-
Why Need to Protect Virtual Machines?
-
How to Check If VM is Encrypted in VMware?
-
How to Encrypt a VM in VMware?
-
How to Protect VMware Virtual Machines?
-
VMware Encryption FAQs
-
Conclusion
In the era of physical data centers, adopting a dual-insurance approach to data security was a relatively simple and straightforward solution. For example, in addition to encrypting individual files and directories, full disk encryption could be applied to on-site servers, ultimately ensuring that any hard drive leaving the data center for repair or disposal was protected—eliminating the potential risk of exposing customer data.
However, in today's world of hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) and virtualization, workloads are virtual, dynamic, mobile, scalable, and fragile. All of this makes maintaining data security more challenging.
Why Need to Protect Virtual Machines?
The rise of virtualization and HCI allows IT teams to quickly deploy hybrid workloads and virtual desktop-integrated infrastructure at both local and remote locations. In this context, hyper-converged systems, which combine computing, networking, and management software into a single device, are essentially “mini-clouds in a box.” The benefits of this approach are undeniable.
However, even though HCI devices are still hosted on-site, their workloads often run on virtual machines rather than directly on physical hardware. This means that today, the real focus of protection is the virtual machines and the data within them, rather than the physical machines themselves.
A significant security issue faced by IT teams is that virtual machines are frequently switched on and off and often exist in a static data state. When a virtual machine is powered down, it becomes a large file that can be copied to a USB drive or shared over the network, posing substantial data security risks.
The solution, though straightforward, is to encrypt the virtual machine itself. Ideally, this should involve client-side encryption independent of the hypervisor, with encryption keys under the company’s control. This ensures that even if the virtual machine is moved to another HCI node, such as a public cloud or a different geographic location, the company retains control over its data at all times.
How to Check If VM is Encrypted in VMware?
To check if a VM is encrypted in VMware, you can follow these steps if you're using VMware vSphere/ESXi:
1. Using vSphere Web Client:
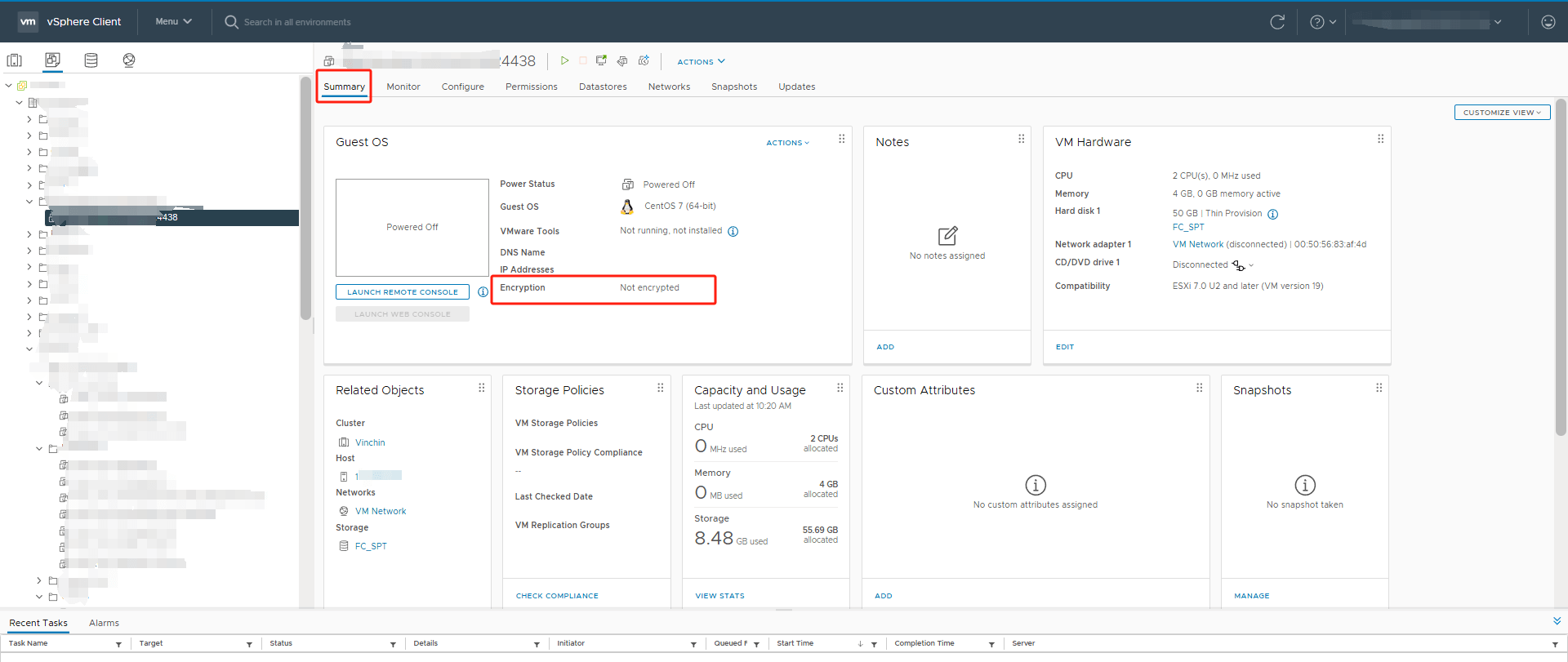
Log in to the vSphere Web Client. Select the virtual machine you want to check.
In the VM's Summary tab, look for the Encryption status. It will show "Encrypted" if the VM is encrypted.
2. Command-Line (vSphere/ESXi):
a. SSH into your ESXi host.
b. Use the “vim-cmd” command to check the encryption status:
vim-cmd vmsvc/get.summary <VMID>
Replace “<VMID>” with the VM's ID. Look for the “encryption” property in the output.
3. Alternatively, check the VM's configuration file (“.vmx”) on the datastore:
cat /vmfs/volumes/<datastore>/<vm_folder>/<vm_name>.vmx | grep "encryption"
How to Encrypt a VM in VMware?
To encrypt a VM using the vSphere Web Client, follow these detailed steps:
Prerequisites
Ensure the following:
1. A vCenter Server is managing your ESXi host.
2. A Key Management Server (KMS) is configured in vCenter.
3. You have the required encryption privileges (e.g., “Cryptographic Operations”).
4. The VM is powered off.
Steps to Encrypt a VM Using vSphere Web Client:
1. Configure the Key Management Server (if not already set up)
Log in to the vSphere Web Client.
Navigate to Menu > vCenter Settings > Key Management Servers.
Click Add KMS, enter the KMS details, and establish a trusted connection.
2. Navigate to the VM.
Select the VM you want to encrypt from the inventory. If the VM is running, right-click it and select Power > Shut Down Guest OS or Power Off.
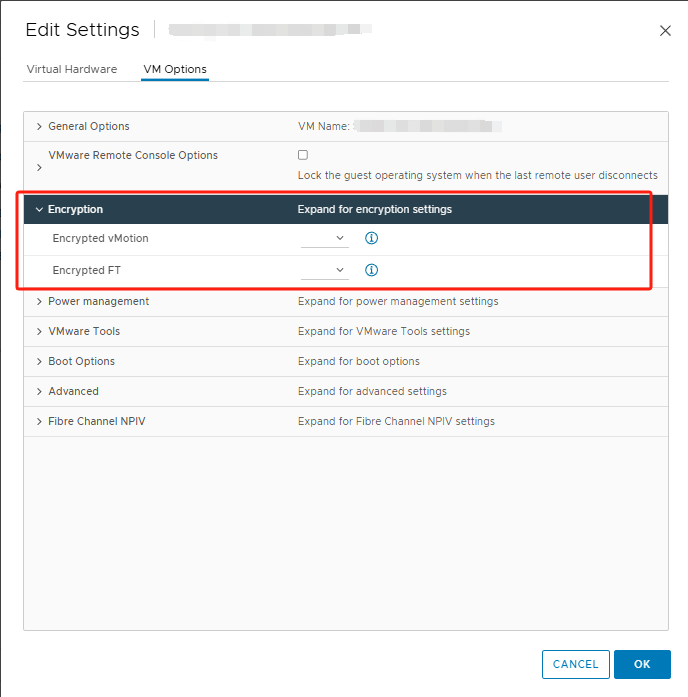
3. Enable VM Encryption
Right-click the VM and select Edit Settings. Go to the VM Options tab. Scroll down to the Encryption section.
Set Encryption to Enabled.
vCenter will communicate with the KMS to generate and assign an encryption key for the VM.
4. Encrypt Disks (if not done automatically)
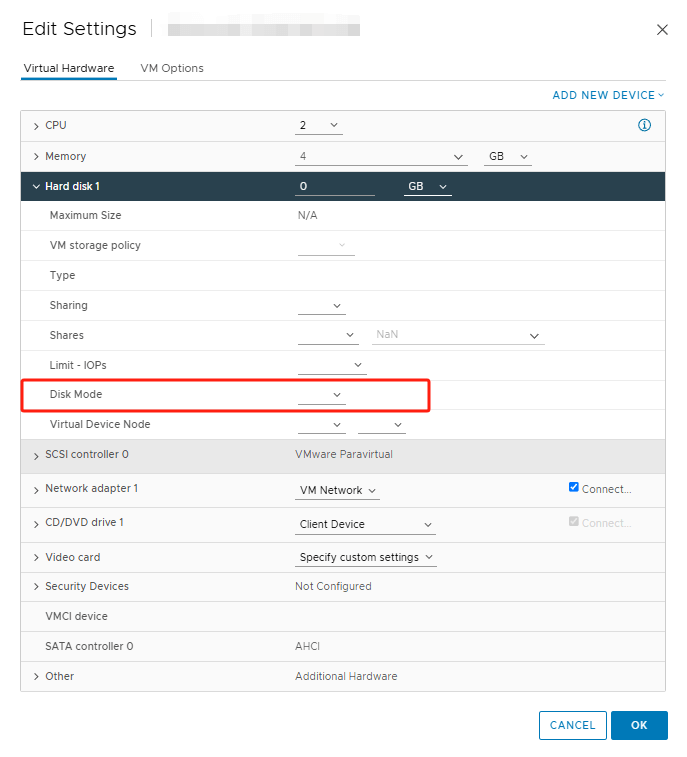
Still in the Edit Settings dialog, expand the Virtual Hardware section.
For each virtual disk:
Click on the disk settings.
Set the Disk Mode to Encrypted.
Click OK to save your changes and start the encryption process.
Once the encryption process is complete, right-click the VM and select Power On.
Verify that the VM boots correctly. And navigate to the VM's Summary tab. Look for an Encryption field indicating the VM is encrypted.
How to Protect VMware Virtual Machines?
In addition to encrypting virtual machines, backing up virtual machines is also an extremely important part of data protection. Protecting VMware virtual machines is crucial to safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring business continuity, and maintaining system integrity against potential threats. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is a robust VMware environment protection solution, which provides advanced backup features, including automatic VM backup, agentless backup, LAN/LAN-Free backup, offsite copy, instant recovery, effective data reduction, cloud archive and etc., strictly following 3-2-1 golden backup architecture to comprehensively secure your data security and integrity in VMware environment.
Besides, data encryption and anti-ransomware protection offer you dual insurance to protect your VMware VM backups. You can also simply migrate data from a VMware host to another virtual platform and vice versa.
Although Vinchin does not currently support backing up encrypted virtual machines, it can back up unencrypted virtual machines, which only takes 4 steps:
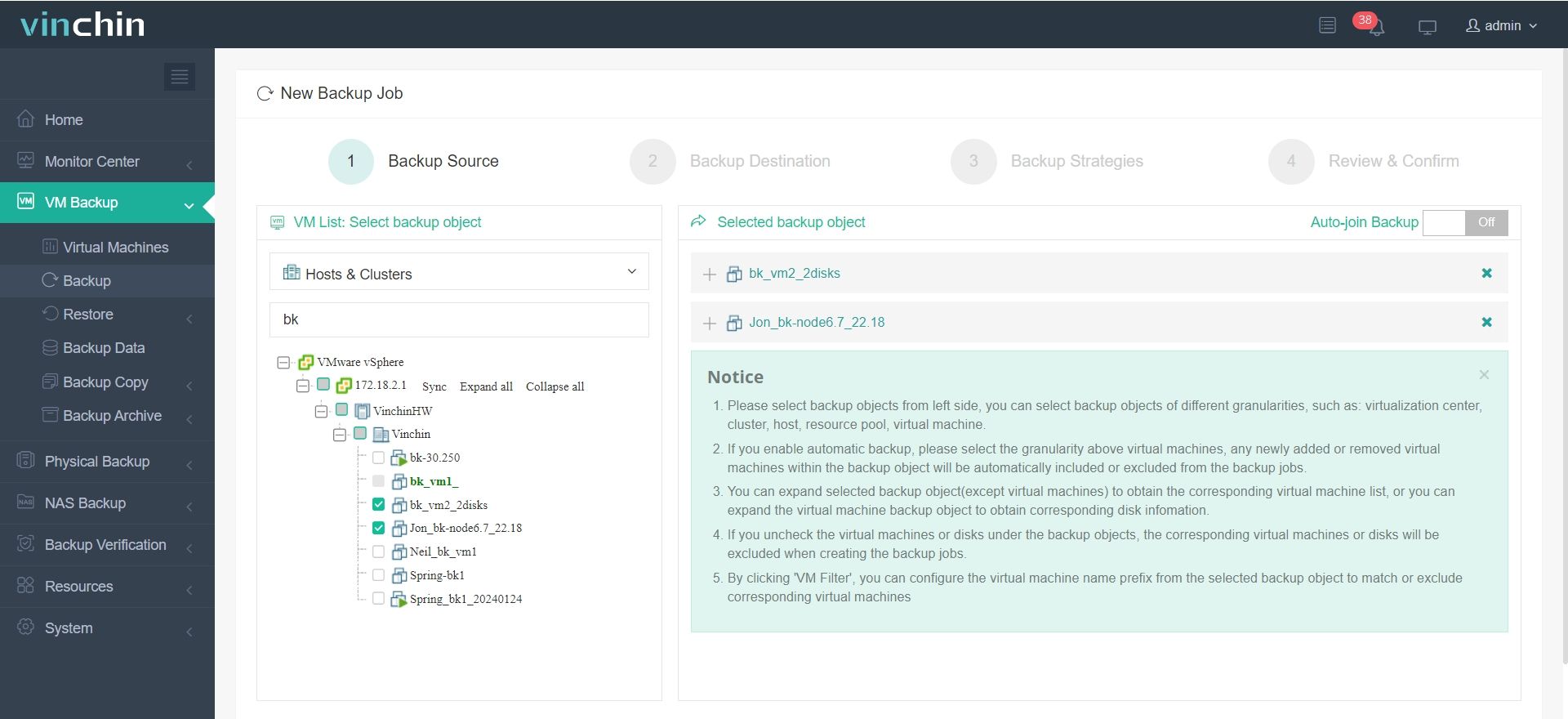
1. Select the backup object.
2. Select backup destination.
3. Configure backup strategies.
4. Review and submit the job.
Try the 60-day full featured free trail of Vinchin Backup & Recovery now to easily protect your VMware data and achieve automated backup and fast recovery!
VMware Encryption FAQs
1. Q: What is a Key Management Server (KMS)?
A KMS is an external server that manages encryption keys. VMware requires a third-party KMS to manage the encryption keys securely.
2. Q: Can I decrypt an encrypted VM?
Yes, VMs can be decrypted by changing their storage policy to a non-encrypted policy, provided you have the necessary permissions and access to the KMS.
Conclusion
In an era where virtualization and hyper-converged infrastructure dominate modern IT environments, safeguarding virtual machines has become a cornerstone of data security. By encrypting virtual machines, IT teams ensure that sensitive data remains secure regardless of where the workload resides—whether on-site, in a remote data center, or in the cloud. Organizations that prioritize VM encryption not only reduce exposure to potential threats but also align with best practices for resilient, future-proof data security in an increasingly virtual world.
Share on:








