-
VHD
-
VHDX
-
VHD vs VHDX
-
How to Work with VHD and VHDX?
-
Backup and Restore Hyper-V with All-in-One Solution
-
VHD vs VHDX FAQs
-
Conclusion
VHD and its successor VHDX are disk image file formats keeping the whole contents of a computer’s hard drive. VHD and VHDX are the native file formats of Microsoft Hyper-V that store files, sectors, disk partitions, OS installation, etc., which, share common and differences in some ways. In this blog, we’re going to explore and find out what are they, how they differ from each other, and how to work with them.
VHD
The Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) is a virtual machine publicly-available image format working as the physical hard disk. Developed by Connectix, the format was used in Microsoft hypervisor later because of the acquisition in 2003.
Features
VHD file is pre-allocated and fixed on the virtual disk space, so the virtual disk size remains constant.
VHD file only uses as much space to store virtual disk data as needed.
A differencing VHD file identifies, records, and manages changes made to the parent virtual disk, so it can restore quickly or create boot images based on the file.
Advantages
VHD format allows multiple operating systems on a single host machine.
VHD format enables users to transfer files from and to the host file system and a VHD file.
VHD format allows for the modification of virtual machines by users using the host servers.
Backup and recovery operations of VHD file is easy.
Users can undo changes made to the VHD file.
Can be used in earlier and more versions of Windows: Windows Server 2008, 2008 R2, and 2012 R2, Windows Vista, Windows 7, and higher versions.
Disadvantages
The maximum storage space of a VHD file is only 2TB.
VHD file doesn’t support live resizing, custom metadata, trimming, and has some problems with data alignment.
When making partitions on the VHD file with Disk Management, you can only select the NTFS or FAT32 file systems.
VHDX
VHDX (Virtual Hard Disk v2) is the replacement format for VHD introduced in Windows 8/ Windows Server 2012 that could be also used by VMware Workstation and VirtualBox. This file format increases the functionality and adaptability of VHD.
Features
The virtual hard disk storage capacity is increased to 64 TB.
Supports custom metadata and its record for data protection.
Logical sector virtual disk size of 4 KB.
Advantages
Track changes to VHDX metadata for data corruption prevention during power outages.
Larger dynamic and differencing disk block sizes to adjust the workload demand of these disks.
Trimming produces smaller file sizes and allows the underlying storage devices to recycle spare space.
Improved virtual hard disk format alignment.
Much bigger storage capacity compared to VHD.
Disadvantages
Supported by fewer OS: Windows Server 2012, Windows 7, and higher versions.
When making partitions on the VHD file with Disk Management, you can only select the NTFS or exFAT file systems.
You may be unable to open the VHDX file because it is not always associated with a VM.
VHD vs VHDX
Format | VHD | VHD |
Supported By | Windows, Citrix, and Oracle. | Windows. |
Supported OS | Windows Server 2008, 2008R2, 2012R2, and 2012 versions. | Windows Server 2012 and later versions. |
Storage Capacity | Maximum 2 TB. | Maximum 64 TB. |
Logical Sector Size | 512 bytes. | 4 KB. |
Data Protection | Less data protection. | Offer strong security guarantees against data corruption by tracking metadata. |
Resizing | Not supported. | Support. |
Data Alignment and Trimming | Meet problems with alignment and do not support Trimming. | Enhanced data alignment and support Trimming. |
Use Case | Developers test software on different OS; Used on previous Hyper-V versions; When you need the greatest adaptability or backward compatibility. | Used on Windows 2012 and above; When you need optimum efficiency and reliability. |
How to Work with VHD and VHDX?
Conversion Notice:
Upgrade your Hyper-V to VHDX-supported versions, then convert VHD to VHDX.
The conversion process is offline.
Do not convert VHD to VHDX if: you created a VM snapshot; you’re copying the VHD using Hyper-V Replica; VHD is the parent to differential hard disks.
Convert VHD to VHDX and VHDX to VHD with Hyper-V Manager
1. Launch Hyper-V Manager, right-click on the VM you want to convert, and click Settings.
2. Select the target disk, and click Next in the Edit Virtual Hard Disk Wizard.
3. On Locate Disk page, click Next.
4. On Choose Action page, choose Convert, and click Next.
5. On Choose Disk Format page, choose either VHD/VHDX for the converted disk format, click Next, and configure Disk Type and storage location for the newly converted format in Configure Disk option. After all this. Click Next.
6. Click Finish on the Summary page. Then wait for the conversion to finish.
7. Replace the original format with the converted format by opening the source file, and clicking on Browse… to find the newly created disk. Then click Open> Ok> Start and test the VM.
8. Remove old files once the new file works fine.
Convert VHD to VHDX with PowerShell
Convert-VHD –Path “vhdfilepath” –DestinationPath “Destination vhdxfilepath”
Convert VHDX to VHD with PowerShell
Convert-VHD -Path ‘vhdxfilepath’ ‘vhdfilepath’
Merge Hyper-V VHD and VHDX
While merging the changes in the differencing disk into the parent disk or other disks, notice that the disk chain is detached, the whole operation is offline, and the differencing disk is destroyed after the merge.
Merge-VHD -Path ‘diskpath.vhd/x’ -DestinationPath ‘diskpath.vhd/x’
Mount Hyper-V VHD and VHDX
Mount-VHD -Path ‘diskpath.vhd/x’
In read-only mode
Mount-VHD -Path ‘diskpath.vhd/x’ -ReadOnly
Dismount VHD and VHDX
Dismount-VHD -Path diskpath.vhd/x
Resize Hyper-V VHD and VHDX
Expand VHDX to XGB.
Resize-VHD -Path 'diskpath.vhdx' -SizeBytes XGB
Shrink VHDX (only applicable) to minimum size.
Resize-VHD -Path 'diskpath.vhdx’ -ToMinimumSize
Move VHDX to another bus/location
Set-VMHardDiskDrive -VMName name -ControllerType IDE -ControllerNumber X -ControllerLocation X -ToControllerType SCSI -ToControllerNumber Y -ToControllerLocation Y
Backup and Restore Hyper-V with All-in-One Solution
Files may be corrupted due to hardware failure, system shutdown, power outage, or malware attacks, and VHD(X) is no exception. To avoid data loss and corruption should any accidents happen, you can back up the files in advance and prepare disaster recovery plans for them.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a comprehensive solution that supports automatic, agentless backups for multiple platforms including Hyper-V, VMware, and others. It offers advanced features such as flexible scheduling, data deduplication, compression, and encryption for secure data transmission. The solution also enables efficient disaster recovery with full and file-level restore options, offsite backup copying for additional protection, and anti-ransomware measures to safeguard backup data.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your Hyper-V VMs with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
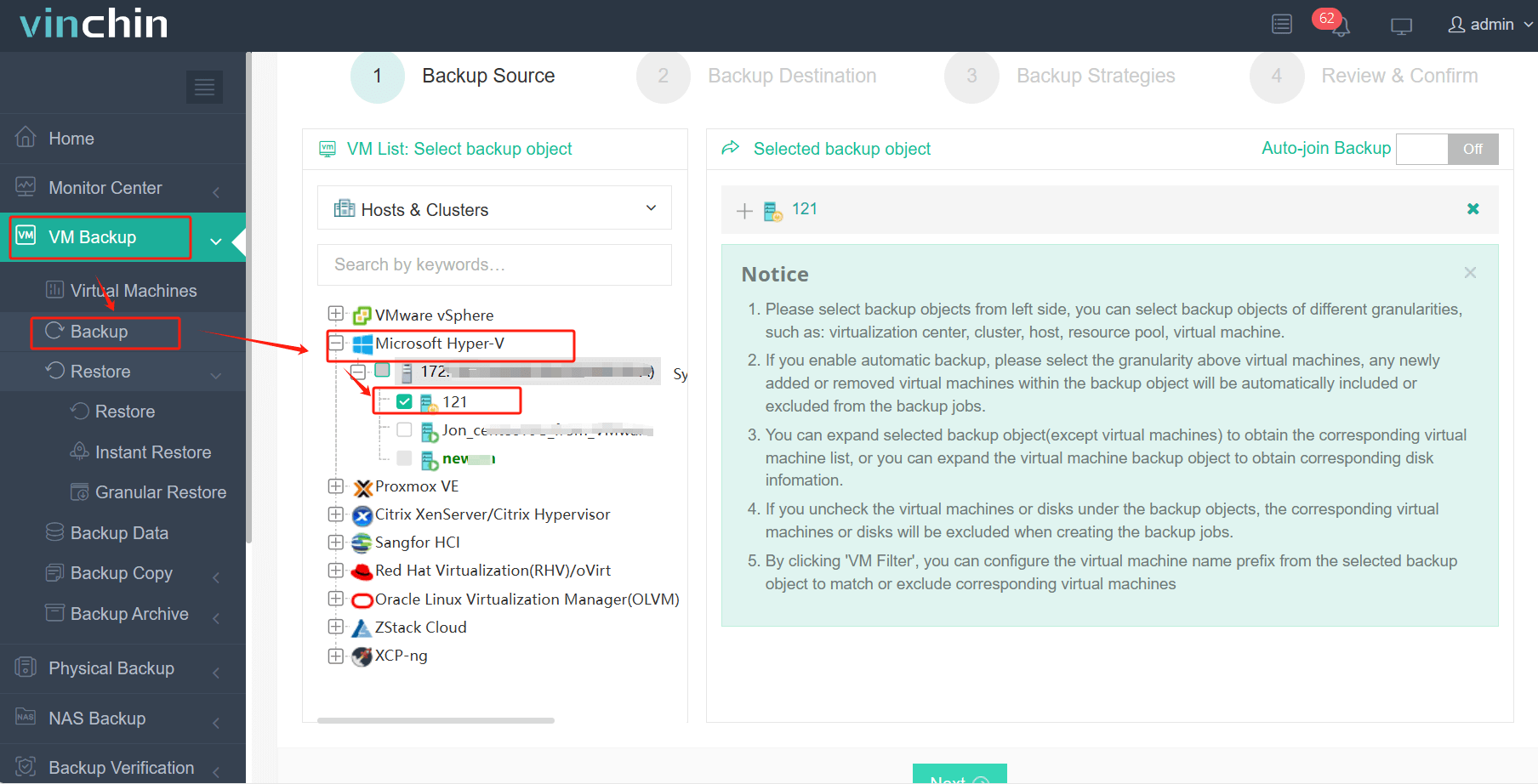
2.Select backup destination.
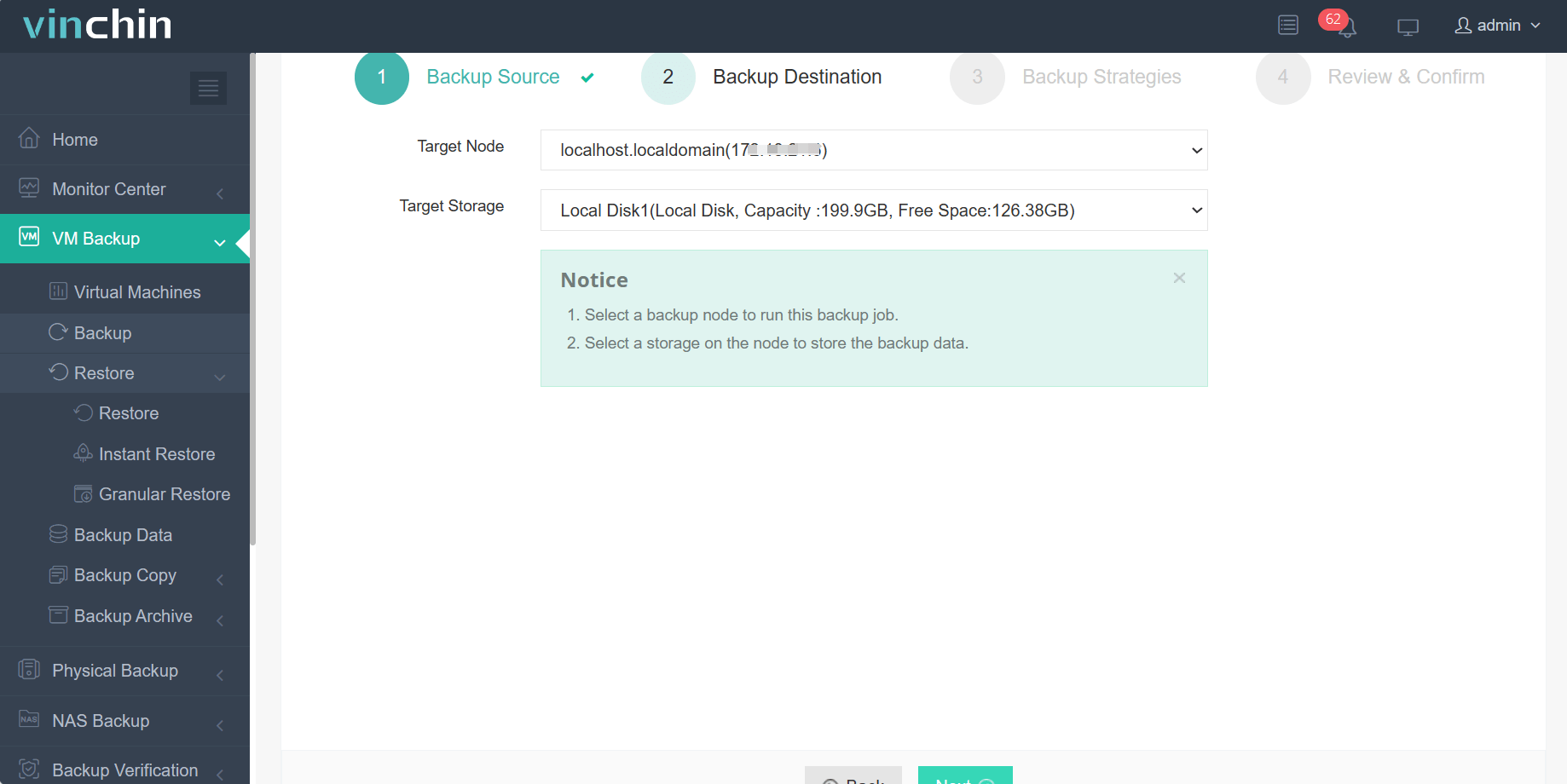
3.Configure backup strategies.
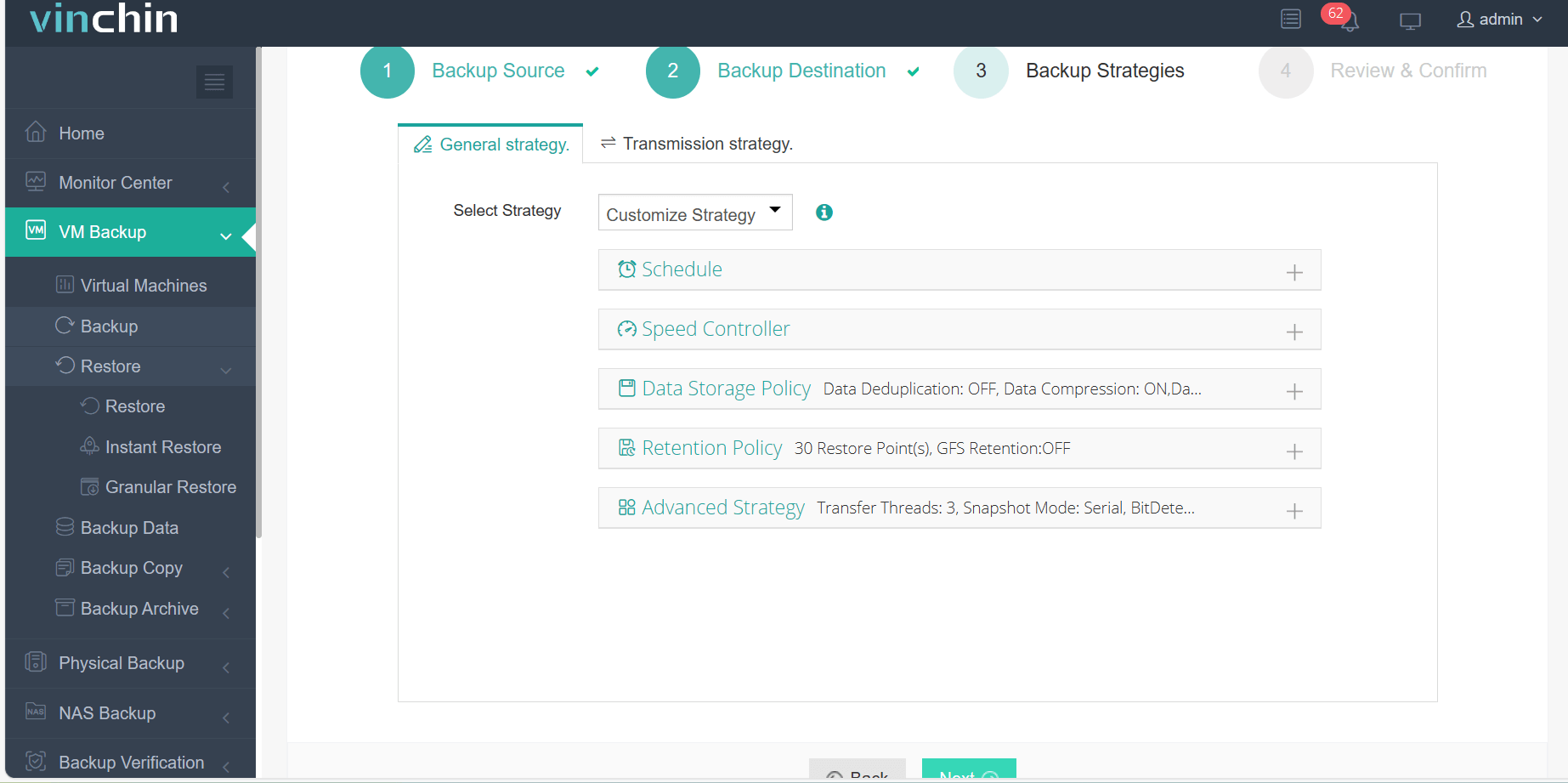
4.Review and submit the job.
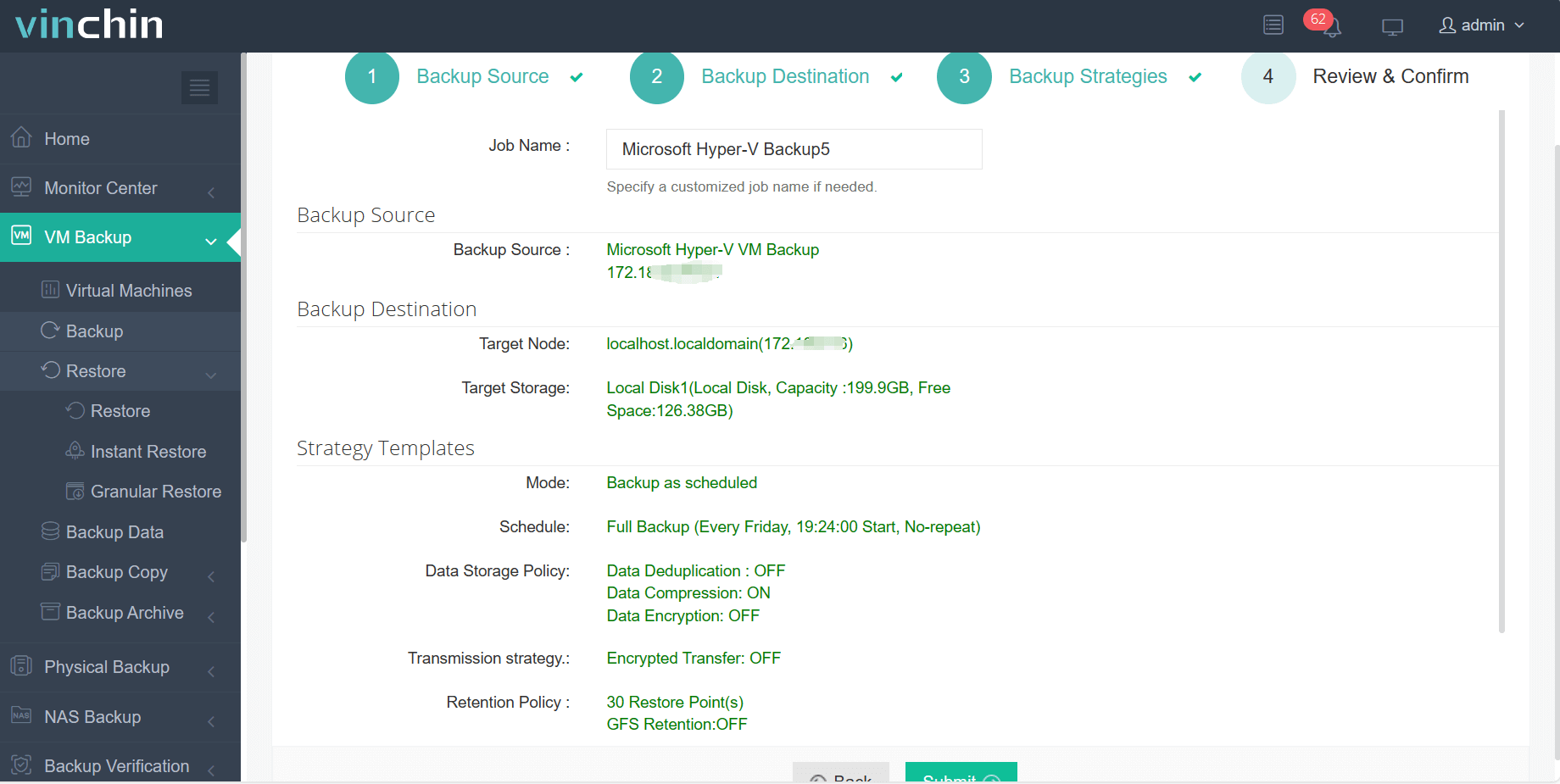
You are more than welcome to download a 60-day full-featured free trial below.
VHD vs VHDX FAQs
1. Q: When should I use VHD over VHDX?
A: Use VHD if you need compatibility with older systems, such as Windows Server 2008 or older hypervisors. However, VHDX is generally preferred for modern environments due to its advanced features.
2. Q: Can I create a fixed-size VHDX disk?
A: Yes, like VHD, VHDX can be created as either a fixed-size or dynamically expanding disk. Fixed-size VHDX disks are allocated the full size immediately, which can lead to better performance in certain scenarios.
Conclusion
Both Hyper-V VHD and VHDX files are essential in virtual environments as virtual hard disks. While the VHD enjoys a long history in Microsoft, the VHDX is developed to keep up with technological progress, so it is safe to say VHDX is recommended as a more efficient file format with enhanced performances than the former.
Use Vinchin Backup & Recovery, a cost-effective option with advanced smart backup and recovery strategies to tailor your needs.
Share on:








