-
What backup technologies are supported by tape drives (libraries)?
-
What are the storage media of tape drives?
-
Vinchin's Data Protection Strategies
-
Different types of tape FAQs
-
Conclusion
Since its birth, tape storage technology has always been the core solution for data backup and long-term archiving due to its large capacity, high reliability and economy. From early audio recording to modern enterprise-level data storage, tape technology has undergone many innovations, resulting in various formats such as DAT, DLT, and LTO to meet the needs of different scenarios. This article will sort out the mainstream tape technology and its storage media to provide a clear perspective for understanding the evolution of data storage.
What backup technologies are supported by tape drives (libraries)?
☑️ DAT Technology
DAT (Digital Audio Tape) technology, also known as digital audio tape technology or 4mm tape drive technology, uses video tape-like technology—rotating heads and helical scanning tracks that traverse the 4mm tape width diagonally to achieve fast data access. Even small tape cassettes can offer high capacity. This technology was later used in 8mm tape cassettes as well. It was originally developed by Hewlett-Packard (HP) and Sony. Based on Helical Scan Recording, this technology converts data into digital form before storing it. Early DAT technology was mainly used for audio recording. With continuous improvements, it was later adopted for data storage. The 4mm DAT has evolved through several stages: DDS-1, DDS-2, DDS-3, and DDS-4, with capacities ranging from 1GB to 12GB. Currently, a single DAT tape can store up to 12GB, and up to 24GB with compression. DAT technology is mainly used in user systems or local area networks.
☑️ 8mm Technology
The 8mm technology was developed by Exabyte in 1987. It uses helical scan technology and is characterized by large tape capacity and high data transfer rates, offering relatively high-capacity storage solutions at a higher price point. The development of 8mm tape drives has gone through several formats including 8200, 8500, 8500c, and 8900 (Mammoth), with capacities ranging from the initial 2GB up to 40GB, and transfer rates reaching up to 6MB/s. The new generation Mammoth-2 technology has further enhanced performance, offering storage capacities up to 170GB (60GB uncompressed) and transfer rates of 30MB/s (12MB/s uncompressed), with great potential for future development.
☑️ DLT Technology
DLT (Digital Linear Tape) technology originated from 1/2 inch tape drives. These 1/2 inch drives appeared early on and were mainly used for real-time data capture, such as call traffic recording in program-controlled switches and seismic signal recording in geological equipment. DLT tapes were co-developed by DEC and Quantum. Due to the large size of the tape, all DLT tape drives are 5.25-inch full-height format. With their high capacity, DLT products are primarily targeted at the mid-to-high-end server market and tape library systems. Current DLT drives offer capacities ranging from 10GB to 80GB, with data transfer speeds from 1.25MB/s to 10MB/s. Another format based on DLT is Super DLT (SDLT), introduced by Quantum in 2001. It incorporates new tape recording technologies based on DLT and uses Laser-Guided Magnetic Recording (LGMR) to increase track density on the tape, thereby enhancing capacity. Current SDLT capacities reach 160GB—nearly three times that of DLT tapes—with a transfer rate of 11MB/s, twice that of DLT.
☑️ LTO Technology
LTO (Linear Tape Open) technology is an open linear tape format protocol. It was jointly developed in November 1997 by HP, IBM, and Seagate. It combines the advantages of linear multi-channel, bidirectional tape formats and improves tape capacity and performance through system-level service features, hardware data compression, optimized track surfaces, and high-efficiency error correction techniques. LTO is an open-format technology that allows users to choose from multiple products and media specifications, improving product compatibility and continuity.
LTO technology has two storage formats: the high-speed open tape format Ultrium and the fast-access open tape format Accelis, each tailored to meet different user requirements. Ultrium uses a single-axis 1/2-inch tape, with a native storage capacity of 100GB, maximum transfer rate of 20MB/s, and compressed capacity of up to 200GB, with room for growth. It is ideal for backup, storage, and archiving applications. The Accelis format focuses on fast data storage and is well suited for automated environments, handling a wide range of online data and recovery applications.
☑️ AIT Technology
AIT stands for Advanced Intelligent Tape. It features advanced technologies such as helical scan and metal evaporated tape, offering outstanding data protection performance. AIT has now evolved to AIT-3. Sony, which develops AIT technology, and Spectra Logic, which focuses on AIT-based products, are actively promoting its adoption. It has now become an industry standard for tape drives. AIT uses a tape cassette that includes a memory chip. This chip records the location of files on the tape, greatly reducing access time.
AIT uses a helical scan recording method, similar to that of home VCRs. This means that in the tape drive, only the drum rotates at high speed, while other components like the tape and servo mechanisms operate at low speed. This compact and reasonable design is easier to build and maintain. In contrast, LTO, DLT, and SDLT all use linear recording, like audio cassette recorders, where the tape moves linearly past a stationary head. To ensure recording speed, the tape must move quickly past the head, requiring complex mechanisms to control tape tension and cool high-speed components and bearings. With identical materials, helical scanning extends the life of the tape.
In terms of application, AIT tape libraries are suitable for enterprise-level data backup. Compared to other products of similar capacity and transfer rates, AIT rack-mounted libraries offer advantages such as smaller size, lower power consumption, larger capacity, and lower cost. For mid-range users, AIT auto-loaders are a good choice.
☑️ VXA Technology
VXA is a tape backup technology developed by Exabyte. It ensures read/write reliability without relying on precise head and track alignment. Unlike streaming tape devices that require expensive precision parts and mechanical components for accurate track alignment, VXA eliminates the problem of tape "backhitching" by automatically adjusting tape motion to match the host’s data transfer rate. This significantly enhances the reliability of both media and drive, optimizing backup and storage processes.
VXA records data in packet format and performs gapless scanning of the data areas on the tape. The technology has evolved from VXA-1 to VXA-2, improving speed and capacity while maintaining high reliability. A single VXA-2 tape cartridge can store up to 160GB (80GB uncompressed) with a data transfer rate of 12MB/s (6MB/s uncompressed).
What are the storage media of tape drives?
The storage media for tape drives is magnetic tape. Currently used types include Metal Particle (MP), Advanced Metal Evaporated (AME), and AME with SmartCleanTM Technology for automatic cleaning.
MP Media
MP tape is standard metal particle tape. It is made by adhering metal powder onto the tape. Typically, MP tapes can withstand 2,000 read/write cycles.
AME Media
AME (Advanced Metal Evaporated) media is made by using laser heating to vaporize metal particles at high temperatures, which are then condensed onto the tape. Compared to MP tapes, AME tapes offer higher recording density, smoother surfaces that reduce head wear, and thinner material that allows longer tape lengths within the same cartridge volume. AME tapes can typically handle 25,000 read/write cycles.
AME Media with Auto-Cleaning
AME tapes with SmartClean technology are designed to enhance reliability. These tapes include a 2-meter cleaning section at the front to automatically clean the tape drum and heads, reducing wear and extending the life of the heads by 30%.
Vinchin's Data Protection Strategies
Faced with complex data storage needs, enterprises not only need reliable technical solutions, but also efficient backup and management tools. For example, Vinchin provides cross-platform, automated data protection solutions based on deep integration of storage architecture, further unleashing the potential of tape and network storage technologies.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery supports both physical and virtual tape libraries as backup storage options, allowing you to store backups on a reliable, long-lasting medium. It supports several types of tape libraries and standlone drives including LTO6 - LTO9, IBM, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, DELL and Quantum.
Vinchin focuses on virtual machine backup, recovery and migration, and supports more than 10 popular virtualization platforms, such as VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, XenServer, oVirt, XCP-ng, etc. With Vinchin, you can easily copy and archive important backup data to tape libraries for long-term retention.
It takes you 4 steps to back up virtual machines to tape storage using Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the virtual machine to be backed up.
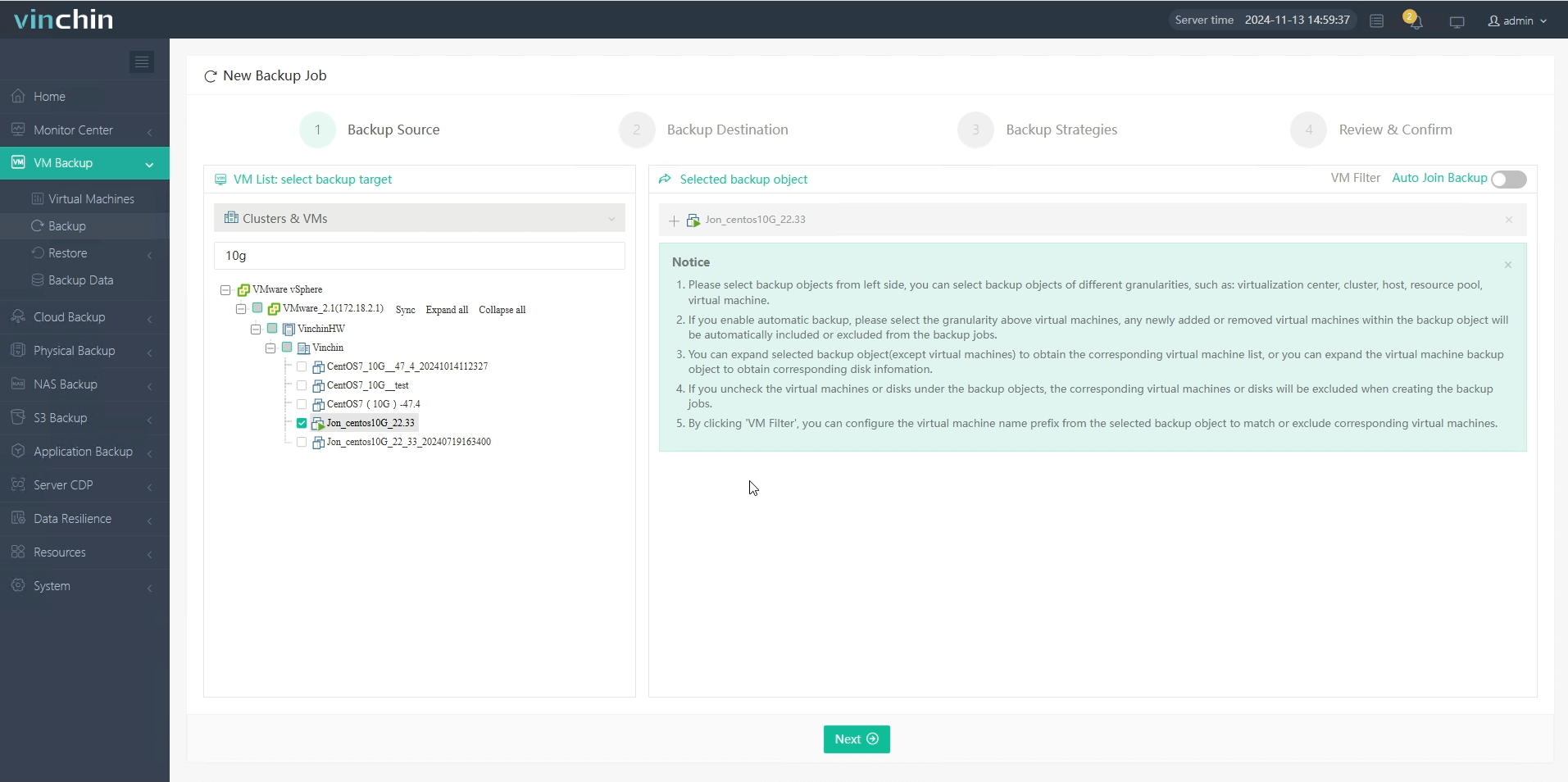
2.Select the backup storage for it.
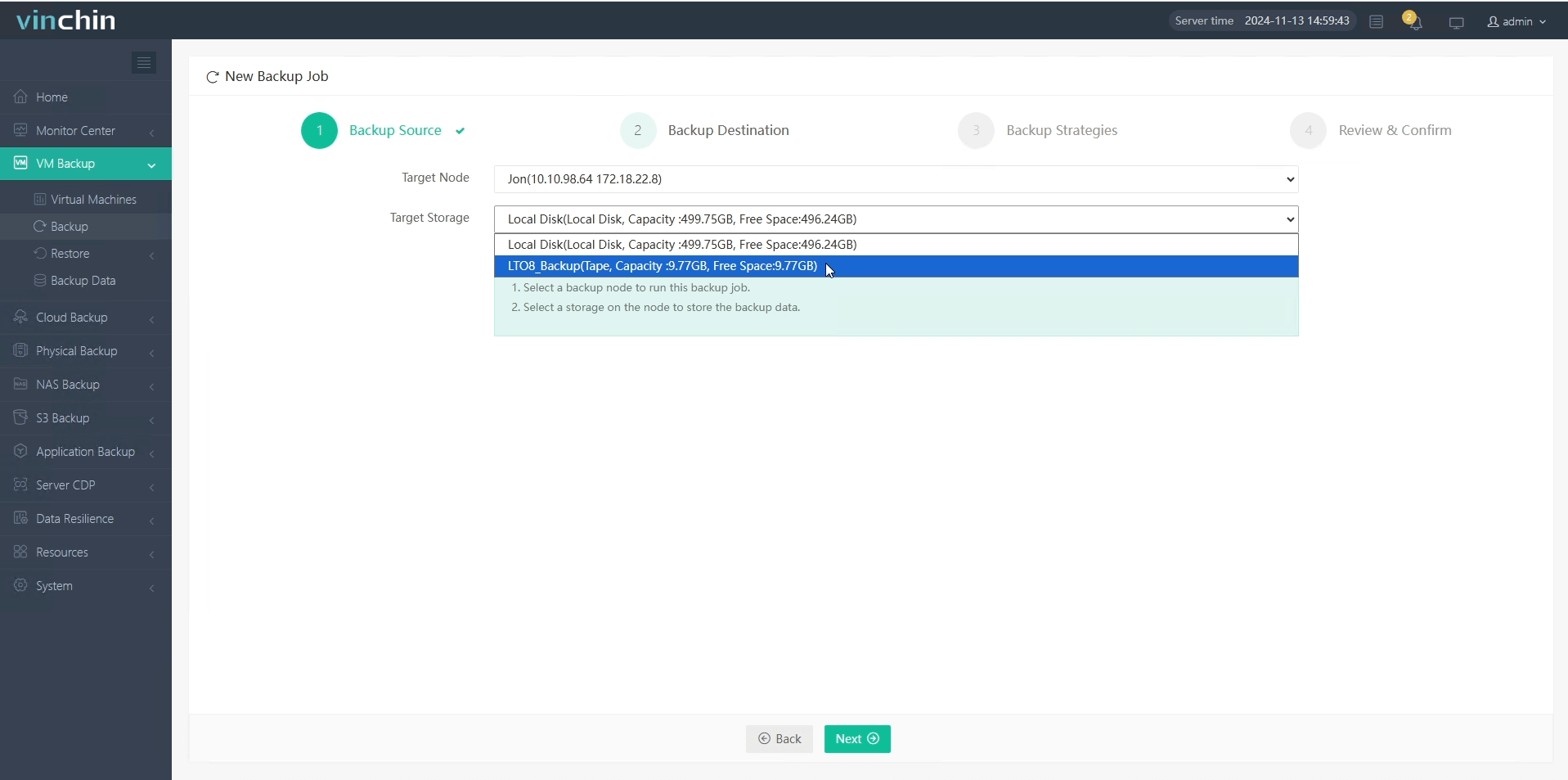
3.Configure the backup strategies.
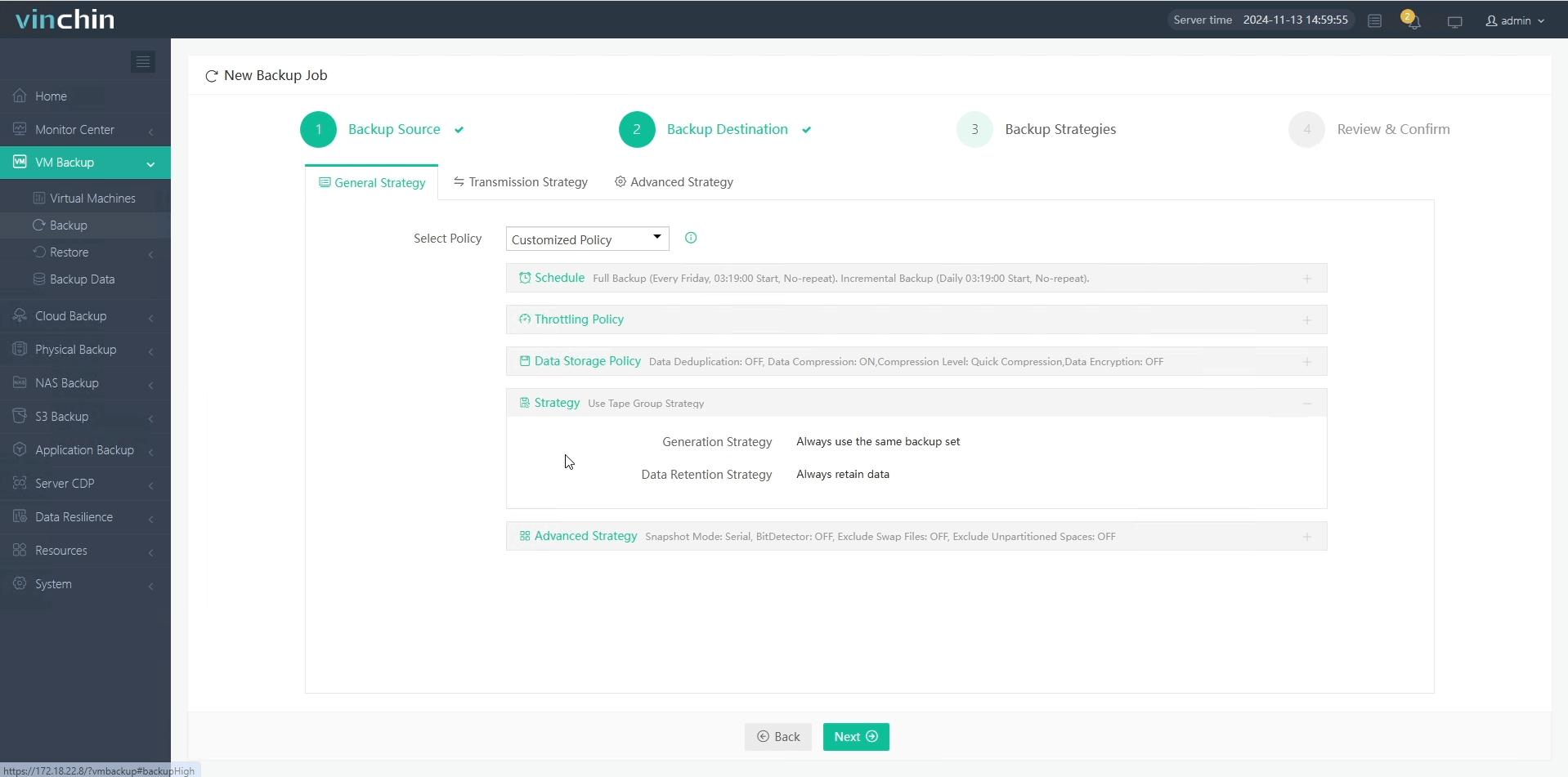
4.Submit the job.
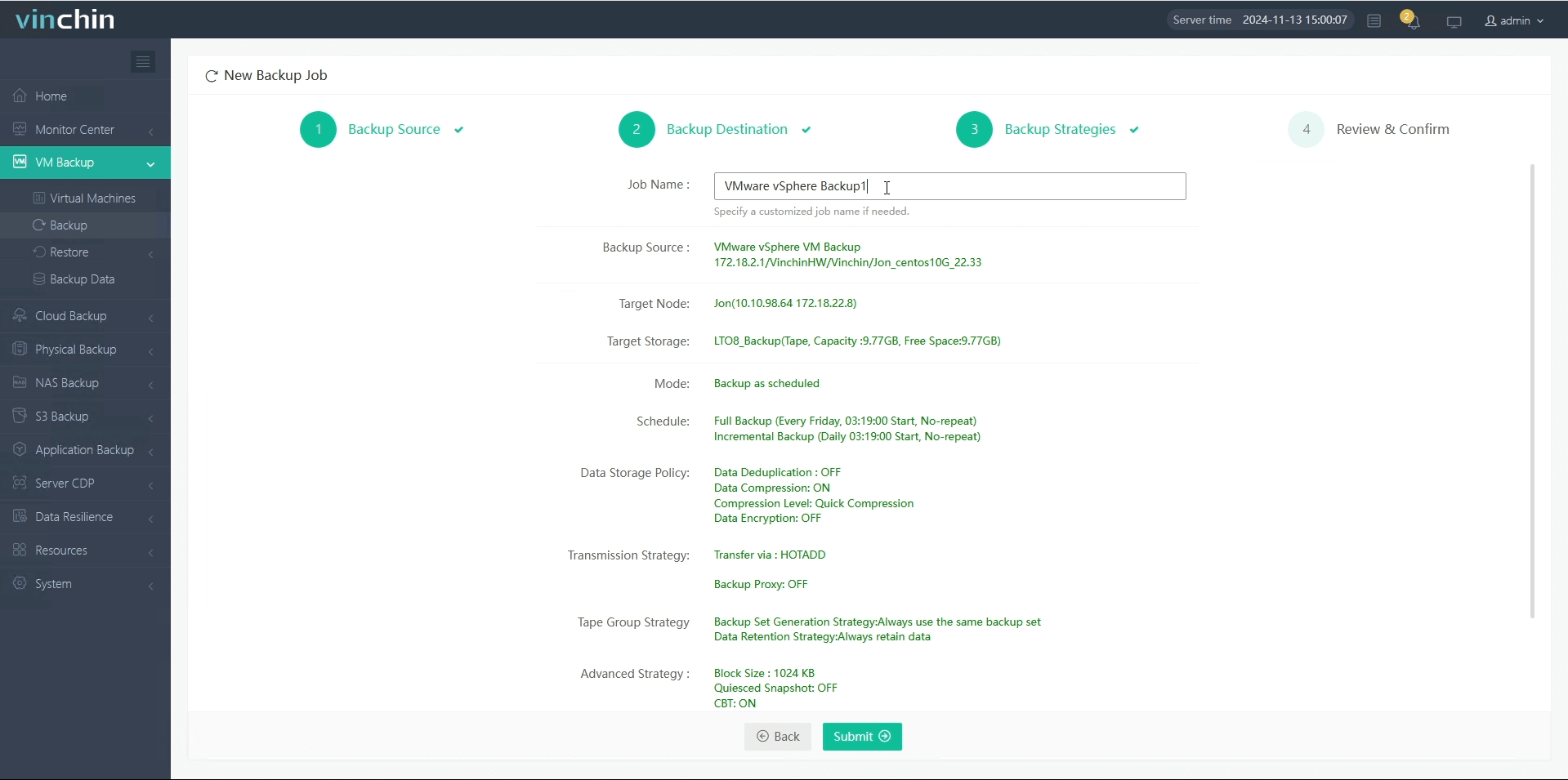
You can click the download button below to try it for 60 days for free and experience more features.
Different types of tape FAQs
1. Are LTO tapes backward compatible?
Yes, most LTO drives can read tapes from two generations back and write to tapes from one generation back. For example, an LTO-9 drive can read LTO-8 and LTO-7, and write to LTO-8.
2. How long does data last on tape?
Depending on storage conditions, data on tape can last 15–30 years or more. Tapes must be stored in a controlled environment to maintain integrity.
Conclusion
From DAT's spiral scanning to LTO's open linear protocol, and from DAS's direct connection to SAN's high-speed fiber network, the collaborative innovation of tape technology and storage architecture continues to push the boundaries of data storage. Despite the rise of cloud storage, tapes remain the cornerstone of massive cold data management due to their low energy consumption, long life, and high security.
Share on:







