-
The Importance of Network Security for SMEs
-
Common Cybersecurity Challenges Faced by SMEs
-
Key Components of Effective Network Security for SMEs
-
Leveraging Technology and Services for Enhanced Security
-
SME Network Security FAQs
-
Conclusion
In today's interconnected digital landscape, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are increasingly reliant on technology to drive their operations, from managing customer data to conducting online transactions. However, this reliance also exposes them to a myriad of cybersecurity risks. The rise of cyber threats such as ransomware, phishing attacks, and data breaches can have devastating consequences for SMEs, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and even business closure. Therefore, understanding and implementing effective network security measures is crucial for the survival and growth of SMEs in the 21st century.
The Importance of Network Security for SMEs
A. Protecting Business Assets
The core assets of an SME include its intellectual property, trade secrets, and sensitive customer information. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of these assets is paramount. Strong network security protocols can prevent unauthorized access, safeguard against data leakage, and ensure that critical systems remain operational during and after a potential attack.
B. Compliance with Regulations
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide have enacted stringent laws to protect consumer privacy and data security. For example, the GDPR in the European Union imposes strict requirements on how businesses must handle personal data. Non-compliance can result in hefty fines and legal action. Thus, SMEs must implement robust network security policies to adhere to these regulations and avoid penalties.
C. Maintaining Customer Trust
Customer trust is the cornerstone of any successful business. A single data breach can erode years of built-up goodwill and lead to a loss of customers. By demonstrating a commitment to network security, SMEs can build a reputation for reliability and professionalism, which can be a competitive advantage in attracting and retaining clients.
Common Cybersecurity Challenges Faced by SMEs
A. Limited Resources
Unlike large corporations, SMEs often operate with limited budgets and staff. This can make it challenging to invest in comprehensive cybersecurity solutions or hire dedicated IT security personnel. As a result, many SMEs may not have the necessary expertise or tools to effectively defend against sophisticated cyber threats.
B. Lack of Awareness
Many SME owners and employees may lack a thorough understanding of cybersecurity risks and best practices. This knowledge gap can lead to complacency and poor security habits, such as using weak passwords, failing to update software, or clicking on suspicious links. Educating stakeholders about the importance of network security is essential for creating a culture of safety within the organization.
C. Rapidly Evolving Threat Landscape
Cybercriminals are constantly developing new tactics, techniques, and procedures to exploit vulnerabilities in networks. SMEs must stay abreast of these emerging threats and adapt their security strategies accordingly. This requires ongoing education, monitoring, and updating of security controls to address the latest risks.
Key Components of Effective Network Security for SMEs
A. Risk Assessment
Before implementing any security measures, SMEs should conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats specific to their business. This process involves evaluating the current state of the network, identifying valuable assets, and determining the impact of a potential breach. Based on the findings, SMEs can prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
B. Firewall and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Firewalls act as the first line of defense by controlling incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. IDS, on the other hand, monitor network activity for suspicious behavior and alert administrators when potential threats are detected. Combining firewalls with IDS provides a layered approach to network security, making it more difficult for attackers to penetrate the system.
C. Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware solutions are essential for protecting against malicious software that can compromise the network. These programs scan files and applications for known threats and can automatically remove or quarantine infected items. Regular updates are necessary to ensure that the software can detect and respond to the latest malware variants.
D. Employee Training and Education
Human error is one of the most common causes of data breaches. SMEs should provide regular training sessions to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, creating strong passwords, and securely handling sensitive information. Encouraging a security-conscious mindset among staff can significantly reduce the risk of internal security incidents.
E. Data Encryption and Backup
Encrypting sensitive data ensures that it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties, even if it is intercepted. Additionally, having a reliable backup strategy in place allows SMEs to quickly recover from data loss or corruption caused by cyberattacks or hardware failures. Regular backups should be stored offsite or in the cloud to protect against physical damage to on-premises infrastructure.
Leveraging Technology and Services for Enhanced Security
To further enhance network security and data protection, SMEs can leverage Vinchin Backup & Recovery, which is a professional solution designed to provide data protection and disaster recovery for virtualized environments. It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc. Tailored for virtual environments, Vinchin offers automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. With data encryption and ransomware protection. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
By integrating Vinchin Backup & Recovery into their network security strategy, SMEs can ensure that their data is protected from loss and easily recoverable in case of a disaster. The solution is scalable, cost-effective, and designed to meet the unique needs of small and medium enterprises.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
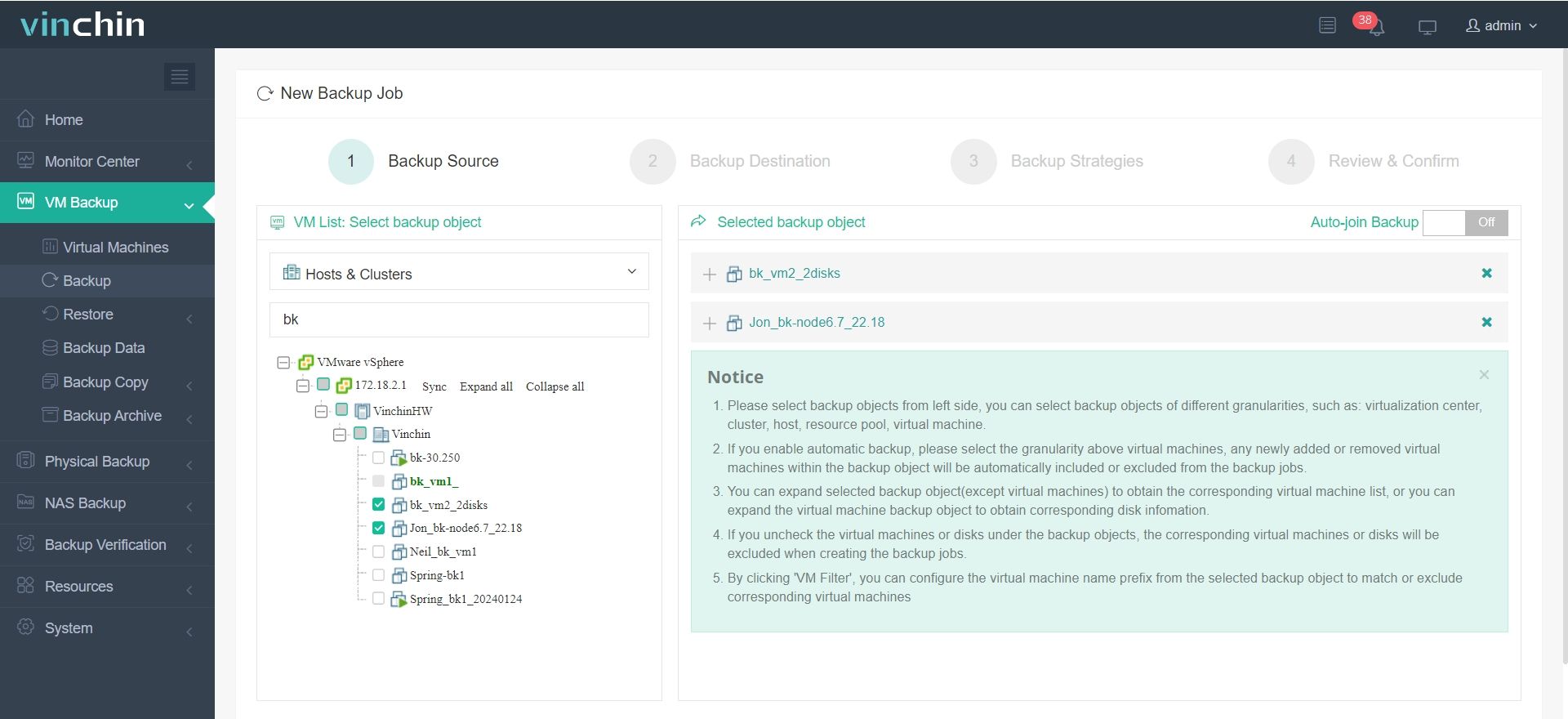
2.Select backup destination.
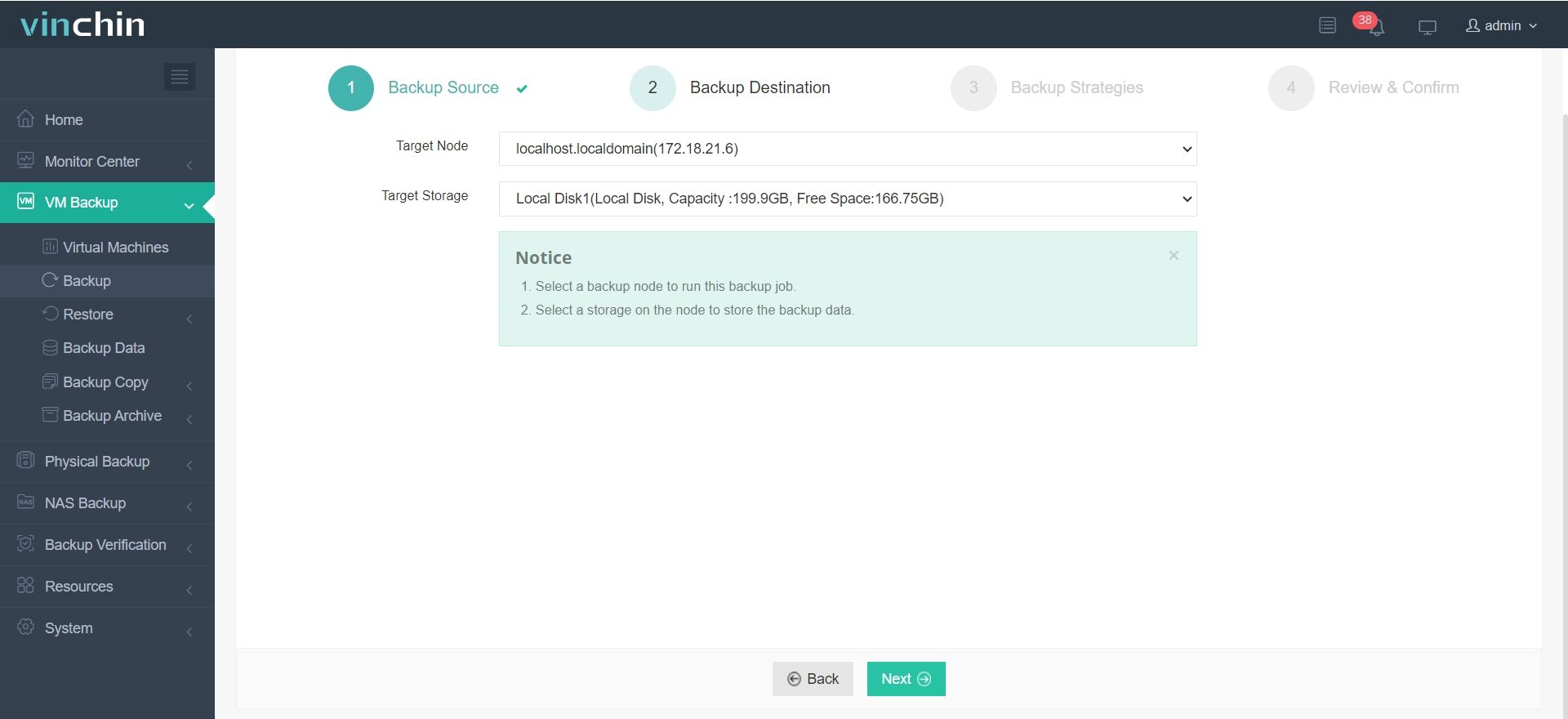
3.Configure backup strategies.
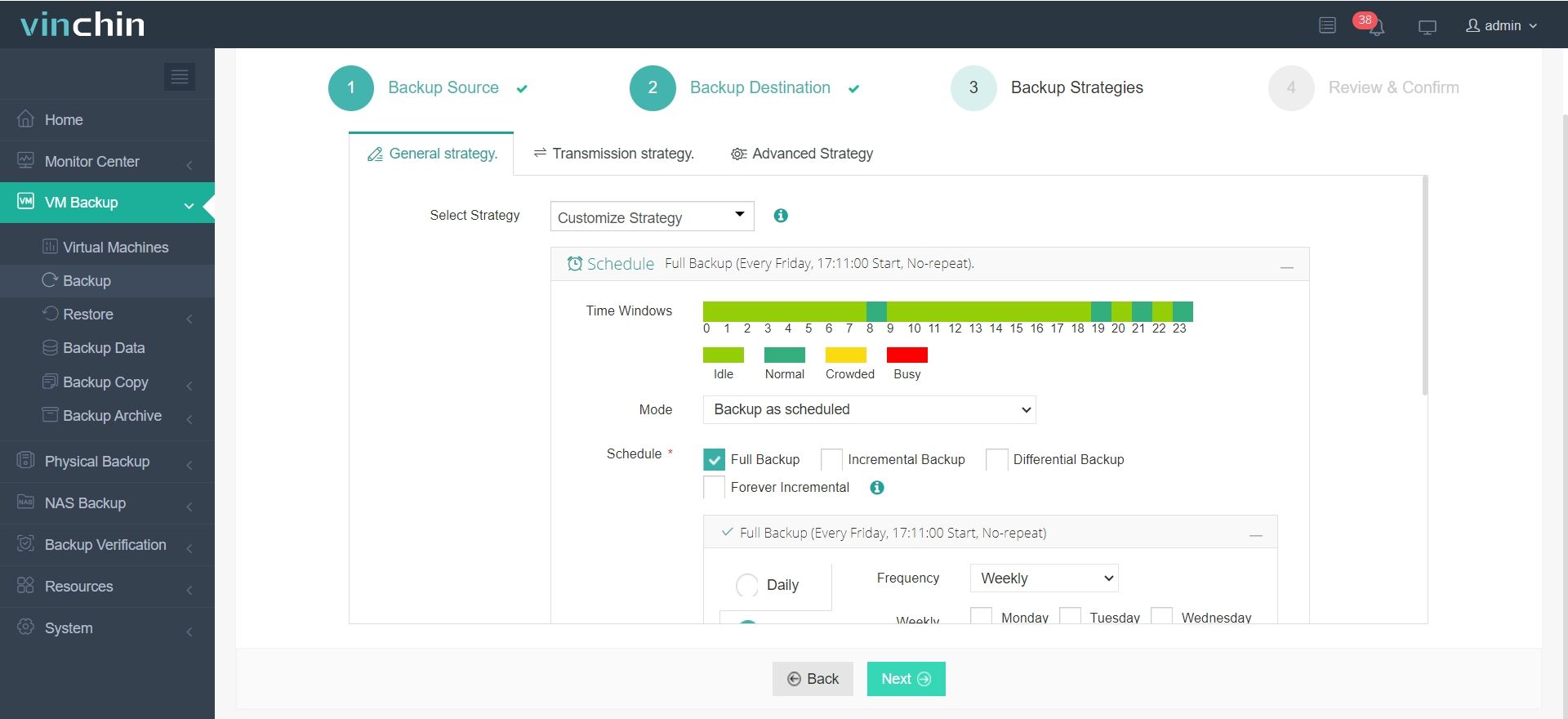
4.Review and submit the job.
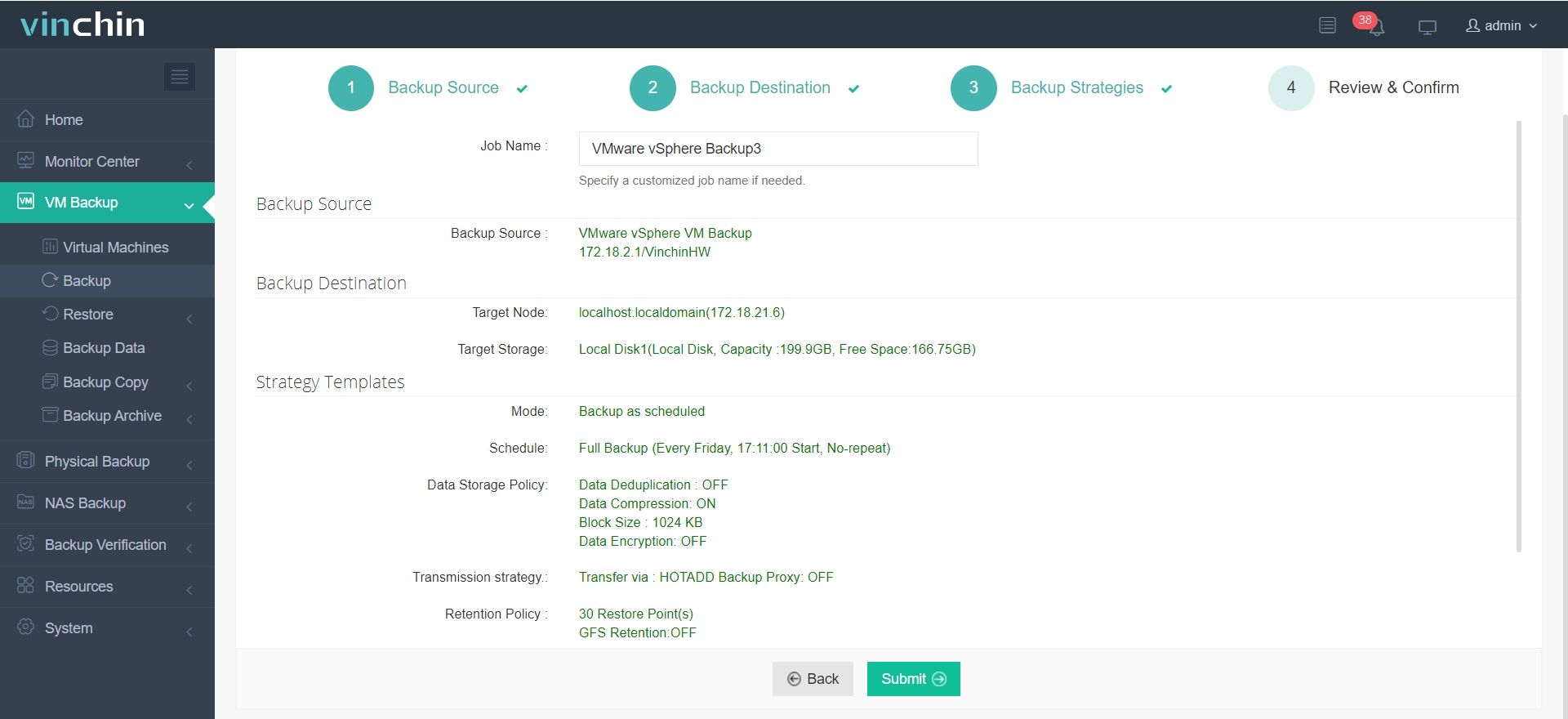
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
SME Network Security FAQs
1. What is a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system, and should SMEs use it?
A SIEM system collects and analyzes security data from across the network to detect and respond to threats in real-time. While it may be more common in larger enterprises, SMEs with sensitive data or regulatory requirements should consider using a managed SIEM service.
2. What is endpoint security, and why is it essential for SMEs?
Endpoint security involves securing devices like laptops, desktops, mobile phones, and tablets that connect to the network. It protects against malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches at the device level.
Conclusion
In the digital age, SMEs must integrate network security into their core strategy, treating it as a value driver rather than a mere safeguard. By embracing advanced technologies and fostering a security-conscious culture, SMEs can protect their assets, build customer trust, and unlock new opportunities. Leadership that prioritizes security will not only defend against threats but also pave the way for sustainable growth and innovation in an interconnected world.
Share on:







