-
Why need to move Proxmox VM disk to another storage?
-
Method 1. Moving Proxmox VM disk using GUI
-
Method 2. Moving Proxmox VM disk using CLI
-
Simplify your Proxmox VE VM protection
-
Proxmox move disk to another storage FAQs
-
Conclusion
Proxmox VE is a powerful open-source server virtualization management platform based on Debian GNU/Linux. It allows users to manage virtual machines, containers, and even full-fledged clusters, all from a single, integrated environment. One of the many tasks you may need to perform in Proxmox is moving a disk from one storage medium to another. This task can be crucial when upgrading storage hardware, optimizing storage usage, or implementing backup strategies. This article will guide you through the process of moving a disk in Proxmox to another disk.
Why need to move Proxmox VM disk to another storage?
There could be several reasons why you might need to move a disk to another storage.
Storage upgrade: If you’re upgrading your storage infrastructure, moving disks to new storage devices can provide better performance, increased capacity, or improved reliability.
Storage optimization: Moving disks between different storage devices allows you to optimize the allocation of resources. You can distribute storage workloads more evenly, balance I/O operations, or allocate specific storage types for different VMs or containers based on their requirements. This can help improve overall system performance and resource utilization.
Storage maintenance: If you encounter issues with a particular storage device, such as disk failures or performance degradation, moving the disks to a different storage location can help isolate the problem. By moving the disks to a known working storage device, you can continue operating your VMs or containers while addressing the storage issues separately.
Method 1. Moving Proxmox VM disk using GUI
Proxmox VE enables the addition of various storage types, such as NFS, iSCSI-LVM, and so forth. This raises the question: is it possible to move the virtual hard disk of a VM, previously created and running on local-lvm, to the newly added NFS or iSCSI-LVM storage?
The answer is “Yes”.
1.Select the VM where the virtual disk needs to be moved, stop the VM, and click Hardware > Hard Disk > Disk Action > Move Storage.
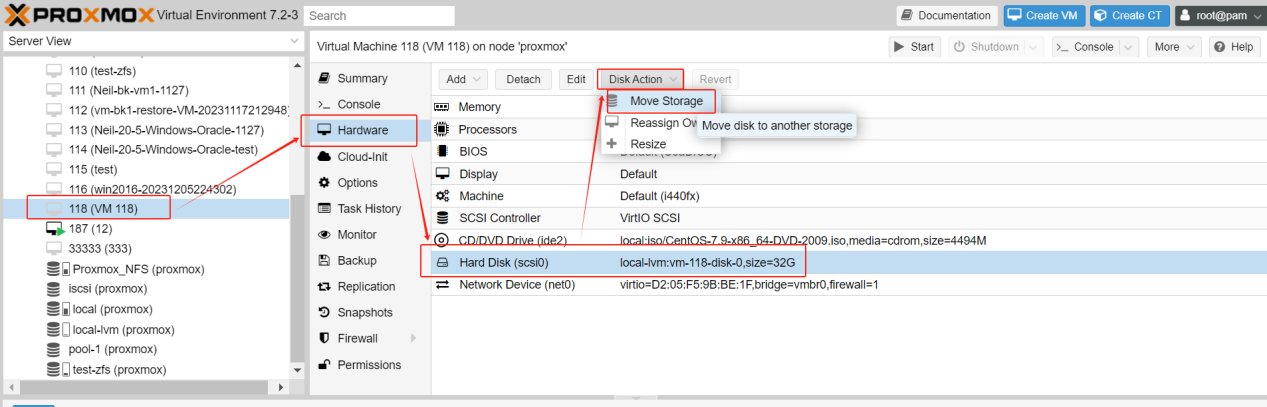 2.Select target storage and format.
2.Select target storage and format.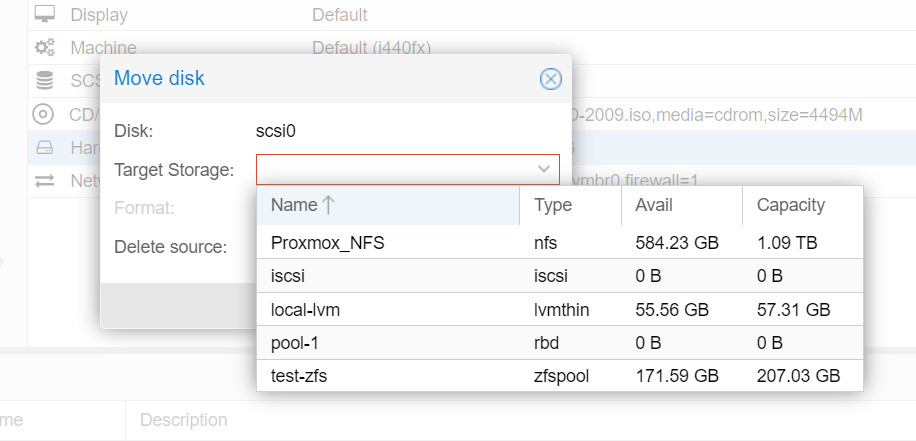
If the Target Storage is on file level, the Format supports three types of virtual disk image formats: Raw disk image, QEMU image format (QCOW2), and VMware image format (VMDK). Proxmox VE suggests using the QEMU image format.
Delete Source: This is the option to delete the original disk. For safety, if you are concerned about potential issues when migrating to new storage or if there’s a need to keep an extra copy for backup purposes, do not check this option.
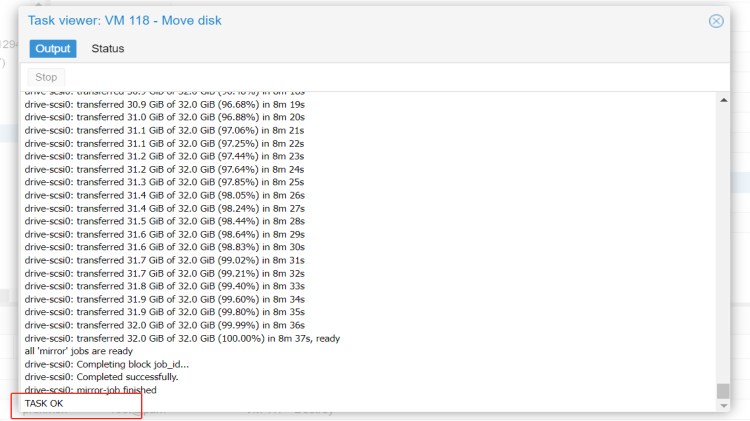
3.Click on Move Disk and wait for the completion of the disk migration.
4. Check the Hard Disk again.
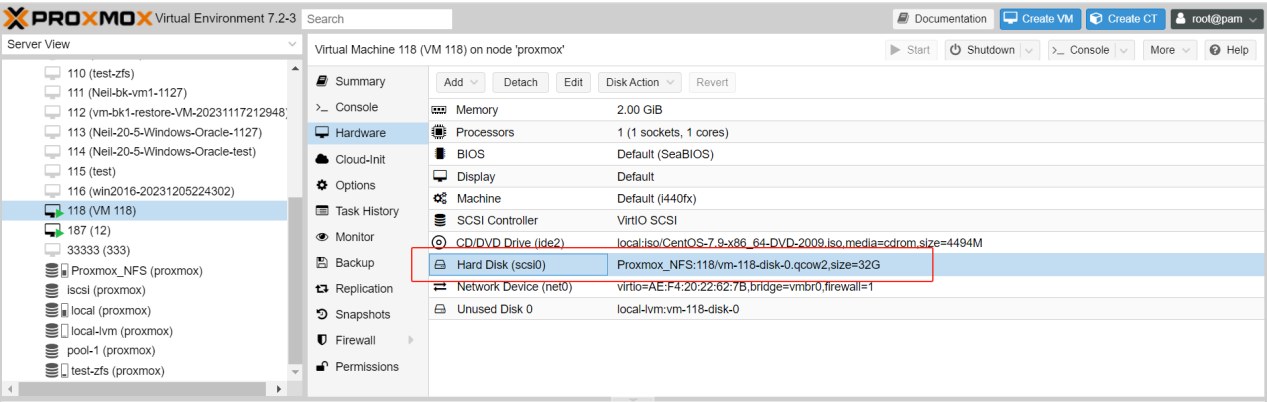
You can find that it has been moved to a new disk, whereas the initial “local-lvm:vm-118-disk-0” has now transformed into “Unused Disk 0”. After confirming that the move was successful, you could proceed with the deletion of the original “Unused Disk”.
Method 2. Moving Proxmox VM disk using CLI
1.Identify the source and target storages
First, you need to identify the source and target storages. You can do this by using the following command:
pvesm status
This command will list all available storage on your Proxmox server. Note down the IDs of the source and target storages.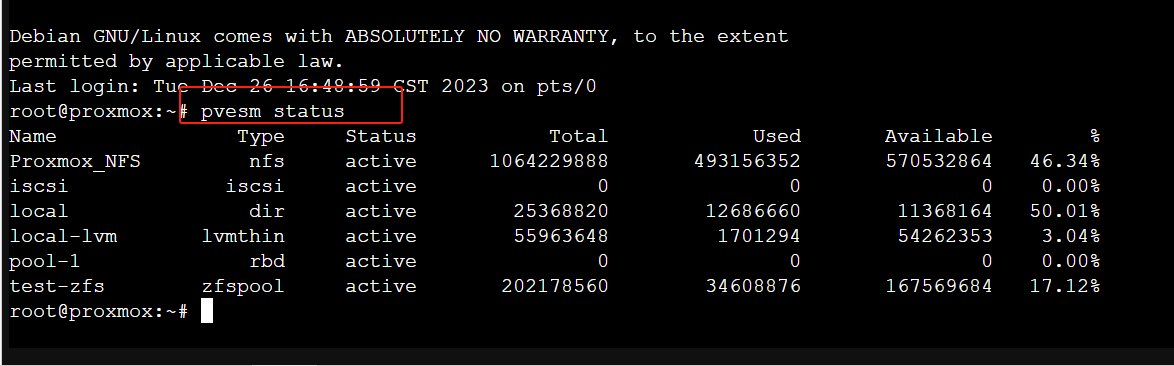
2.Shut down the virtual machine
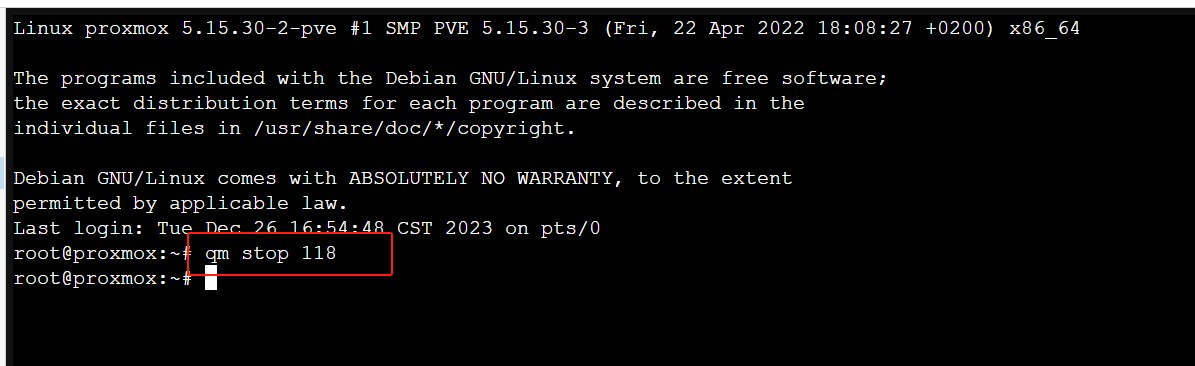
Using the following command, replacing “VMID” with your virtual machine’s ID:
qm stop VMID
3.Check the configuration of the VM to see a list of its disks and their IDs. You can do this with the following command:
qm config VMID
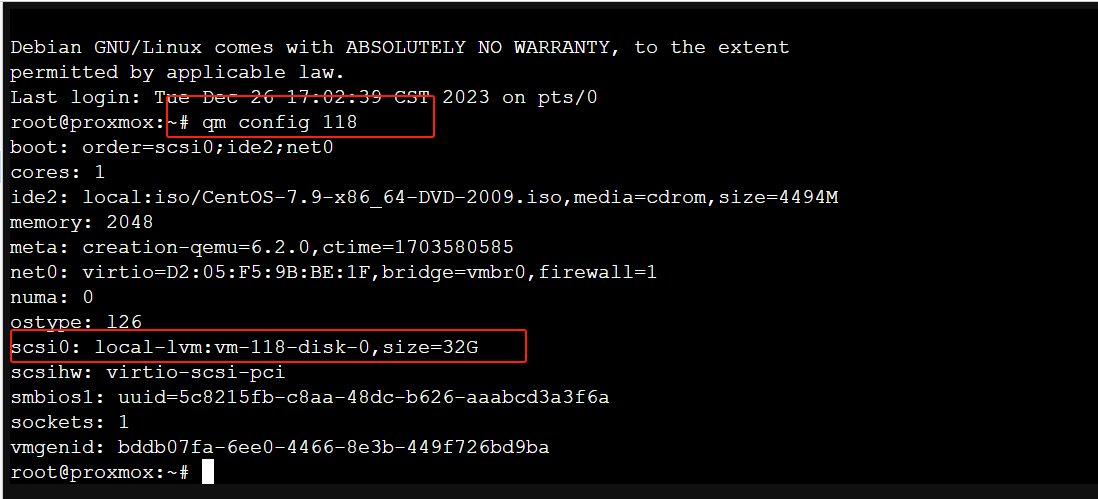
You should see a line for each disk that looks something like this:
scsi0: local-lvm:vm-118-disk-0
In this example, “scsi0” is the disk ID.
4.Move the disk
Using the following command:
qm move_disk VMID source_disk target_storage
Replace “VMID” with your virtual machine’s ID, “source_disk” with the disk you want to move, and “target_storage” with the ID of the storage you want to move the disk to.
5.Start the virtual machine
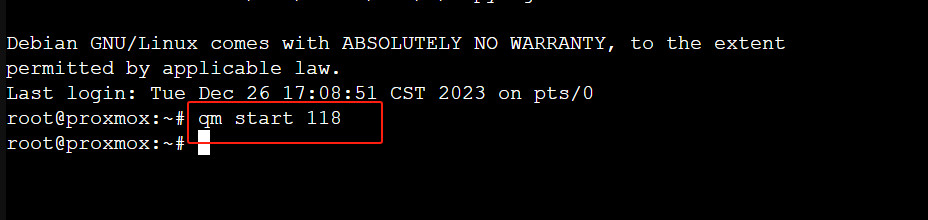
After the disk has been moved, you can start the VM again using the following command:
qm start VMID
6.Verify the migration
Verify that the disk has been moved successfully. You can do this by checking the VM’s hardware. Use the following command again:
qm config VMID
The disk should now be listed under the new storage.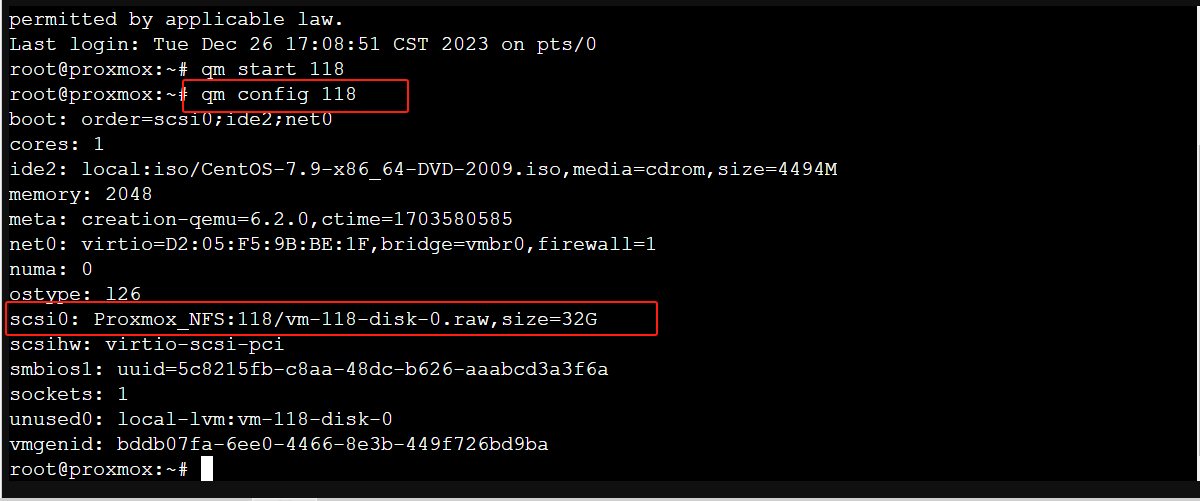
Simplify your Proxmox VE VM protection
There’s always the risk of unexpected issues. This could include hardware failures, network interruptions, power issues, or other unforeseen problems. Therefore, if your data is important to you, it’s crucial to back up before moving the disk. That way, if anything goes wrong, you can restore your data from the backup.
You can use Vinchin Backup & Recovery to back up your Proxmox virtual machines. It is a robust Proxmox VE environment protection solution, which provides advanced backup features, including automatic VM backup, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free backup, offsite copy, instant recovery, effective data reduction, cloud archive and etc., strictly following 3-2-1 golden backup architecture to comprehensively secure your data security and integrity in Proxmox VE beyond replication.
Besides, data encryption and anti-ransomware protection offer you dual insurance to protect your Proxmox VE VM backups. You can also simply migrate data from a Proxmox host to another virtual platform and vice versa.
It only takes 4 steps for you to backup Proxmox VE VMs:
1. Select the backup object.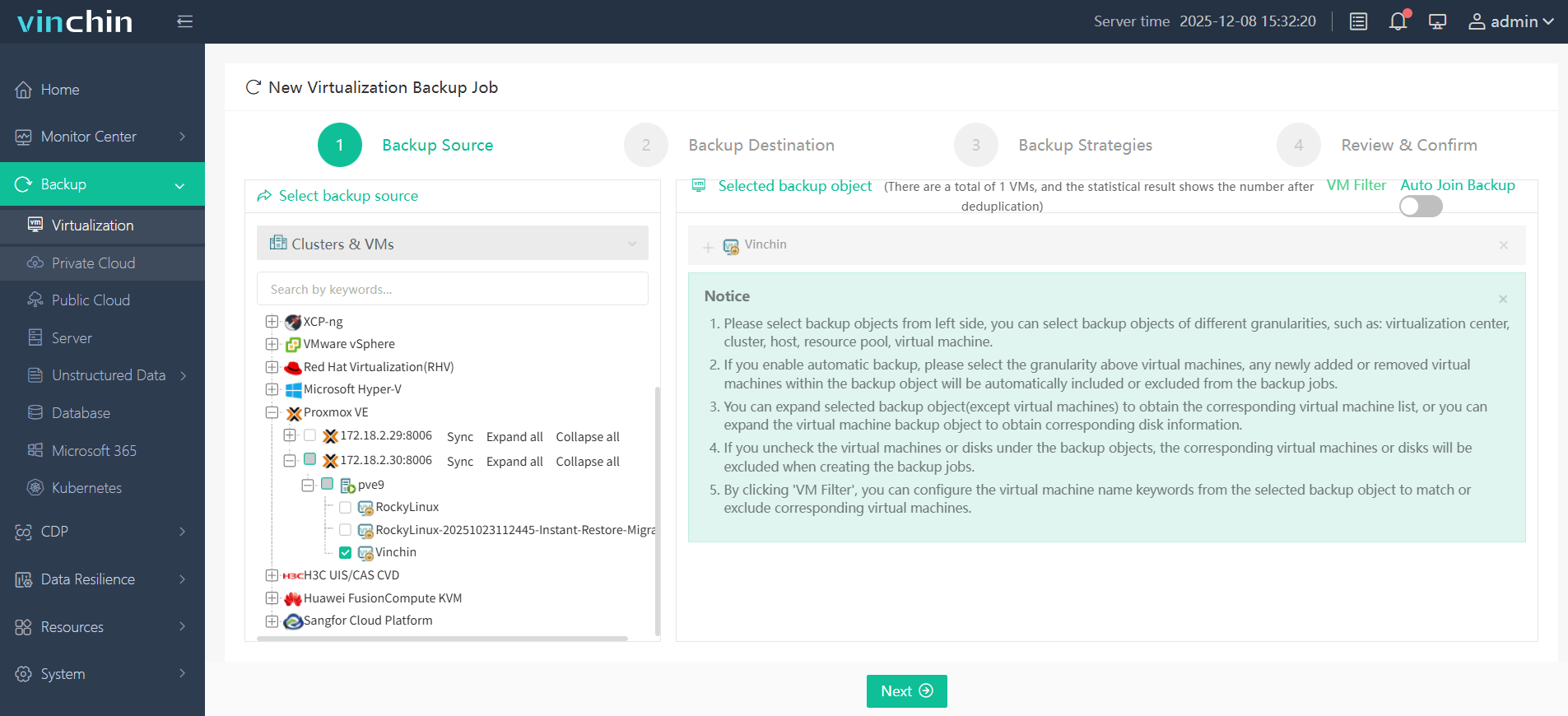
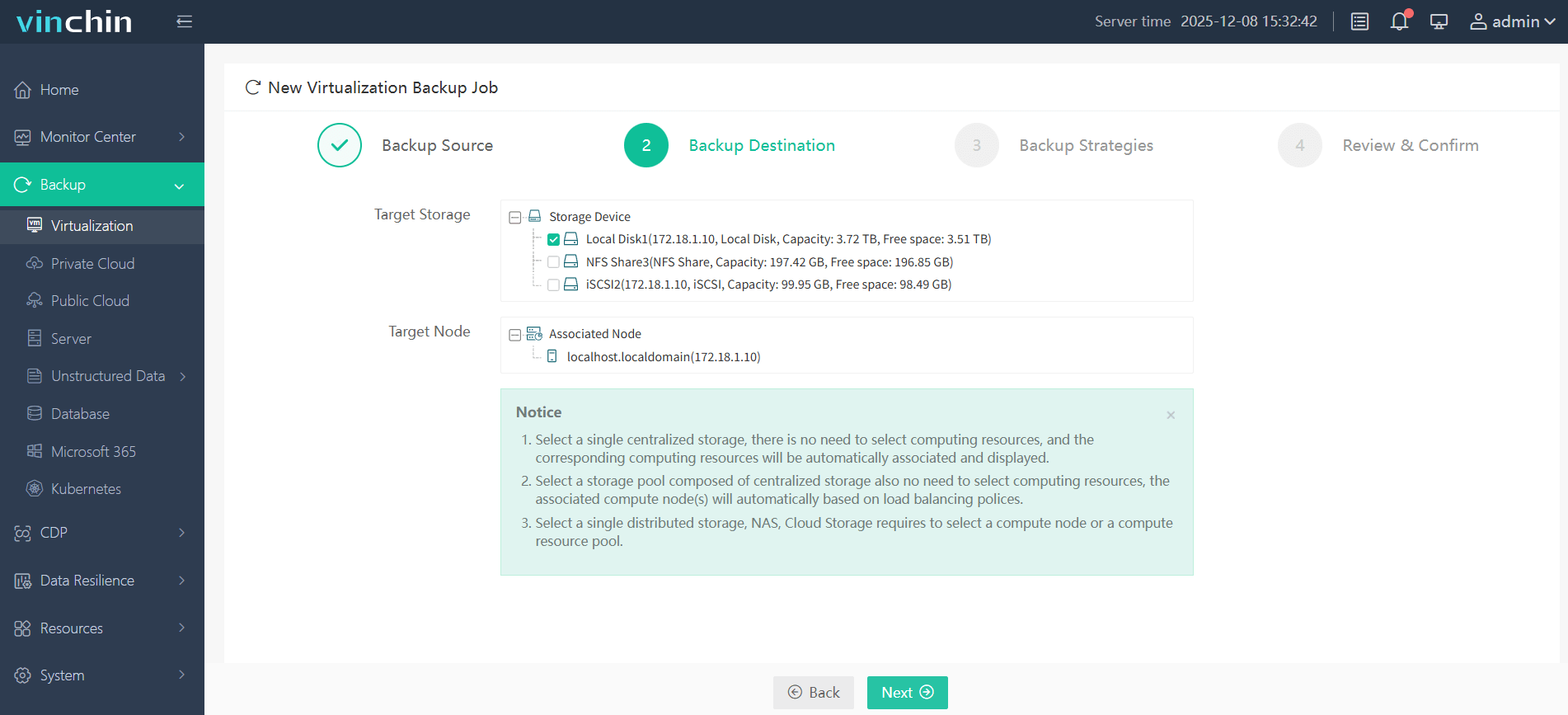
2. Select backup destination.
3. Select backup strategies.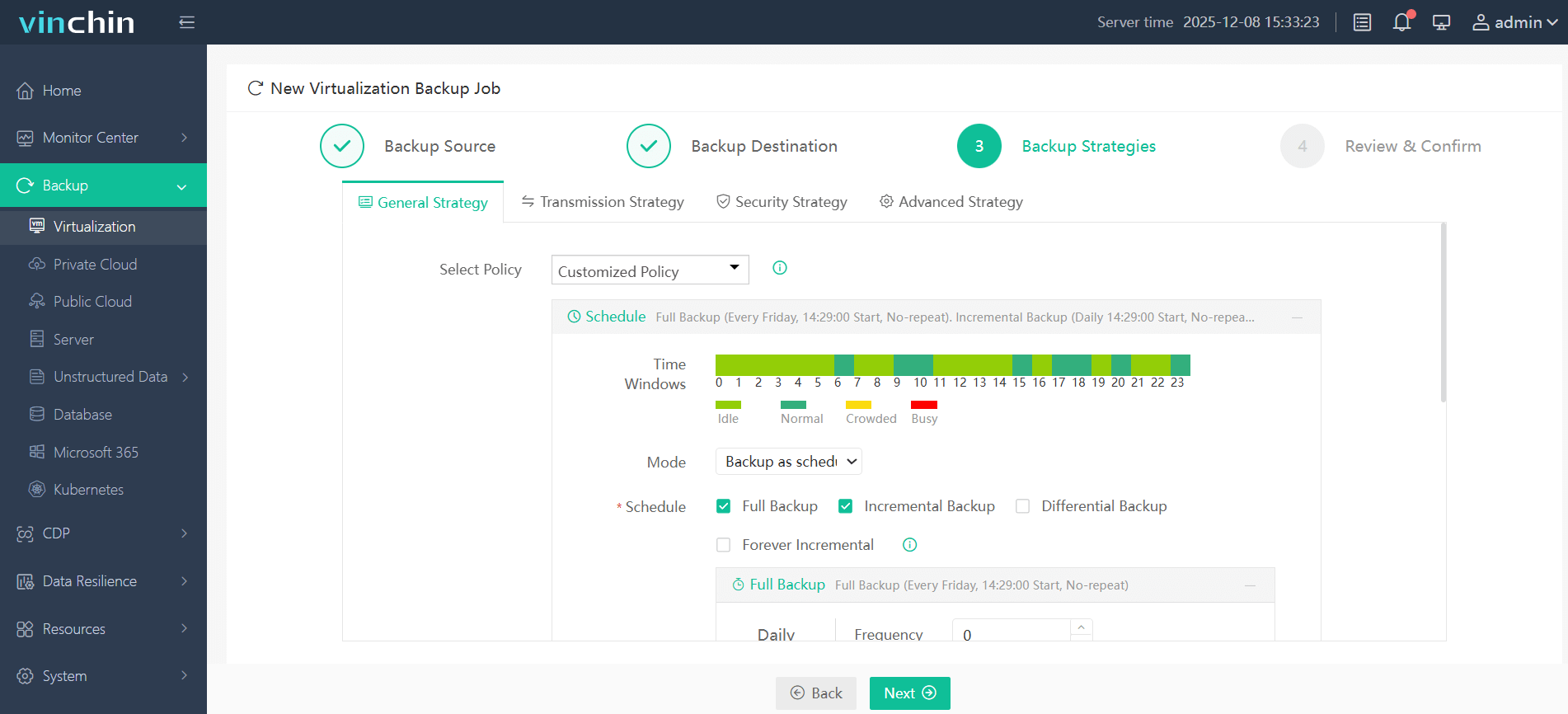
4. Review and submit the job.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery, a solution trusted by thousands of companies worldwide, offers a comprehensive backup strategy when moving a disk to another storage in Proxmox VE. Start benefiting from this robust system with a 60-day full-featured trial! Share your specific Proxmox VE environment needs with us, and we will provide a custom solution that fits seamlessly with your IT infrastructure.
Proxmox move disk to another storage FAQs
1.Q: Which is better Proxmox or ESXi?
A: Proxmox VE and VMware ESXi are both powerful virtualization platforms, but they have some key differences. Here is a comprehensive comparison between Proxmox and VMware ESXi. Whether you choose Proxmox or VMware ESXi, prioritizing effective virtual machine protection and backup is critical. Explore third-party solutions like Vinchin Backup & Recovery for comprehensive, flexible backup options.
2.Q: How does one introduce new storage within Proxmox?
A: Within Proxmox’s Web User Interface, opt for “Datacenter”, subsequently select “Storage”, then press “Add”, following which you should pick the intended variety of storage. Input the essential data, such as ID, storage path, and so on, culminating in a click on “Add”.
Conclusion
Migrating VM disks within Proxmox is a critical task for optimizing storage resources, enhancing performance, and maintaining a flexible virtualization environment. This comprehensive guide covers the detailed steps for that. By following these detailed instructions, you can successfully optimize your virtualized environment while minimizing the risk of data loss or operational disruptions.
Share on:









