-
What is ISO 27001 Backup Policy?
-
The Importance of ISO 27001 to Enterprises
-
How Can Enterprises Protect Data to Meet ISO 27001 Standards?
-
Collaborating with Vinchin to Enhance Data Protection
-
ISO 27001 Backup Policy FAQs
-
Conclusion
With the rapid development of information technology, organizations are increasingly dependent on IT systems, as information technology permeates almost every aspect of society and daily life worldwide. Consequently, protecting information and preventing its damage and leakage have become pressing issues for organizations today.
To address these challenges, ISO 27001 certification was introduced. It is an information security management system (ISMS) certification that effectively ensures the reliability of enterprises in the field of information security, reduces the risk of data breaches, and better preserves core data.
What is ISO 27001 Backup Policy?
ISO 27001 is an information security management system certification adopted by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) from the British Standards Institution's BS 7799-2 standard. It encompasses various aspects of information security management, including policy formulation, organizational structure, risk management, training, and communication.
The ISO/IEC 27001 standard broadly addresses information security and provides the best business practices and principles for implementing, maintaining, and managing information security within organizations. It also serves as a basis for third-party certification.
The ISO 27001 ISMS is currently the most widely recognized and internationally applicable comprehensive solution for information security. As a representative standard for information security management systems, it has been widely accepted and recognized globally, providing organizations of all types and sizes with an effective method for addressing information security issues.
The Importance of ISO 27001 to Enterprises
(1) Enhancing Management Capabilities
ISO 27001 provides enterprises with a structured framework for managing information security risks. By implementing this standard, organizations can identify vulnerabilities, establish robust controls, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This systematic approach not only improves risk management but also streamlines internal processes, enhancing overall operational efficiency. As a result, enterprises are better equipped to protect sensitive data, minimize disruptions, and adapt to evolving threats.
(2) Building Trust and Competitiveness
Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a company’s commitment to safeguarding information and maintaining high security standards. This assurance builds trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, making the organization a preferred choice in competitive markets. By showcasing their dedication to protecting data, enterprises can differentiate themselves from competitors, gain a stronger market position, and attract more business opportunities.
(3) Standardizing Operations
ISO 27001 promotes consistency in security practices by encouraging the adoption of standardized policies, procedures, and controls. This ensures that all employees across the organization follow a unified approach to managing information security. Standardized operations reduce the likelihood of errors and inconsistencies, improving the quality and reliability of business processes.
(4) Supporting Sustainable IT Development
A key benefit of ISO 27001 is its emphasis on continuous improvement, which aligns with sustainable IT practices. By regularly reviewing and updating security measures, enterprises can stay resilient against emerging threats while optimizing resource utilization.
How Can Enterprises Protect Data to Meet ISO 27001 Standards?
1. Establish an Information Security Management System (ISMS)
Enterprises should establish an ISMS that complies with ISO 27001 requirements. By conducting risk assessments, they can identify security threats and vulnerabilities to data assets, evaluate their impacts and likelihood, and implement corresponding control measures. Clearly define the scope of information security and ensure management and employee commitment to security management through policies and objectives.
2. Control Access Rights
To protect sensitive data, enterprises must implement strict access control policies, including the principle of least privilege to ensure employees only access data and systems within their responsibilities. Additionally, multi-factor authentication (MFA) can enhance login security, and user activities should be audited through logs to promptly detect and address anomalies.
3. Data Protection and Encryption
Enterprises should classify data and implement appropriate protection measures based on sensitivity, such as encrypting data in transit and at rest (using strong encryption algorithms like AES). Regular local and remote backup processes should be established to ensure critical data can be quickly restored in case of disaster, avoiding business disruptions.
4. Secure IT Infrastructure
Securing IT infrastructure is vital for ISO 27001 compliance. This includes protecting network boundaries with firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS), regularly updating systems and software to patch vulnerabilities, and strengthening physical security measures such as access controls and monitoring devices to safeguard equipment and data centers.
5. Employee Training and Awareness
Employees are the first line of defense for information security. Organizations should conduct regular security awareness training to teach employees how to recognize phishing emails, protect passwords, and adhere to company security policies. Simulated exercises can test employees’ ability to respond to security threats, ensuring they possess the necessary awareness and skills.
6. Documentation and Recordkeeping
Documentation is the foundation of ISO 27001 compliance. Enterprises must record all risk management plans, security policies, procedures, and training activities, as well as maintain reports of internal audits and external evaluations. Comprehensive documentation serves not only as proof of compliance but also as a critical reference for optimizing the information security system.
Collaborating with Vinchin to Enhance Data Protection
When collaborating with third parties, enterprises should conduct security reviews to ensure they meet corresponding standards. Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides enterprises with a reliable and efficient data protection solution that aligns with GDPR standards. By leveraging Vinchin’s advanced technologies, businesses can enhance their backup and disaster recovery processes, ensuring critical data remains secure and recoverable in any situation.
It supports various virtual platforms like VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, Proxmox, XCP-ng, etc., and database, NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server, etc., offering advanced features such as automated backups, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free options, offsite copying, instant recovery, data deduplication, and cloud archiving. Additionally, it facilitates VM migration across different hypervisors for seamless virtual environment transitions.
It only takes 4 steps to backup your virtual machine with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1.Select the backup object.
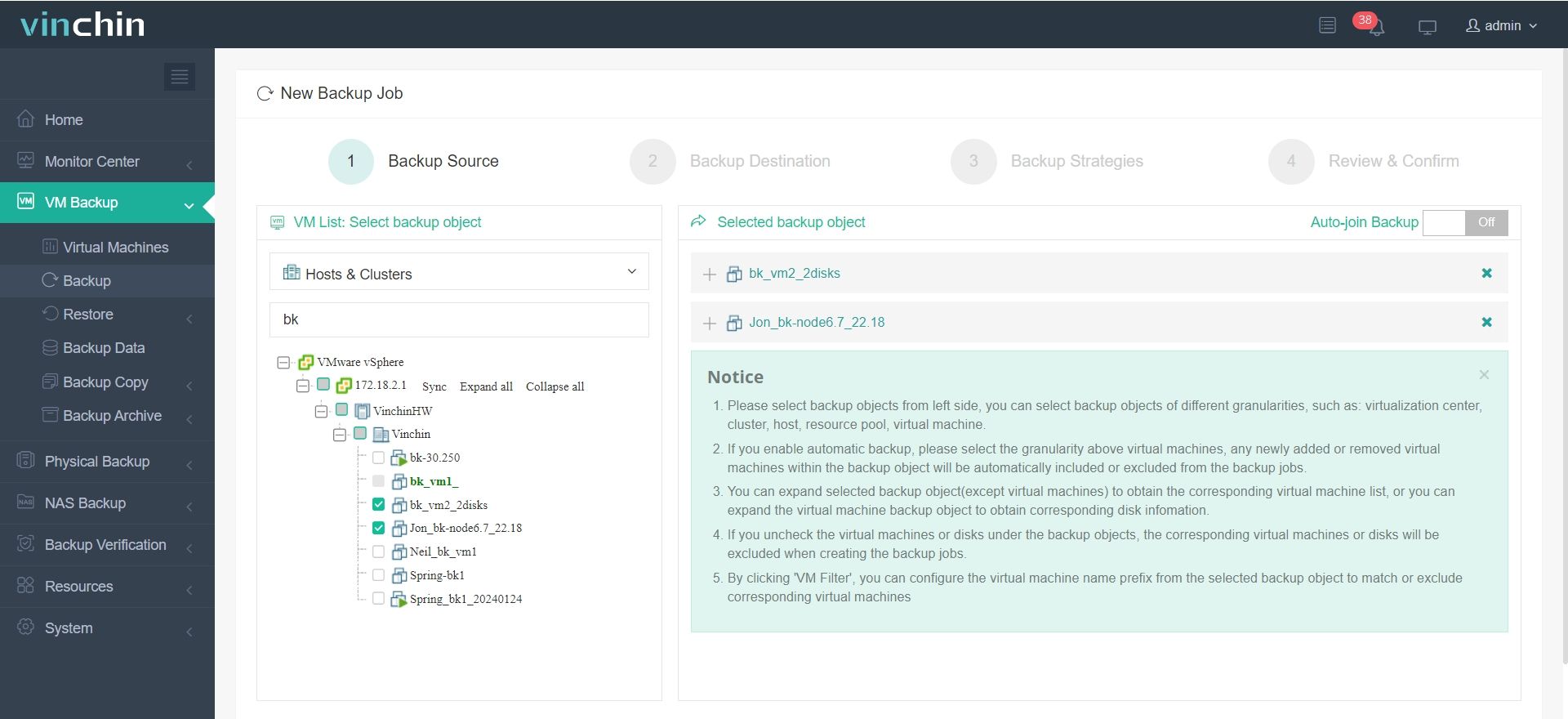
2.Select backup destination.
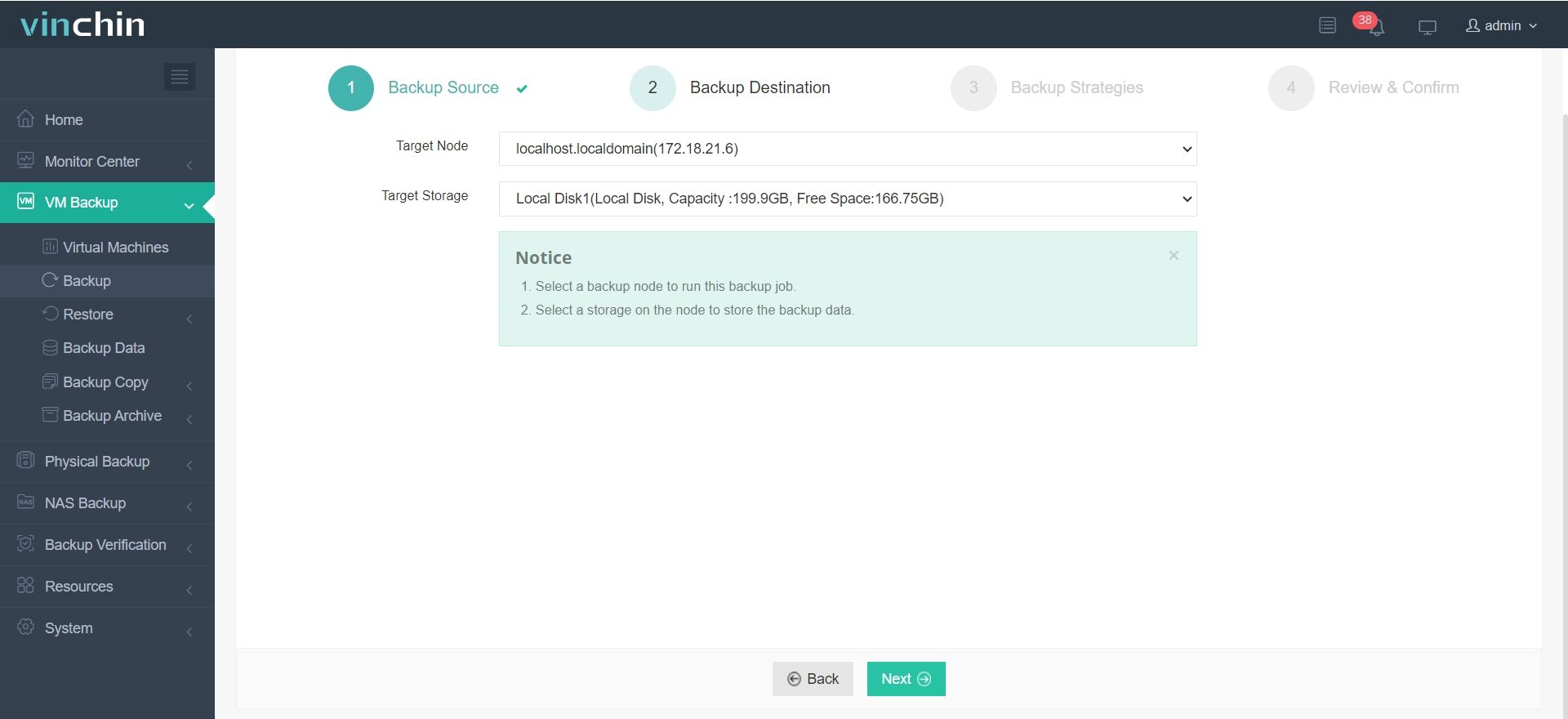
3.Configure backup strategies.
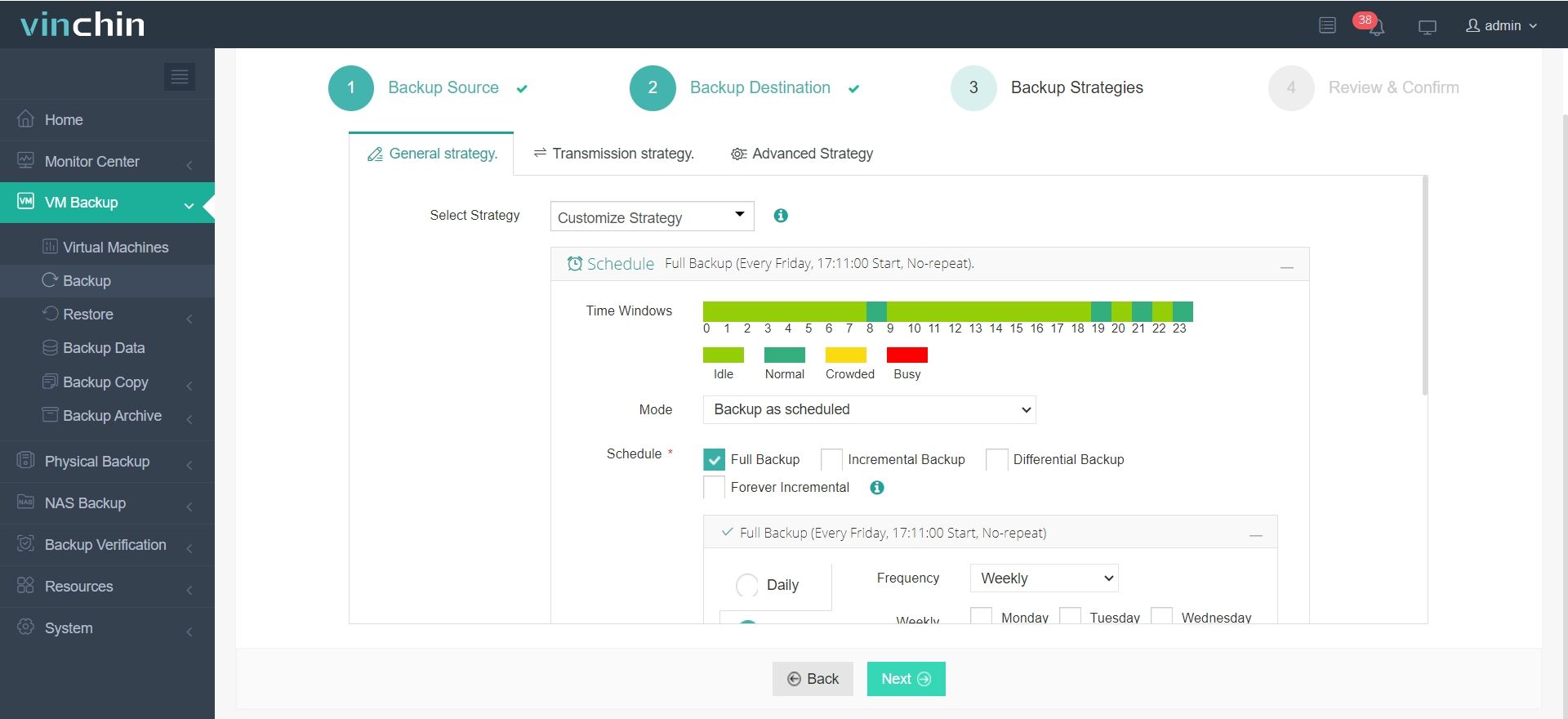
4.Review and submit the job.
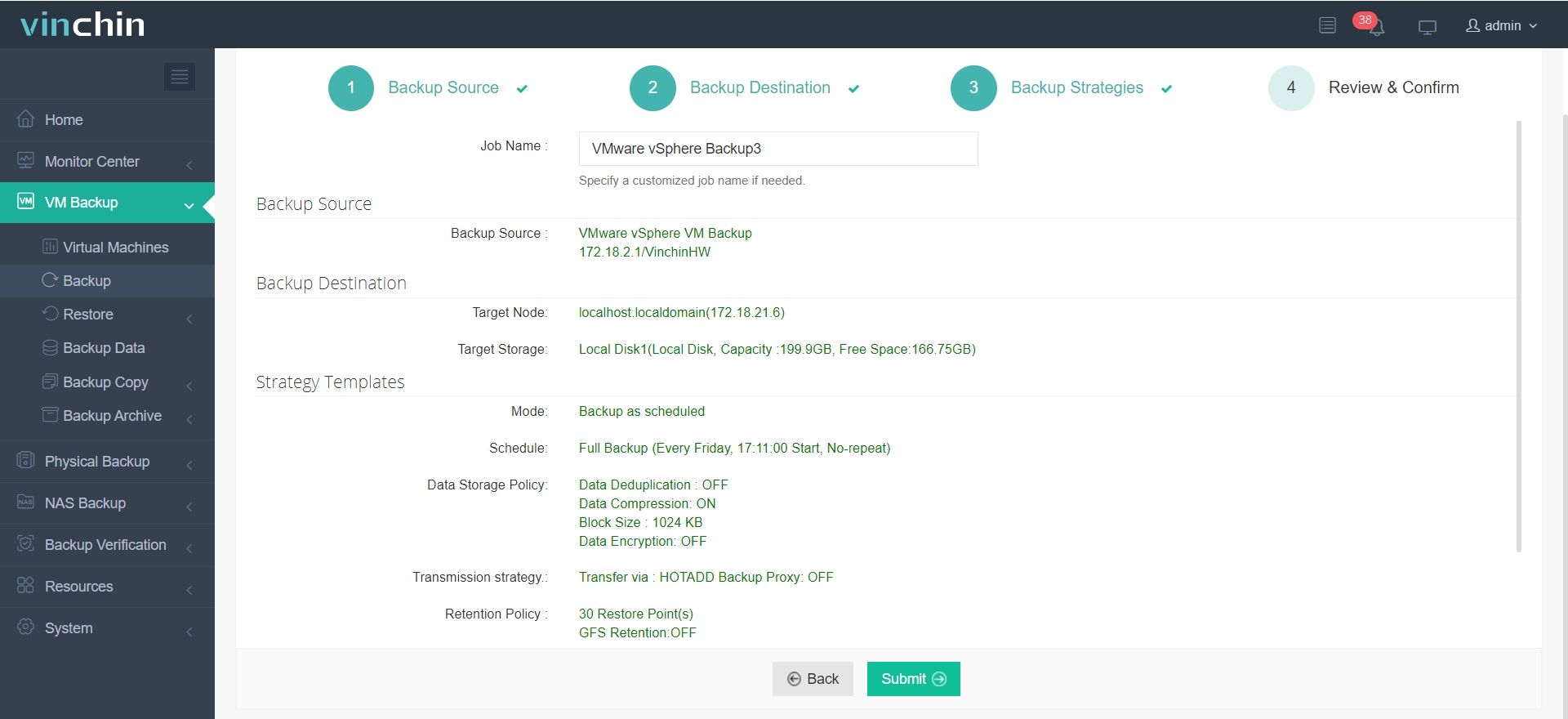
Discover the power of this comprehensive system firsthand with a free 60-day trial! Leave your specific needs, and you will get a customized solution that fits your IT environment perfectly.
ISO 27001 Backup Policy FAQs
1. Q: What is the difference between a backup policy and a business continuity plan?
A backup policy focuses specifically on data protection through regular backups, while a business continuity plan (BCP) is a broader strategy that includes backup and recovery but also addresses other aspects of maintaining critical business operations (e.g., personnel, facilities, communication) during a disaster. The backup policy is a component of the BCP.
2. Q: What is the difference between backup and archiving?
Backup is the process of creating copies of current data to protect against loss, corruption, or disaster. It is typically done regularly (e.g., daily, weekly) and focuses on data that is actively used. Archiving, on the other hand, is the long-term storage of data that is no longer actively used but may need to be retained for legal, regulatory, or historical purposes. Archived data is typically less frequently accessed and may not be subject to the same recovery time objectives as backup data.
Conclusion
ISO 27001 certification represents a robust framework for managing and securing information in today’s data-driven world. By implementing its principles, organizations can improve management capabilities, build trust, and standardize operations. Furthermore, compliance with ISO 27001 enhances resilience against cyber threats and supports sustainable IT development.
With Vinchin, businesses can ensure data security, reduce the risk of breaches, and maintain continuity in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
Share on:








