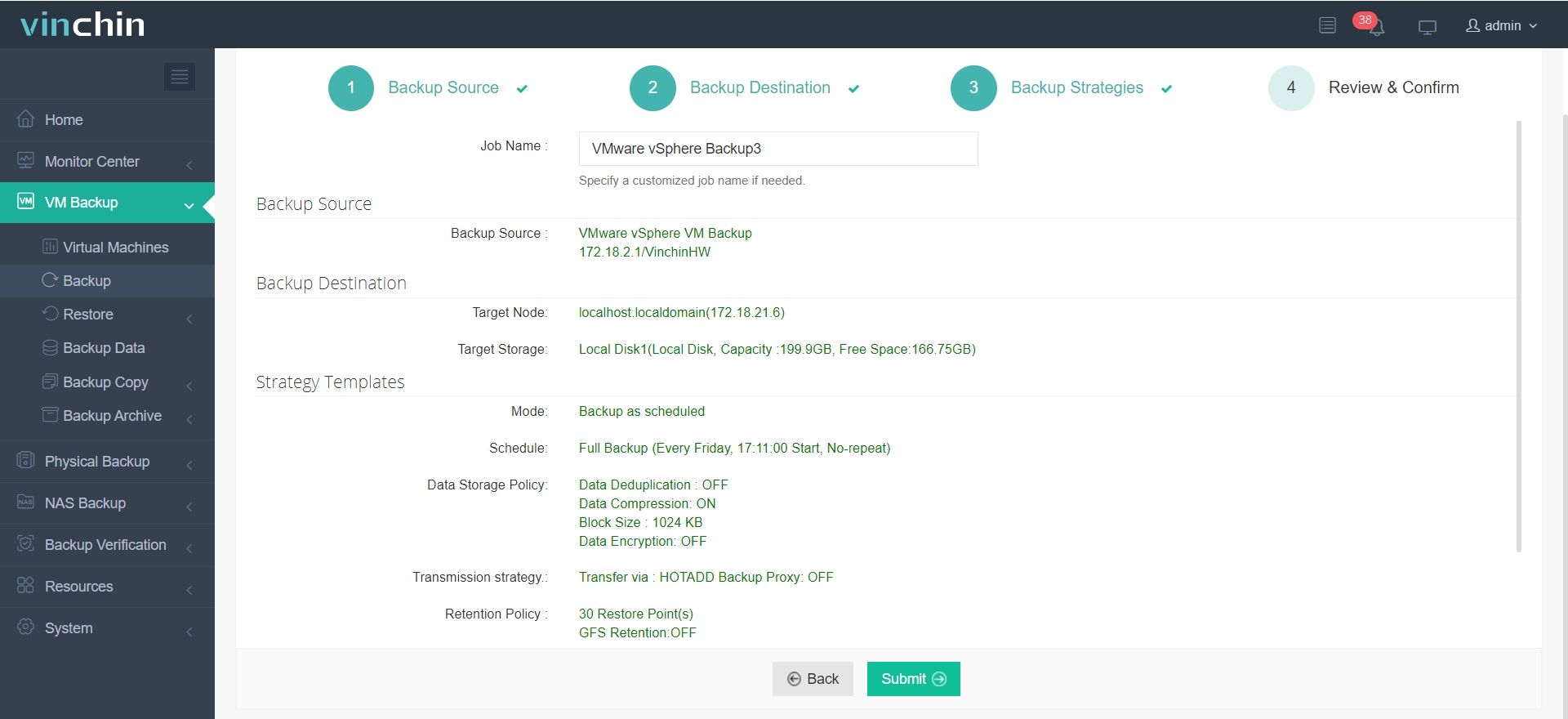
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery FAQs
1. What is the role of cloud computing in BCDR?
Cloud services provide scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for backup, data replication, and failover. Cloud-based DR allows businesses to recover critical systems faster and from anywhere.
2. What is the 3-2-1 backup rule?
The 3-2-1 backup rule states that you should have 3 copies of your data, stored on 2 different types of media, with 1 copy stored offsite.
Conclusion
Business continuity and disaster recovery are vital for organizations to maintain resilience and safeguard against potential disruptions. By implementing a comprehensive BCDR plan, businesses can minimize downtime and ensure seamless operations. Leveraging advanced solutions like Vinchin Backup & Recovery further enhances an organization's ability to recover swiftly and efficiently in the face of disasters.
Share on:







