-
What is vSphere networking?
-
Key components in vSphere networking
-
vSphere Standard Switch vs. Distributed Switch
-
NIC teaming and load balancing
-
The role of VLANs in vSphere networking
-
Advanced vSphere networking Features
-
How to configure vSphere networking for ESXi hosts?
-
How to configure ESXi VM networking?
-
Best practices for vSphere networking
-
Protecting Your Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
ESXi networking FAQs
-
Conclusion
vSphere Networking is the backbone of your virtual environment. It links physical devices with virtual machines and lets your ESXi hosts talk to each other and to external networks. In this guide, you will learn the basics of vSphere networking, its key components, and best practices. We write in clear and short sentences so that readers from all over the world can easily follow along.
What is vSphere networking?
vSphere networking connects your physical world with your virtual world. A physical network uses real switches and cables. A virtual network runs inside your ESXi hosts. It uses software switches that work like physical ones. These switches forward traffic between VMs, between hosts, and to the physical network. The most common switches in vSphere are the standard switch and the distributed switch.
Key components in vSphere networking
Several components make up the vSphere network. First, port groups are like templates. They define settings like bandwidth limits and VLAN tagging. Each port group attaches to a vSwitch. Next, VMkernel networking provides connectivity for host management, vMotion, and storage tasks. This network layer handles critical services for your ESXi host.
Another important element is NIC teaming. This combines two or more physical adapters. It helps share the network load and offers backup if one adapter fails. Finally, VLANs split your physical network into smaller groups. This segmentation increases security and performance.
vSphere Standard Switch vs. Distributed Switch
A vSphere Standard Switch (vSS) works much like a physical Ethernet switch. It is simple to set up and is available with all versions of vSphere. Each ESXi host has its own standard switch. You connect physical network adapters to the vSS to reach the outside world.
A vSphere Distributed Switch (vDS) is more advanced. It acts as one switch across all the hosts in your data center. You set it up in vCenter Server. The vDS offers central management and more advanced features, such as better load balancing and traffic monitoring. This means VMs keep the same network settings even as they move between hosts.
How virtual switches connect to the physical world?
Virtual switches need physical links to work with your real network. Each vSwitch connects to one or more physical Ethernet adapters, called uplinks. A standard switch uses these uplinks to join your virtual network to the physical network. With a distributed switch, the configuration is pushed from vCenter to every host. This ensures that the network settings are consistent across your data center.
When a VM sends a packet, the vSwitch makes sure it reaches the correct destination. If the destination is on a different network, the packet travels out through a physical adapter. A physical switch then routes the packet to the proper location. This simple process keeps your network running smoothly.
NIC teaming and load balancing
NIC teaming is key to a robust network. By combining several physical adapters into a team, you gain both load balancing and failover protection. Load balancing spreads network traffic evenly across the team. If one adapter fails, the others continue to carry the load. This makes your network more reliable and can improve performance during high traffic.
You can use different teaming policies. For standard switches, the default option is to route traffic based on the virtual port number. With distributed switches, you can choose to balance based on the physical NIC load. These options help make sure that no single adapter becomes overloaded.
The role of VLANs in vSphere networking
VLANs divide your network into smaller, logical segments. With VLAN tagging, you can isolate traffic by function or department. In vSphere, you set the VLAN ID in a port group. When a VM connects to that port group, it sends and receives only the traffic for that VLAN. This makes your network more secure and easier to manage.
VLANs also help reduce broadcast traffic. They keep each segment smaller and more efficient. When you design your network, plan your VLANs carefully. They are a powerful tool for separating management, production, and storage traffic.
Advanced vSphere networking Features
The distributed switch offers many advanced features. With a vDS, you have central control over networking across all hosts. You can monitor traffic, set up Quality of Service (QoS) rules, and use more advanced load balancing options. NSX adds another layer of network virtualization. It can create logical segments on top of your distributed switch. NSX settings are managed outside of vCenter, but they work alongside your standard vSphere networking features.
These advanced features make it easier to scale your network. They also help you manage resources and ensure that critical traffic, like vMotion and storage, always gets the bandwidth it needs.
How to configure vSphere networking for ESXi hosts?
1. Log in to vSphere Client:
Connect to your ESXi host or vCenter Server using the vSphere Client.
2. Create a Standard Virtual Switch:
Navigate to Networking in the left pane > select the Virtual switches tab > click Add standard virtual switch > in the wizard, enter a name for it > leave other settings at their default values and click Add
3. Add Uplinks to the vSwitch:
Select the newly created vSwitch > click the Actions menu and choose Add uplink > in the uplink wizard, select the physical network adapters (NICs) you wish to use. You can choose two NICs for redundancy > click Save
4. Configure a VMkernel NIC for Host Services:
Go to the Networking section and select the VMkernel NICs tab > click Add VMkernel NIC > choose to create a new port group > specify the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway as required > optionally, assign a VLAN ID if your management network uses one > click Create
5. Create Additional Port Groups:
In the Networking section, go to the Port groups tab > click Add port group > enter a descriptive name > select the appropriate vSwitch > specify a VLAN ID if needed > click Add
6. Review and Test:
Confirm that the new vSwitch, uplinks, VMkernel NIC, and port groups appear correctly and then test connectivity
How to configure ESXi VM networking?
It is best practice to power off the VM before making network changes.
1. Edit VM Settings:
In the vSphere Client, expand Virtual Machines in the left pane > right-click on the target VM and select Edit settings
2. Assign the Correct Network Adapter:
In the Virtual Hardware tab, locate the network adapter > in the adapter’s drop-down menu, choose the port group that corresponds to the desired network
3. Save and Power On:
Click Save to apply the changes > power on the VM
4. Verify Network Connectivity:
Inside the VM, check that the IP address is assigned correctly and then test connectivity.
Best practices for vSphere networking
A good network design starts with careful planning. Here are a few best practices:
Plan your physical layout. Ensure that your physical switches, cables, and adapters are set up for redundancy.
Use NIC teaming. Combine adapters to improve load balancing and protect against failure.
Segment your traffic with VLANs. Use VLANs to separate management, production, and storage networks.
Monitor network performance. Tools in vCenter can help you track traffic and find issues early.
Secure your vSwitches. Set security options such as rejecting promiscuous mode, MAC address changes, and forged transmits unless you have a specific need.
Following these tips can make your virtual network more reliable and secure.
Protecting Your Virtual Machines with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
While setting up your network is critical, protecting your virtual machines is just as important. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a robust solution that safeguards your VMs. It is designed work with a range of workloads like VMware, Hyper-V, Proxmox, . Vinchin supports virtual machine backup and migration with ease. It uses features like instant recovery, changed block tracking, and VM backup verification. These features let you restore systems quickly and keep your backup data safe for long-term retention.
The web console is simple and direct. You can set up backup jobs and monitor their status with ease. See how to create a VMware backup job in 4 steps:
1. Select the ESXi VMs
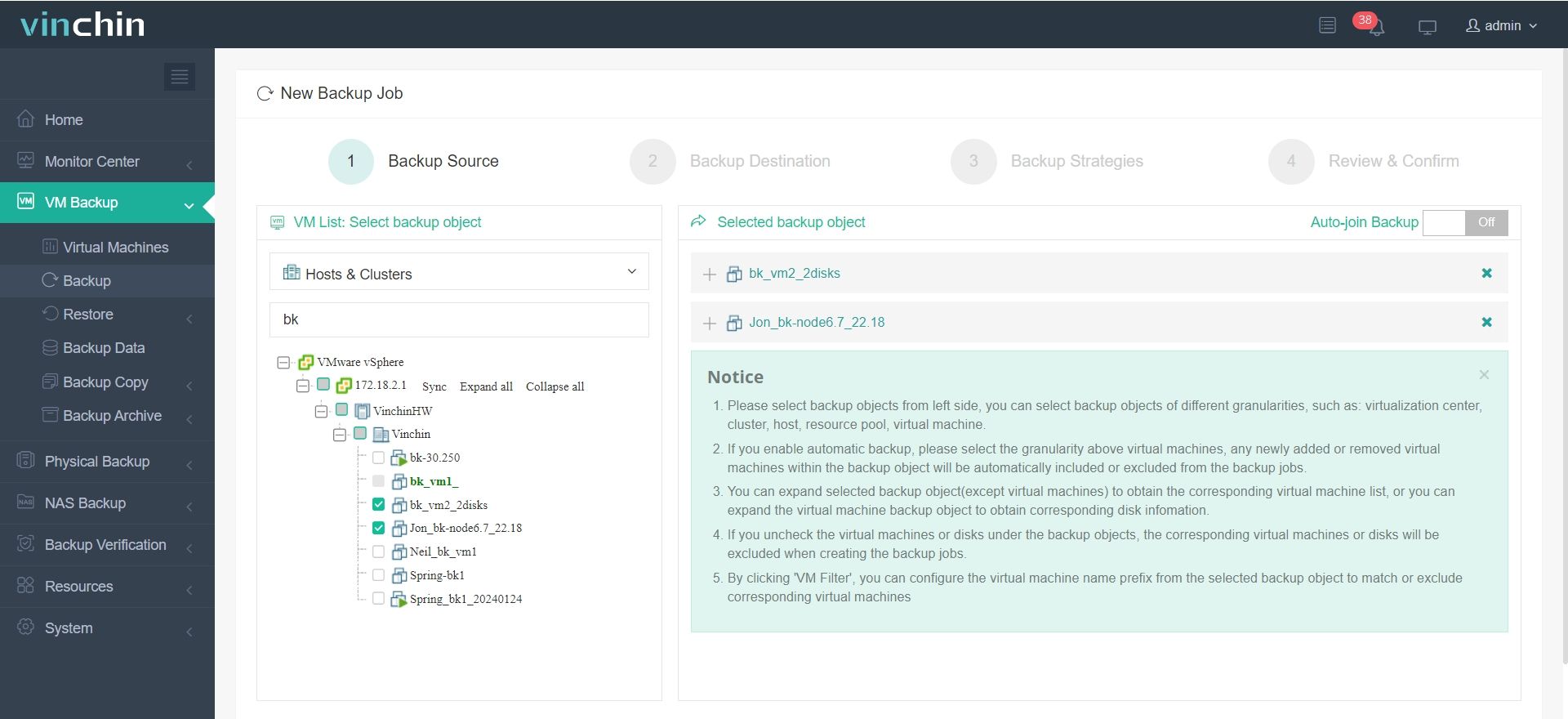
2. Select the backup storage
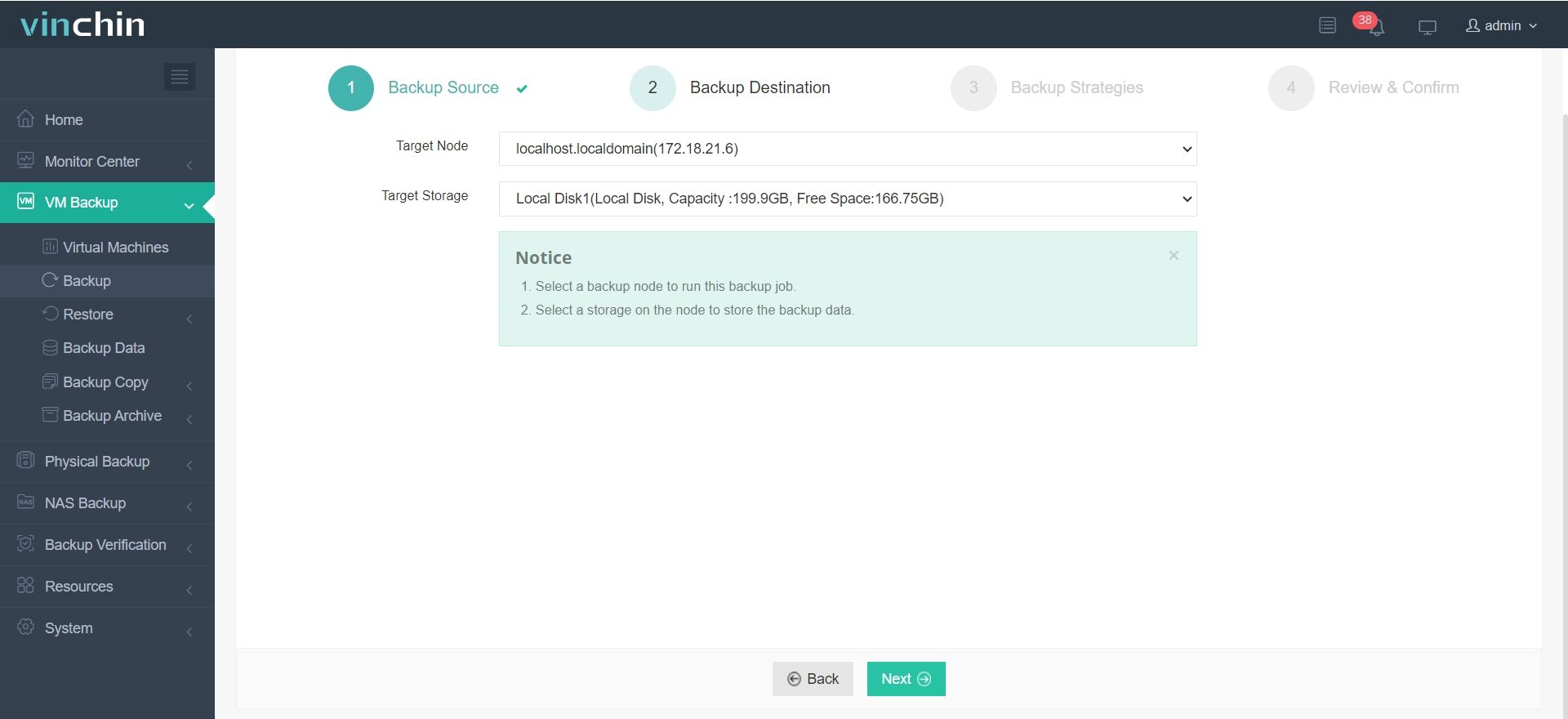
3. Select the strategies
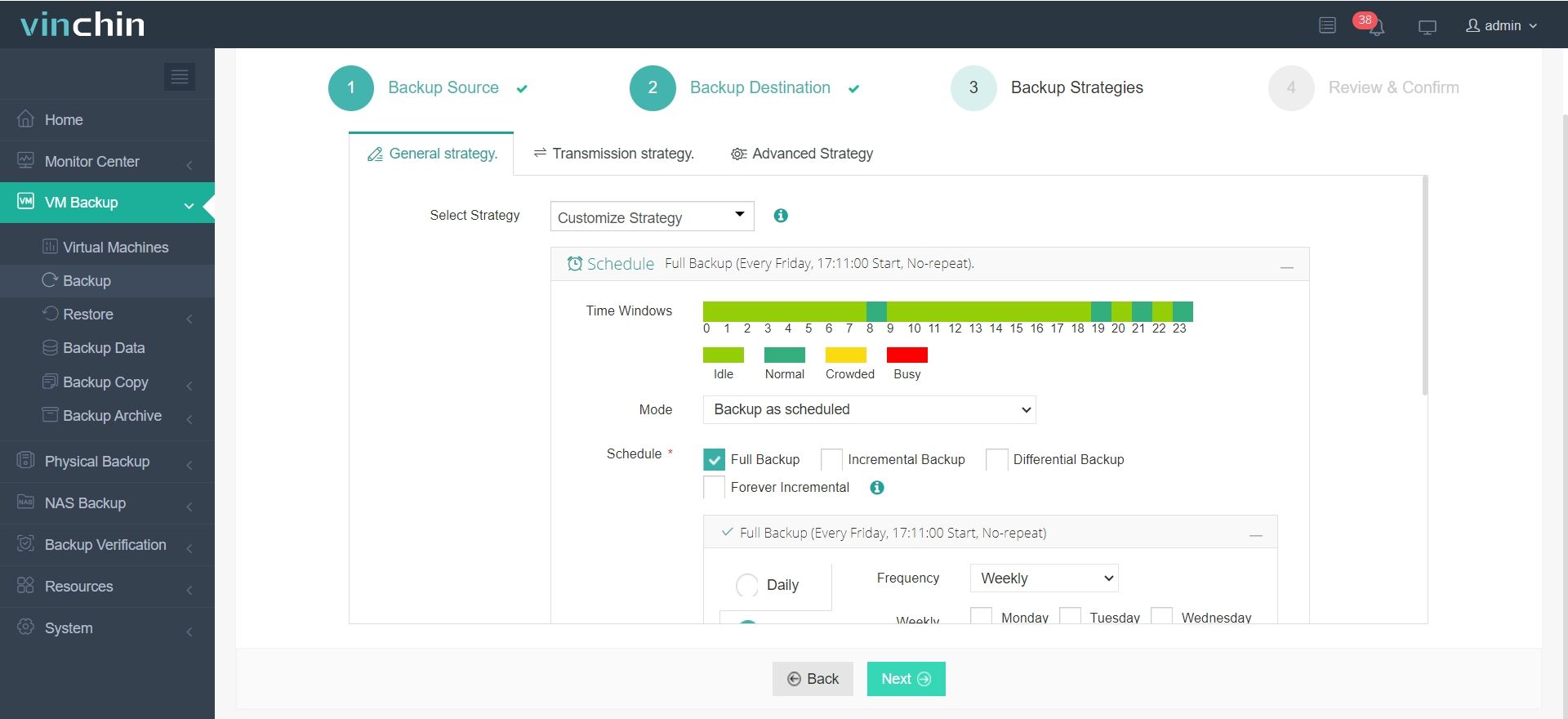
4. Submit the job
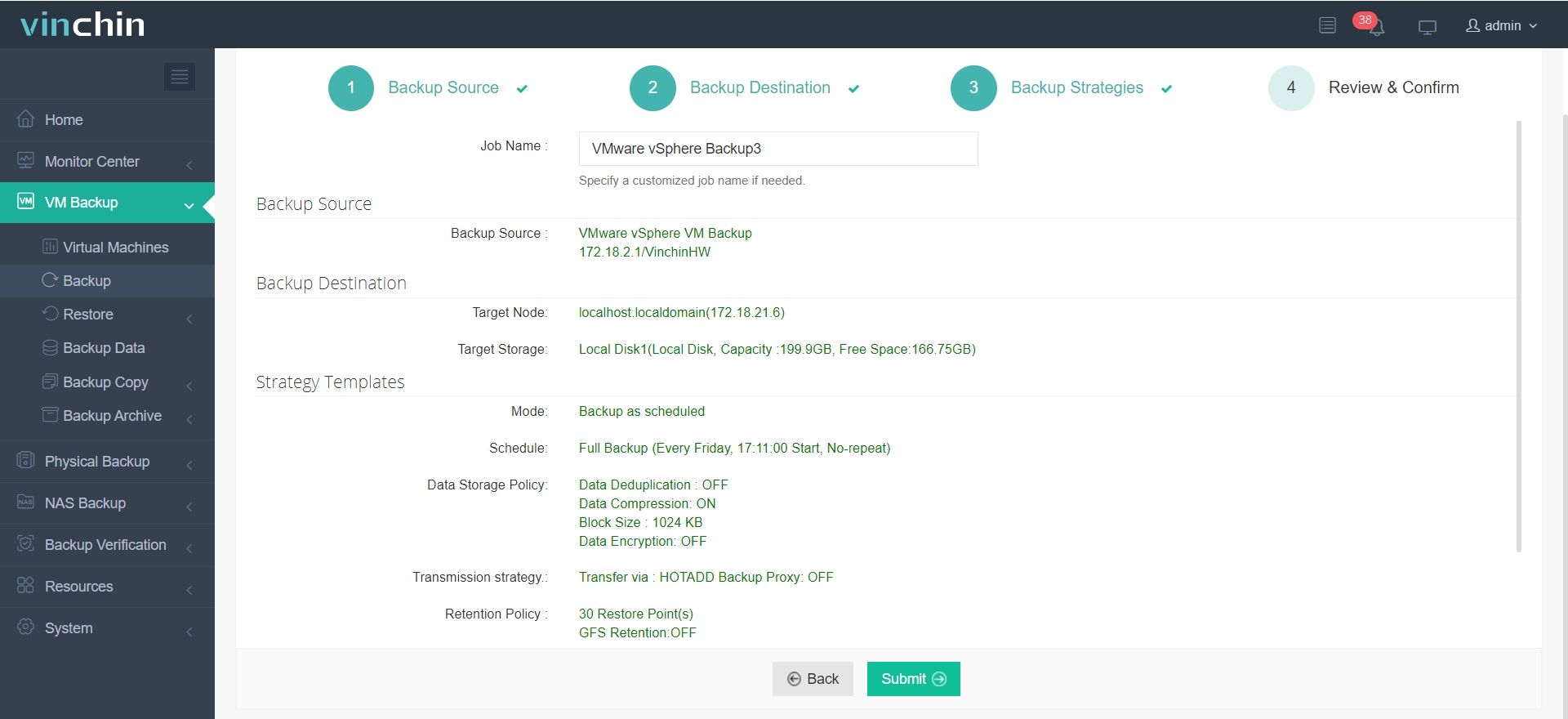
Global customers trust Vinchin for its high ratings and proven performance. Try Vinchin Backup & Recovery with a 60-day full-featured free trial. Click the button below to download the package and deploy easily. Protect your virtual environment with a solution that is built for reliability and simplicity.
ESXi networking FAQs
1. How do I verify that the ESXi host’s network is working?
Log in to the vSphere Client and use built-in tools like esxtop or vmkping to check uplink status and connectivity.
2. Can I change the IP settings for a VMkernel NIC?
Yes. In the Networking section, select the VMkernel NIC, edit its settings, and update the IP address, subnet mask, or gateway as needed.
Conclusion
vSphere networking is at the heart of a stable virtual environment. It connects physical and virtual worlds with simple concepts and powerful tools. Review your network settings, follow best practices, and consider a robust backup solution to keep your environment running smoothly.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery offers an excellent way to secure your data. With a simple web console and a trusted global customer base, Vinchin makes it easy to protect your virtual environment. Don’s miss out on the free trial.
Share on:






