-
What is Oracle Data Guard?
-
What is GoldenGate?
-
What is CDP (Continuous Data Protection)?
-
What is Oracle RMAN Backup and Recovery?
-
What is Active Database Duplication?
-
Professional Oracle Disaster Recovery Solution
-
Oracle Disaster Recovery FAQs
-
Conclusion
As information technology rapidly develops and the amount of data continues to grow, the availability and reliability of databases have become crucial indicators within enterprise information systems. Various factors, such as data center system failures, network failures, and hardware failures, may impact the connectivity and data integrity of database systems in enterprise infrastructures. To ensure the smooth operation of businesses, how to achieve stability and high availability in database systems has become one of the top concerns for information system administrators. Against this backdrop, database disaster recovery and backup technologies are receiving increasing attention.
Oracle is a highly popular database system, known for its complexity and maturity, but it also presents issues such as single points of failure and unexpected data loss. For enterprises, it is essential to implement disaster recovery for Oracle databases through various methods. Below, we explore different approaches to Oracle database disaster recovery.
What is Oracle Data Guard?
Oracle Data Guard provides a data synchronization technology to achieve high availability, enhanced performance, and automated failover for Oracle databases. It creates and maintains multiple standby databases for the primary database. Changes to the primary database are automatically transmitted to the standby databases, ensuring no data is lost during this process. Data Guard offers two types of standby databases: physical standby and logical standby databases. Although both achieve data consistency between the primary and standby databases through archived logs, the processes differ. A physical standby database ensures data consistency by transferring and applying Redo logs, while a logical standby database synchronizes data by analyzing Redo logs and converting the data changes into SQL transactions. The difference lies in the fact that the former is based on physical file replication, whereas the latter is based on SQL logic replay.
What is GoldenGate?
GoldenGate is a log-based structured data replication technology. It captures incremental changes by parsing the source database’s online or archived logs and applies these changes to the target database, enabling synchronization between the source and target databases. GoldenGate can perform large-scale real-time data replication (with a delay of approximately five seconds) across heterogeneous IT infrastructures, including nearly all commonly used operating system platforms and database platforms. As a result, it can be applied in multiple scenarios such as emergency systems, online reporting, real-time data warehouse provisioning, transaction tracking, data synchronization, and disaster recovery. Since GoldenGate captures changes by filtering and analyzing logs, it can achieve cross-platform database replication and synchronization of non-Oracle databases.
What is CDP (Continuous Data Protection)?
CDP (Continuous Data Protection) is one of the most popular data protection technologies today. It is typically defined in the industry as a method that captures or tracks data changes and stores them independently of the production data, ensuring that data can be restored to any previous point in time. CDP systems can be implemented based on blocks, files, or applications, providing recovery objects with fine recovery granularity and enabling nearly infinite recovery points.
What is Oracle RMAN Backup and Recovery?
Oracle RMAN (Recovery Manager) is a built-in backup and recovery tool specifically designed for Oracle databases, offering a comprehensive data protection solution. It can perform physical backups, restore databases, and manage backup files. RMAN supports full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups, and can back up critical database components such as data files, control files, and log files. Combined with archived logs, RMAN can achieve Point-in-Time recovery to ensure data consistency. Additionally, RMAN offers automated recovery features, allowing it to intelligently identify corrupted data and recover it from backups, significantly simplifying the disaster recovery process. RMAN can also integrate with Oracle Enterprise Manager, providing a graphical management interface and backup policy scheduling, facilitating highly automated backup and recovery operations.
What is Active Database Duplication?
Oracle’s Active Database Duplication is a technology that replicates databases over the network to create copies of the target database without relying on existing backup files. It reads active data directly from the source database and replicates it to the target system, making it suitable for quickly building development, testing, or disaster recovery environments. Active Duplication can transfer an entire database from the primary server to a replica server without requiring a backup, and the source database can remain online and continue processing transactions during the replication process. This process is managed by Oracle RMAN, streamlining database cloning operations.
Professional Oracle Disaster Recovery Solution
Vinchin Backup & Recovery provides an efficient backup and disaster recovery solution for Oracle databases, ensuring business continuity and data security. It supports full, incremental, and differential backups of Oracle databases, making the backup process simple and efficient. With built-in deduplication and compression technology, Vinchin optimizes storage space utilization, reduces the size of backup files and data transfer time.
In terms of disaster recovery, Vinchin supports cross-platform recovery and off-site recovery, Combined with its flexible recovery strategy, users can quickly recover Oracle databases when disasters occur, reducing downtime and data loss risks. In addition, the visual management interface provided by Vinchin makes backup and recovery operations intuitive and easy to use, making it easier for IT administrators to monitor and manage multi-site disaster recovery tasks.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery simplifies Oracle backup within 4 steps after the database backup preparation:
1. Select the Oracle database
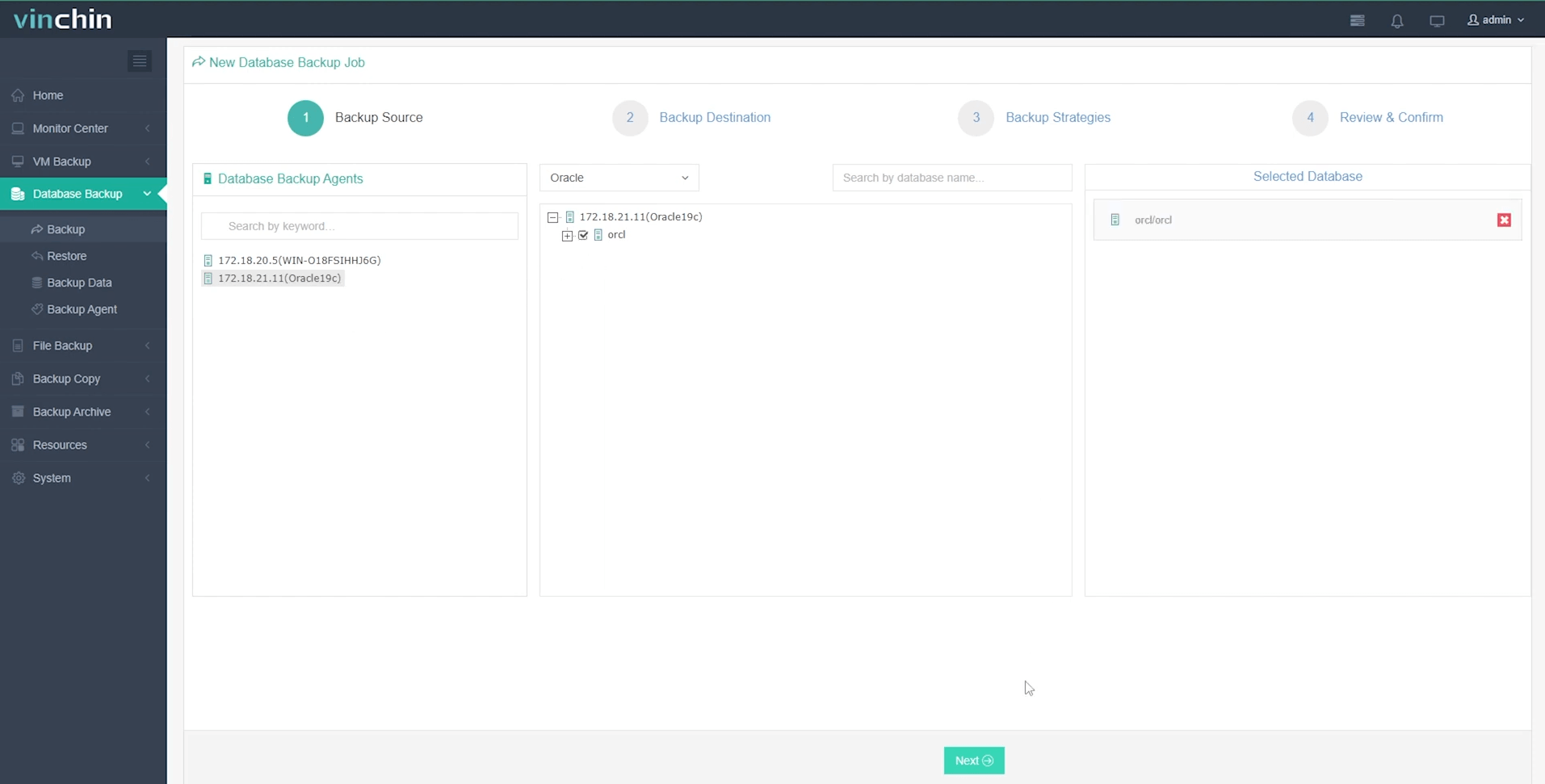
2. Select the backup storage

3. Select the backup strategies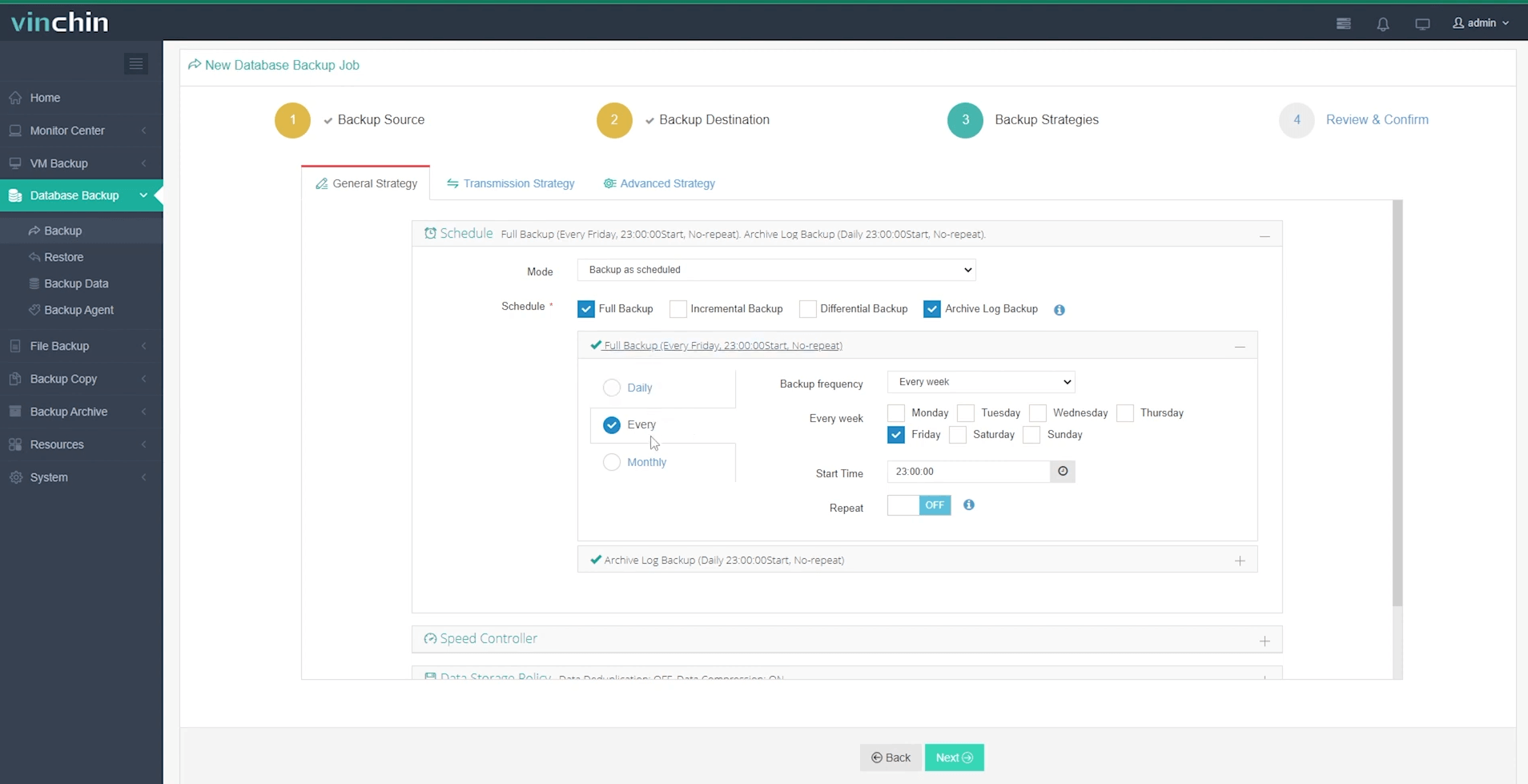
4. Submit the job
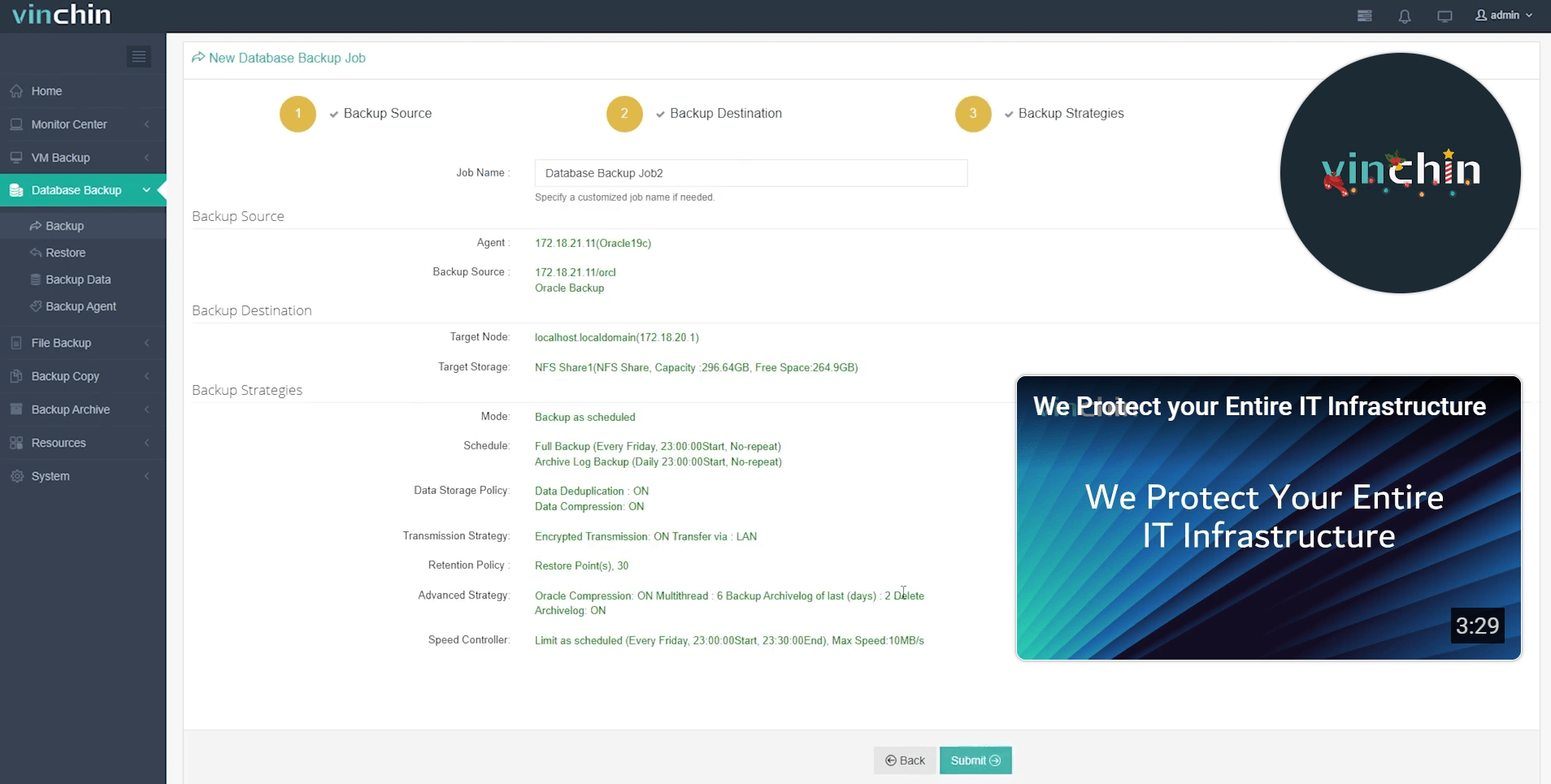
It also supports VMware, Hyper-V, XenServer, XCP-ng, oVirt, RHV, OpenStack, Proxmox, etc. and NAS, file server, Linux & Windows Server. More features waiting for you to discover.
Come on and experience the full capabilities of this robust system with a complimentary 60-day trial! Contact us with your requirements, and you will receive a tailored solution for your IT landscape.
Oracle Disaster Recovery FAQs
1. Q: What is the difference between Active and Passive Standby Databases?
A: Active Standby: Can perform read-only operations and can be promoted to become the primary if necessary.
Passive Standby: Does not serve any application requests but maintains a copy of the primary database's data.
2. Q: What types of recovery does Oracle support?
A: Oracle supports several types of recovery, including:
Incomplete Recovery: Restoring a database to a point before the last backup.
Complete Recovery: Restoring a database to the exact state it was in at the time of failure.
Point-in-Time Recovery: Restoring a database to a specific point in time.
Flashback Database: A feature allowing the database to be restored to any point in time within a retention period without affecting the physical files.
Conclusion
In practice, choosing a disaster recovery method that suits the specific business needs is crucial. You should select appropriate disaster recovery technologies based on your business requirements and actual conditions to enable database systems to achieve disaster recovery, prevent vulnerability attacks, and avoid operational errors.
Share on:





