-
What is VDI?
-
What is VHD?
-
What is VMDK?
-
How to Convert VDI to VHD and Vice Versa?
-
How to Convert VDI to VMDK and Vice Versa?
-
How to Convert VHD to VMDK and Vice Versa?
-
How to easily convert virtual machine?
-
FAQs for VDI, VHD and VMDK Selection
-
Conclusion
In computing, a disk image is a computer file that contains the contents and structure of a disk or the whole storage device. Similarly, there also are various disk images or virtual disks in virtualization that play the part of traditional hard disks. They come in different formats hinging on virtualization creators.
Virtual Disk Image (VDI), Virtual Hard Disk (VHD), and Virtual Machine Disk (VMDK) are the most widely used, which may come from all sorts of platforms, they can be used interchangeably. But which is better for you and how to convert them if you prefer the other one?
What is VDI?
VDI (Virtual Disk Image) is the default virtual disk format of Oracle VirtualBox running on macOS, Windows, Linux, and Solaris hosts. VirtualBox also supports Microsoft VHD/VHDX and VMware VMDK file formats, which can be copied and created by the Virtual Media Manager of VirtualBox but they have to be converted to VDI first if you want to maintain them.
Features:
It is portable and can be used in other virtualizations like VMware and Microsoft.
Allows fixed-size and dynamically allocated storage.
Supports remote access, snapshotting, and sparse allocation.
Pros:
High-level redundancy.
Lessen the data loss impact on the VMs.
Smaller size than VHD/VHDX with better performance.
High-level data security.
High availability of accessing VDI from the cloud, desktop, mobile, etc.
Cons:
Doesn’t support incremental backups.
Slower than VMDK.
VDI format conversion to other formats is now always possible.
You cannot roll out an image to the desktop clients unless they are VirtualBox.
What is VHD?
VHD (Virtual Hard Disk) is the now-defunct disk format of Microsoft Hyper-V and Virtual Server, originally developed by Connectix. Despite its popularity among virtualization products, Microsoft replaced it with VHDX (Virtual Hard Disk v2) as the default format with a larger storage capacity of 64 TB.
Features:
Reside as files on the host operating systems.
Supports fixed and dynamic disk sizing, differencing, and snapshots.
Microsoft PowerShell scripts can convert VHD to VHDX.
Modify the VM configurations directly from the host server.
Use several OS in one HDD without additional partitions.
Pros:
Easily create pre-built configurations.
Create multiple users for one OS, and the changes made in one OS won’t affect others.
Easily undo and redo the changes to the VHD/VHDX file.
Can recover corrupted, unreadable, deleted, or damaged data.
Multi-user isolation ensures when one instance crashes, the others wouldn’t.
Cons:
Corrupted VHD/VHDX files can crash Windows.
Possible malware vectors against the VM.
The storage limit of a VHD file is 2TB.
Blocked VHD cannot resize the memory.
What is VMDK?
VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk) is a virtual disk drive format formerly exclusive to VMware applications and later becomes an open format widely employed across virtualizations, like VirtualBox and Hyper-V.
Features:
Supports snapshotting, and sparse allocation that allows file expansion on demand.
Protects RAID within SAN.
Easily clone the physical HDD.
Allows physical hard disk cloning and offsite backup.
62 TB storage since vSphere 5.5.
Pros:
Efficient use of space with advanced features like 64K sub-blocks.
Less overhead due to sub-block representation.
High data security with snapshots and Continuous Data Protection.
Can be easily migrated or moved to servers with live migration.
Allows incremental backup and thus faster backup speed.
Recreates and restarts VMs with VMDK files.
Transform a physical pc into a virtual disk.
Cons:
Hard to restore the lost VMDK disk data.
How to Convert VDI to VHD and Vice Versa?
1. Convert VDI to VHD
a. Power off the VM before. Click File in VirtualBox to start Virtual Media Manager.
b. Select the disk attached to the VM to migrate and click Copy.
c. Choose VHD file format in the disk copy option.
d. Choose disk dynamic for less disk usage and testing or fixed size for production and high disk utilization usage.
e. Select the VHD file path and start copying.
2. Convert VHD to VDI
Launch VBoxManage.exe (under C:Program FilesOracleVirtualBox) and run the following command:
sudo vboxmanage clonehd inputFileName.vhd outputFileName.vdi --format vdi
How to Convert VDI to VMDK and Vice Versa?
1. Convert VDI to VMDK
a. Power off the VM. Click File in VirtualBox to start Virtual Media Manager.
b. Click the VDI file to convert and then click Copy.
c. Select VMDK from the pop-up window and then click Next.
d. Enter the new file name and click Copy.
e. The conversion from VDI to VMDK begins.
2. Convert VMDK to VDI
You can attach the VMDK file to the VirtualBox Media Manager, then boot the VM OS from the file without converting it. If you need to convert the files, follow this guide:
Use VBoxManage.exe to convert.
“C:Program filesOracleVirtualboxvboxmanage” clonehd inputFileName.vmdk outputFileName.vdi –format VDIHow to Convert VHD to
How to Convert VHD to VMDK and Vice Versa?
1. Convert VHD to VMDK
Use VBoxManage.exe and convert.
“C:Program filesOracleVirtualboxvboxmanage” clonehd inputFileName.vhd outputFileName.vmdk –format vmdk
Or refer to more methods to convert Hyper-V (VHD) to VMware (VMDK).
2. Convert VMDK to VHD
a. Export VMware VMs to OVF template.
b. Launch PowerShell and input the following command to add the converter module.
Import-Module “MVMCfilepathMicrosoft Virtual Machine ConverterMvmcCmdlet.psd1”
c. Convert VMDK to VHD(X).
ConvertTo-MvmcVirtualHardDisk -SourceLiteralPath “VMDKfilepath.vmdk” -VhdType Fixedsize/DynamicHardDisk -VhdFormat vhd/vhdx -DestinationLiteralPath “newfilepath ewfilename.vhd/vhdx”
Find more conversion ways to migrate VMware (VMDK) to Hyper-V (VHD/X).
How to easily convert virtual machine?
For enterprises, you should choose professional solution for V2V to protect data and seamlessly switch to new environment. Vinchin Backup & Recovery is an agentless solution for 10+ virtualizations like VMware and Hyper-V (Virtualbox is not included), 6 databases, Linux & Windows Servers, NAS, and centrally manages the backups in a web-based console. With the backup VMs, you can directly restore them to another virtualization platforms for V2V migration.
This robust solution can let you experience various easy backup strategies and fast disaster recovery options within the software, such as backup schedules, GFS retention, Email alerts, etc.
● Save storage and cost: deduplicating and compressing 50% of data to save more space for newly written data.
● Anti-ransomware data protection: safeguard all backups saved in the software and backup server with backup storage protection, double data encryption, and data archiving to public clouds.
● Offsite backup copy: save another backup copy to a distant location for an emergency.
● File-level recovery: target specific folders/files to save resources.
For example, after you create the backup of VMware, you can migrate the VM to Hyper-Vin 4 steps.
1. Select the backup of VMware VM
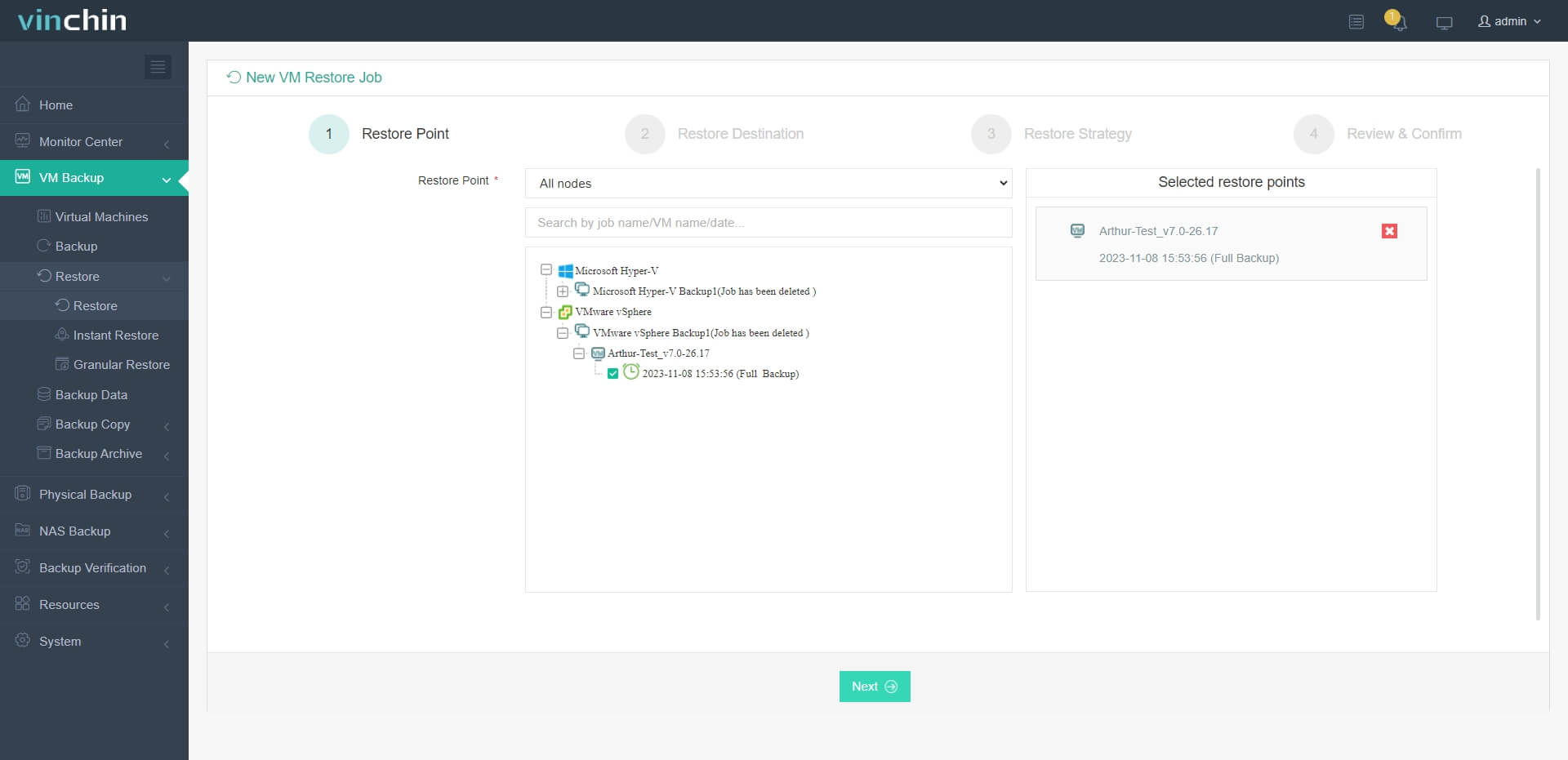
2. Select the Hyper-V host as destination
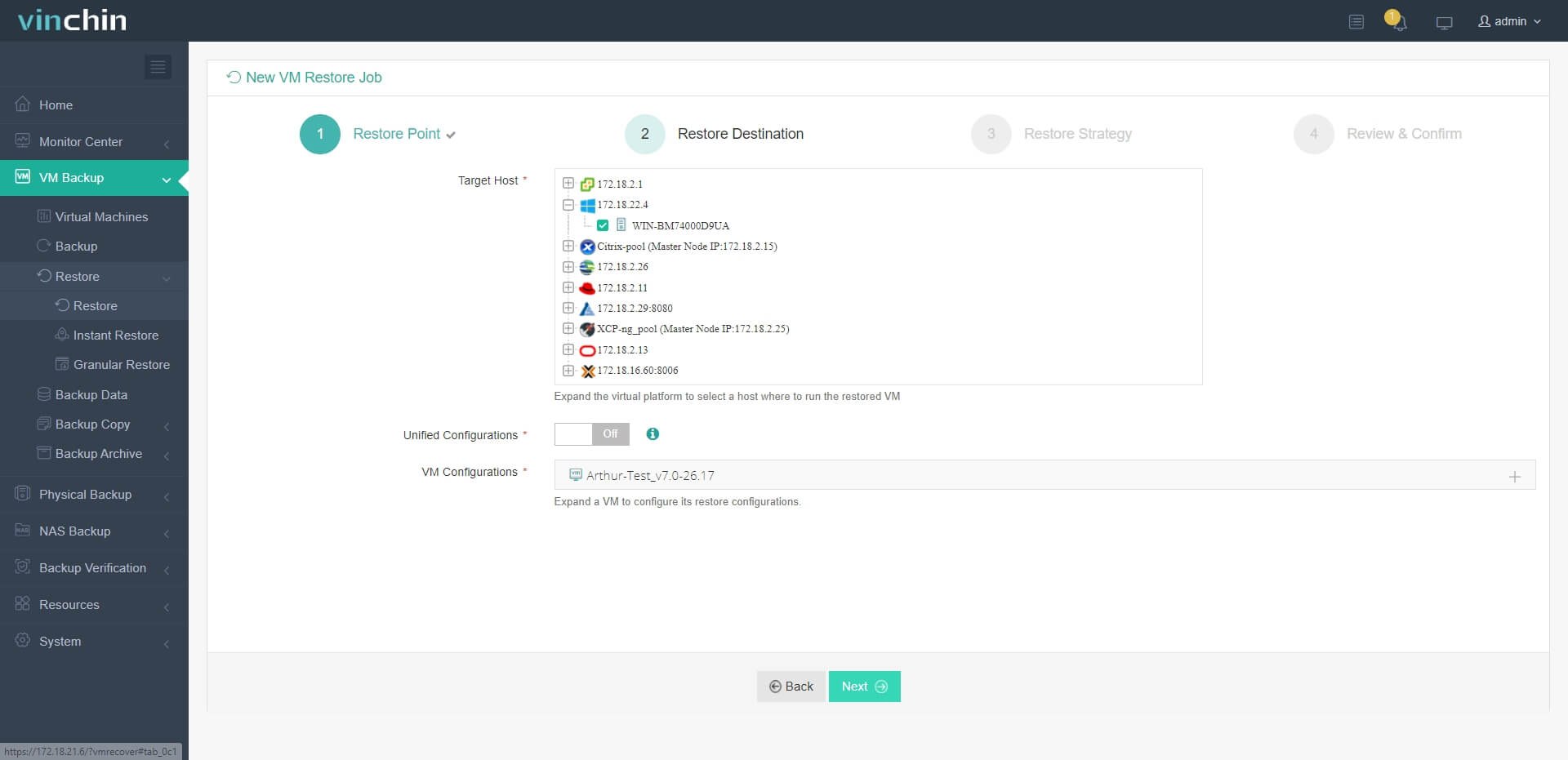
3. Select strategies
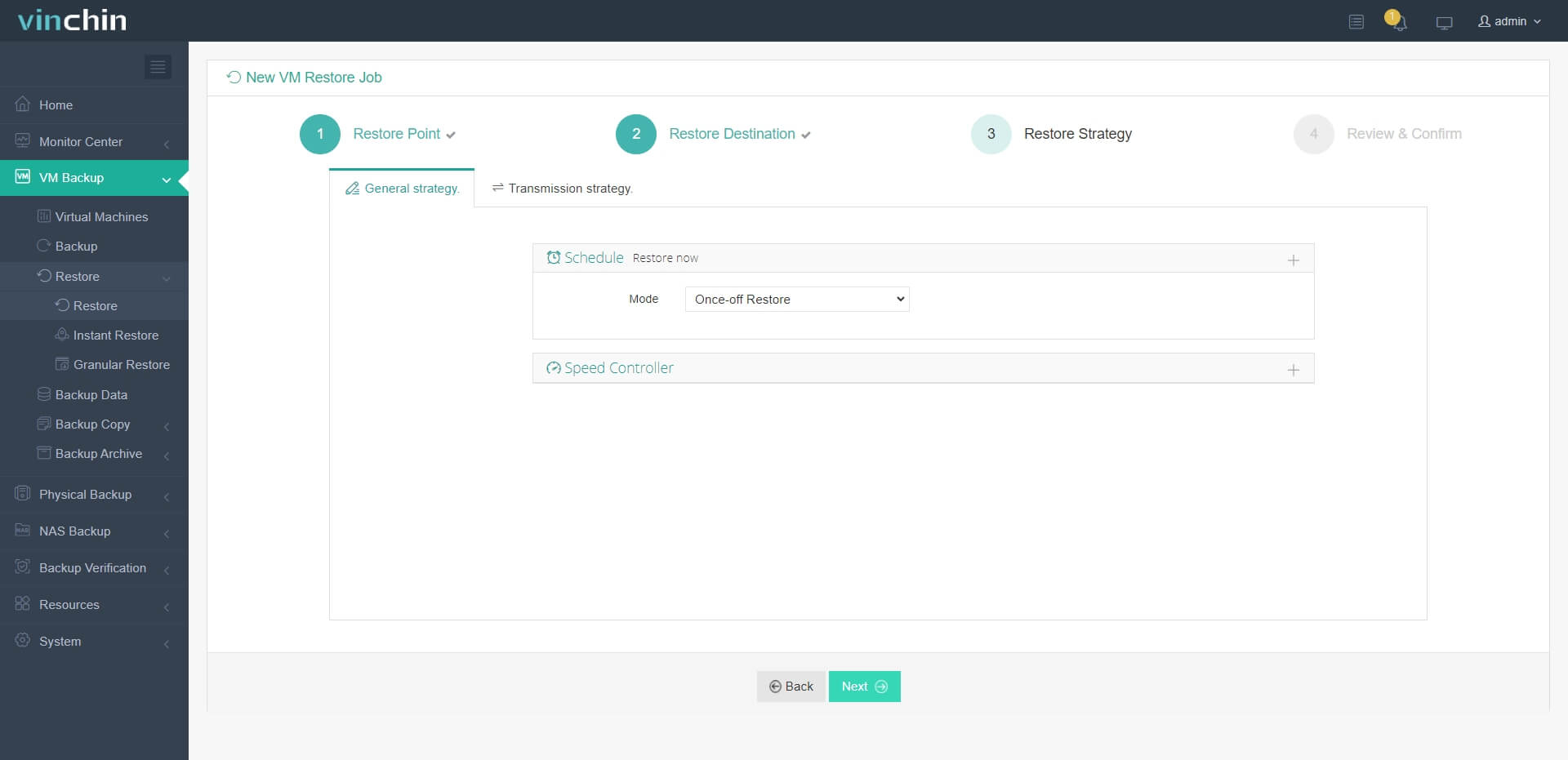
4. Submit the job
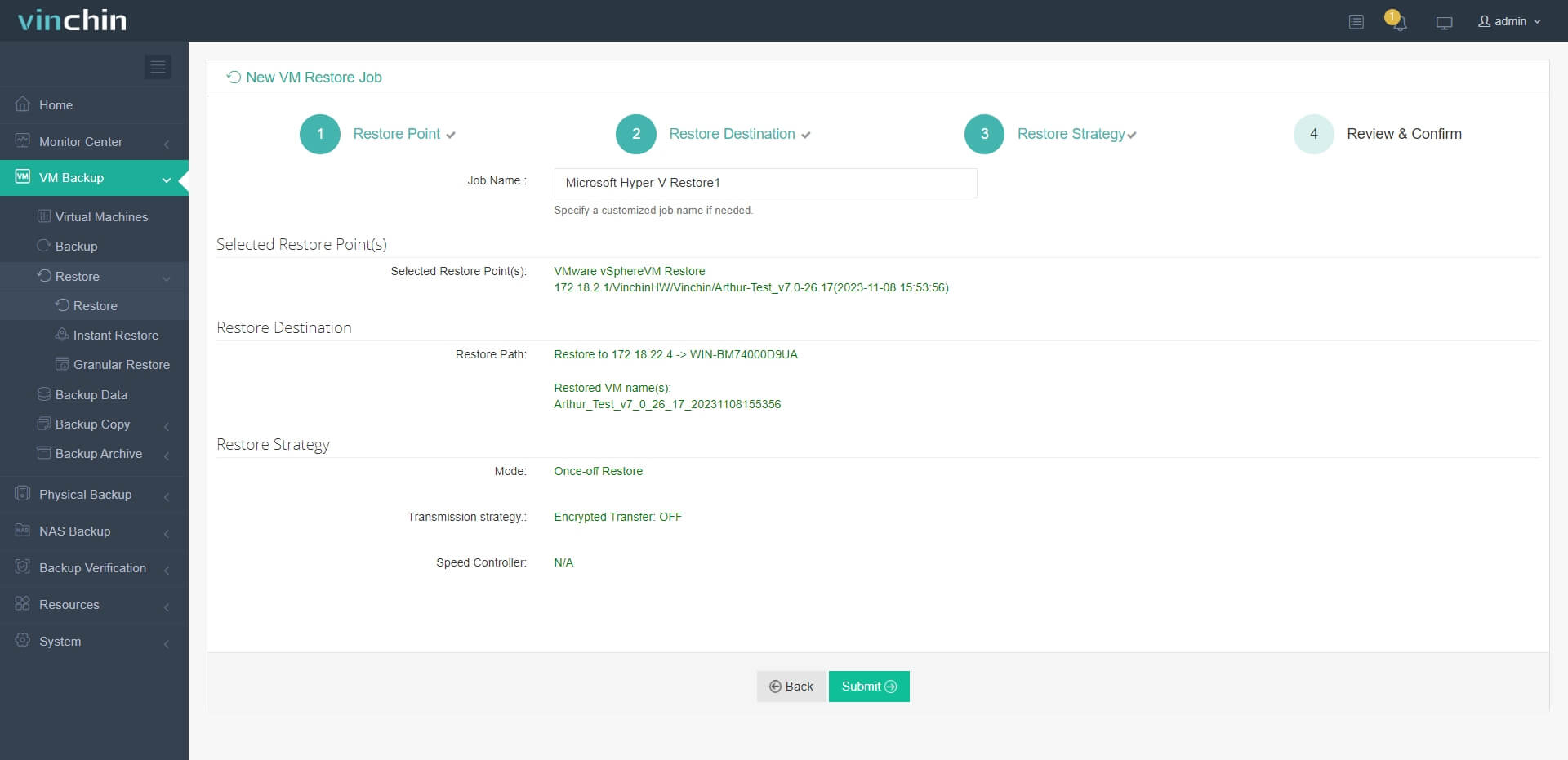
Want to use it immediately? Download the 60-day full-featured free trial and protect your critical data now.
FAQs for VDI, VHD and VMDK Selection
1. Which format of virtual disk is best for performance?
As you can see, vdi, vhd, and vmdk are used in different virtualization platforms and have their own advantages and disadvantages so it is meaningless to compare their performance. If you are testing a virtualization solution, try evaluating it in every aspect.
2. Which type of virtual disk is best for VMware?
For VMware virtual machine, only VMDK is supported so if you want to migrate VM to VMware, you need to convert the virtual disk or use Vinchin Backup & Recovery to migrate it directly.
Conclusion
VDI, VHD, and VMDK are 3 different virtual disk formats from Oracle, Microsoft, and VMware, and each of them has different features and functions. You can use these formats according to your needs and virtualized infrastructures. Sometimes, you may need to convert the file format into another for data migration.
If you need professional data protection and V2V migration solution, you can use Vinchin Backup & Recovery. Don't miss the free trial.
Share on:







