-
Why you should choose XenServer?
-
What is XenConvert?
-
What are the XenConvert alternative solutions for P2V?
-
How to protect VM data?
-
XenServer P2V FAQs
-
Wrap Up
Virtualization stands as an important part for modern IT infrastructure due to its higher resource utilization and flexibility. By deploying type-1 or type-2 hypervisor on the physical server, you can create multiple virtual machines with different operating systems at once to achieve diversified business purposes. Since enterprise-grade IT operation requirements and preferences vary from industries and company scales, there are many virtual platform vendors, which all bring their own advantages in specific areas, available for users to choose. Among all products in the market, XenServer (Currently Citrix Hypervisor) is definitely one of the most popular choices.
Why you should choose XenServer?
XenServer is a powerful open-source virtual platform that enables users to easily build their own scalable virtual environments through a centralized management console, XenCenter. It is based on Xen Hypervisor, a type-1 hypervisor that directly runs on the physical hardware without a host operating system installation needed first. Because of its direct access to hardware resources, upper-level virtual machines can hence have higher efficiency.
XenServer has both free and commercial editions that fit users with different needs and budgets. The free edition contains most basic features including multi-server management, live VM migration, shared storage connectivity, etc., while commercial editions offer more advanced features like active directory integration, dynamic memory control, and HA (High Availability) for more flexible virtual machine operations. For more detailed edition comparison of XenServer, you can refer to the official documents of Citrix online.
The installation of XenServer is so simple that usually only takes users about 10 minutes to settle things done. If you’re currently still using physical servers but trying to make a physical-to-virtual switch, with goals to efficiently manage Windows and Linux systems, then XenServer can be the best choice of yours.
After choosing the right virtual platform, another problem might raise here: what if I want to directly migrate my old business data to the new XenServer VMs? Is there any way to simply achieve the goal? Well, Citrix used to offer a solution for users who ask the same question: XenConvert.
What is XenConvert?
XenConvert is a P2V conversion tool provided by Citrix to help users convert IT workloads from servers or desktop computers running Windows to virtual machines, virtual appliances, virtual disks, or virtual disks attached to Provisioning Services in XenServer.
XenConvert is very easy to use, and it will run on the physical Windows server, and convert the disk into a disk image in VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) format, or a XVA template that can be imported into XenServer host.
However, as useful as XenConvert is, Citrix still chose to deprecate it several years ago, and it is now unavailable for download from the official website.
What are the XenConvert alternative solutions for P2V?
Although XenConvert is no longer available, don’t worry, you still have other options to achieve the goal. Furthermore, since XenConvert only supports P2V migration of Windows-based servers, if the migration target you want is a Linux server, you might still need another method to do this anyway.
The first most common alternative solution is that, you can image the physical server using Clonezilla, create a new virtual machine on the XenServer host, and restore the image files to the new XenServer VM.
For the second solution, you can first convert the physical server to a Hyper-V VM using Disk2vhd, export as VHD, and import it to XenServer.
For the third solution, you can directly create VHD of the physical Linux server using dd command lines, and import it to the XenServer host.
As you can see, you can always find a way to migrate data to XenServer, and it’s just a little bit more complicated on the operational process.
How to protect VM data?
Apart from enjoying the convenience XenServer brings, choosing a suitable backup solution is also crucial to make sure data, the fundamental of the IT system, can always be safe and recoverable. After all, data is the heart of business in today’s digitalization age.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a robust backup and disaster recovery solution that supports multiple virtualization platforms, including XenServer/Citrix Hypervisor, VMware, Hyper-V, Red Hat Virtualization, Proxmox, and others, offering agentless, incremental, and full VM backups. It enhances data protection with features like deduplication, compression, V2V migration, instant VM restore, granular file-level recovery, encryption and ransomware protection.
The centralized web console facilitates easy setup and management of backup jobs, scheduling, and monitoring, while also enabling robust disaster recovery. To backup XenServer VMs, just following these 4 steps:
1. Select the backup object.
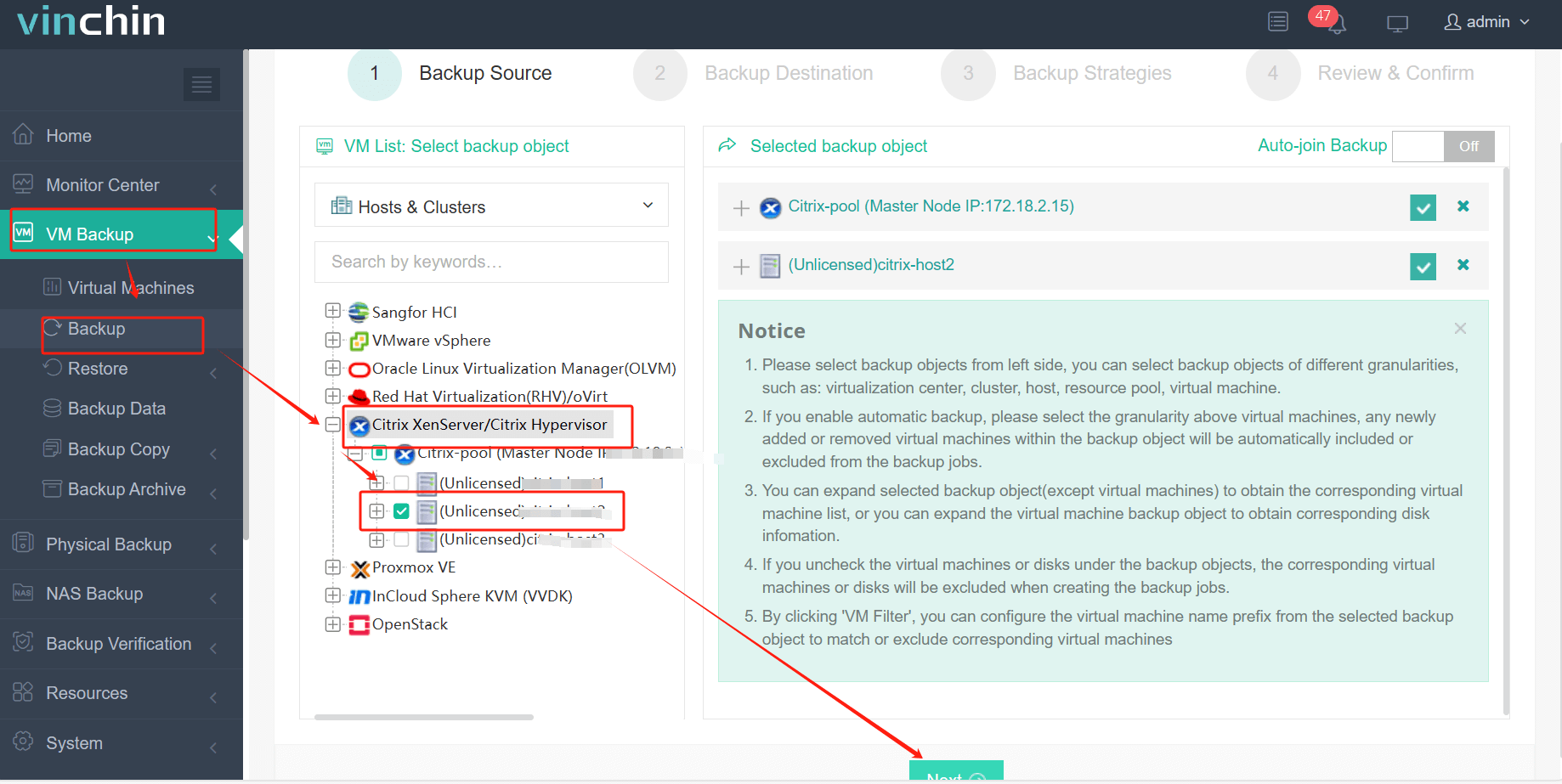
2. Select backup destination.
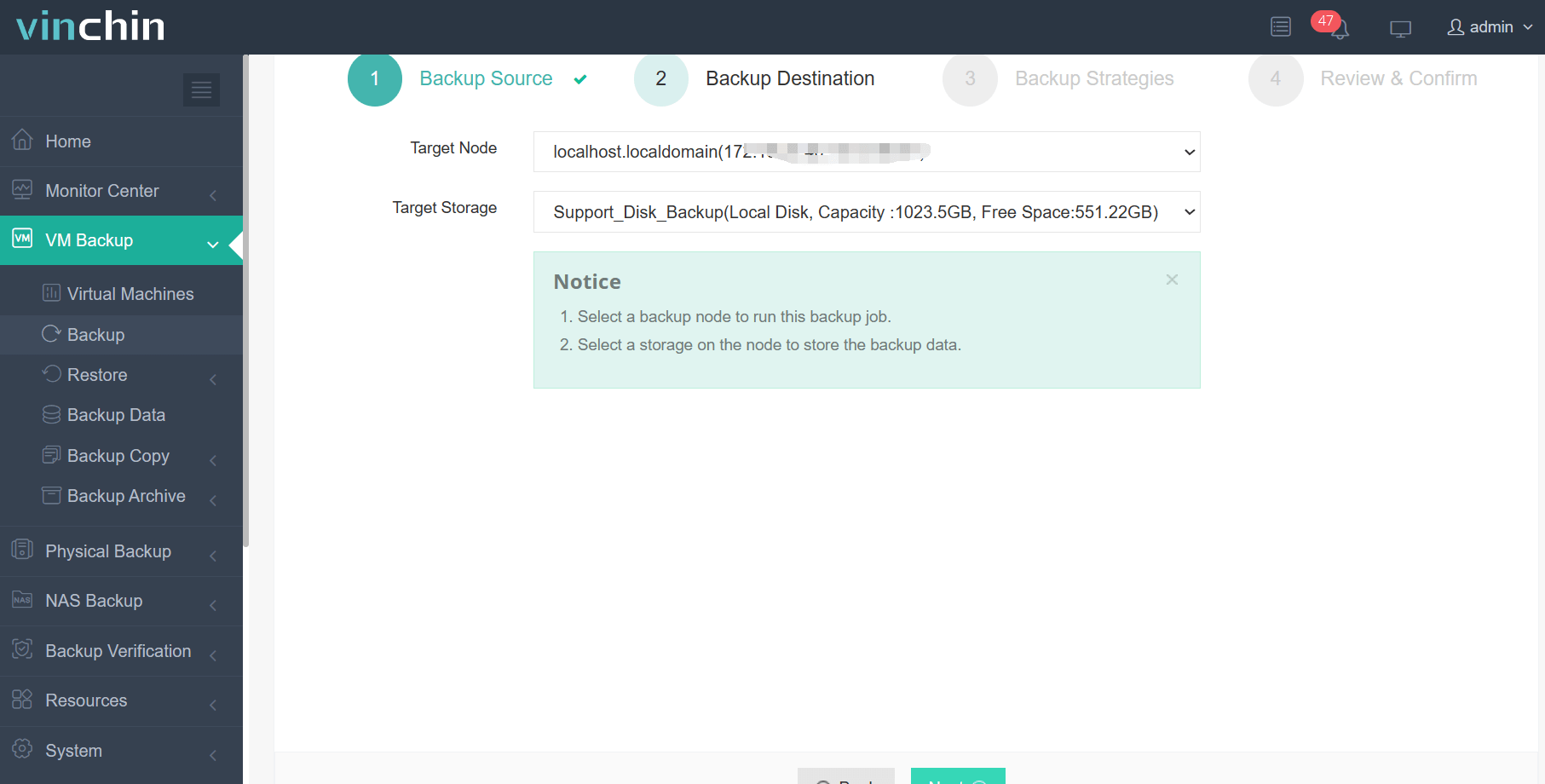
3. Selecting backup strategies.
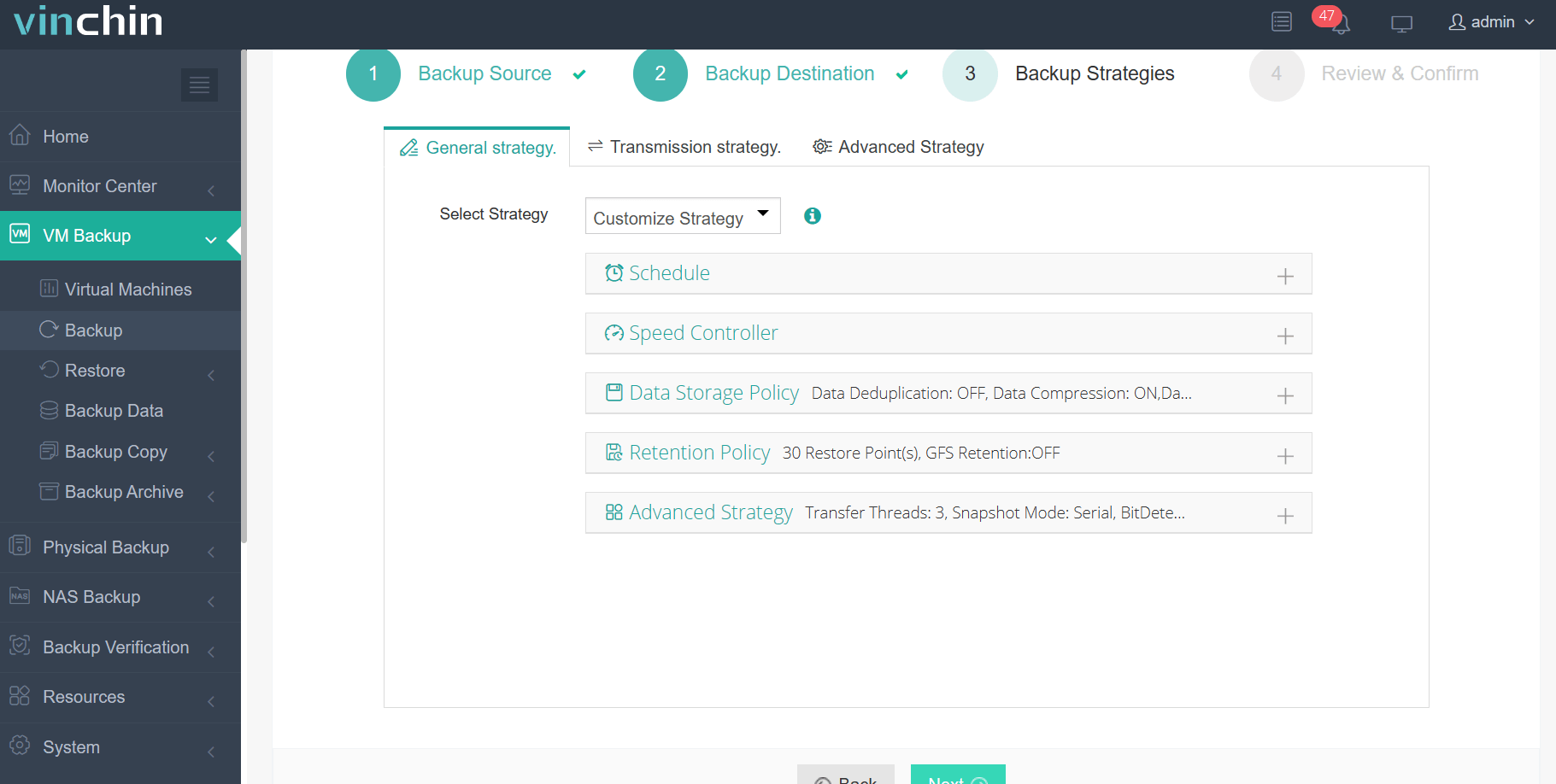
4. Review and submit the job.
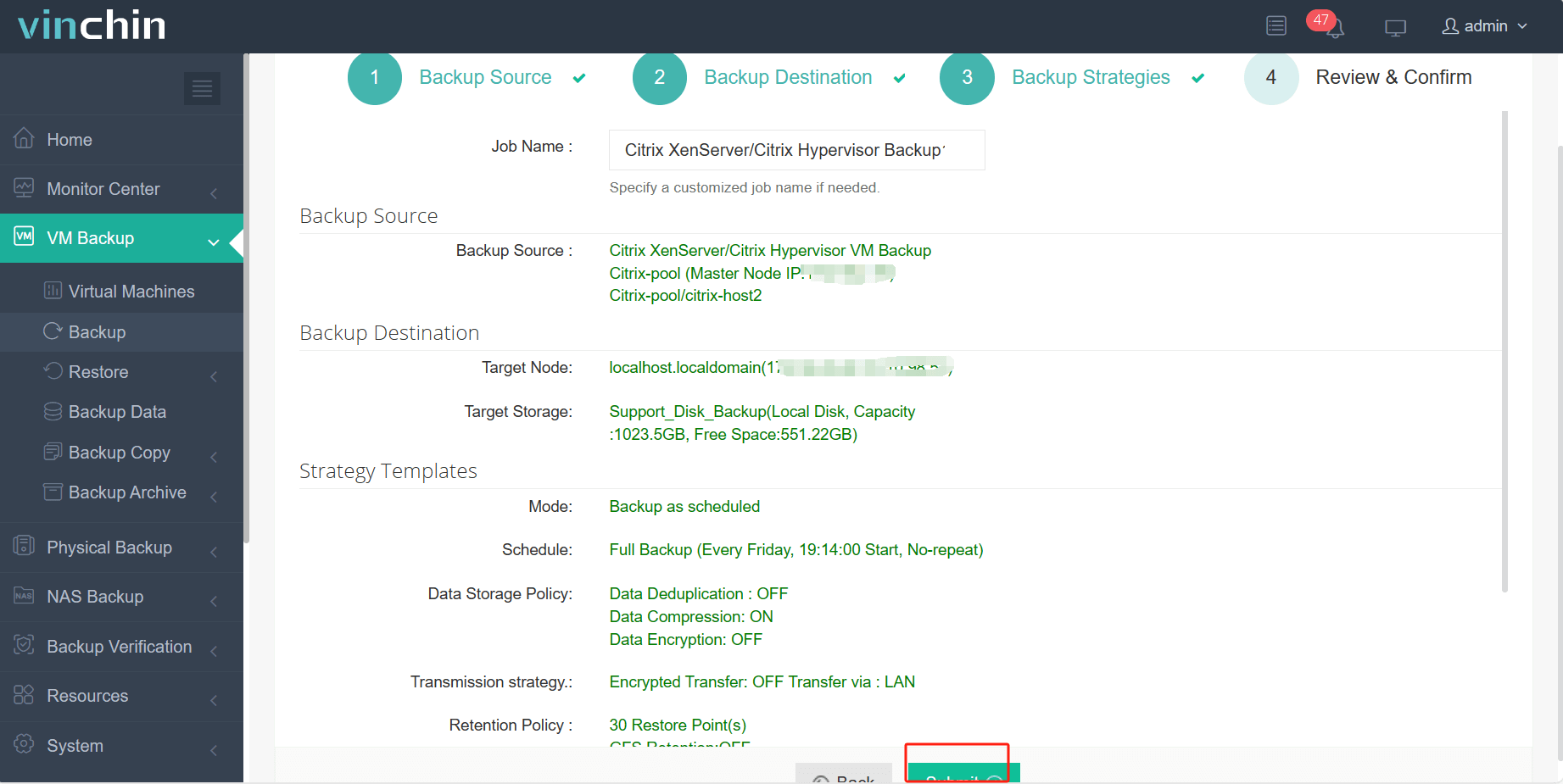
Vinchin Backup & Recovery has been selected by thousands of companies and you can also start to use this powerful system with a 60-day full-featured trial! Also, contact us and leave your needs, and then you will receive a solution according to your IT environment.
XenServer P2V FAQs
1. Q: What is the difference between a physical server and a virtual server?
A: A physical server is a standalone hardware device, while a virtual server is a software-defined instance running on a physical server, allowing multiple virtual servers to share the resources of a single physical machine.
2. Q: What are the disadvantages of a physical server?
A: Physical servers can have several disadvantages, including higher costs due to the need for dedicated hardware, less efficient resource utilization as they often run at underutilized capacity, limited scalability as adding new resources requires purchasing additional hardware, increased energy consumption and heat generation, and more complex disaster recovery and business continuity planning. Additionally, physical servers require more physical space and may have longer deployment times compared to virtual servers.
Wrap Up
XenServer is a powerful open-source virtualization solution that suits enterprise-grade users who want to build a scalable and agile IT environment. If you consider switching your workloads to a virtual platform, XenServer can be an excellent choice. This blog introduces some ways that are suitable for both Windows and Linux systems to help you migrate data from physical servers to XenServer, making the disadvantage of deprecated XenConvert that only supports P2V migration of Windows servers up.
For data protection after the migration, Vinchin Backup & Recovery can be a useful tool for this, which performs as a highly compatible all-in-one solution providing a wide range of virtual machine backup and restore features, making XenServer backup and VM recovery easy to configure and manage.
Share on:







