-
Method 1: Hyper-V Manager to restart VM Hyper-V
-
Method 2: Restart the VM using PowerShell commands
-
Method 3: Reboot virtual machine via Remote Desktop connection
-
Method 4: Troubleshooting and solutions
-
Method 5: Automatic restart configuration
-
Recommended: use Vinchin for reliable VM backup
-
Hyper-V restart VM FAQs
-
Conclusion
When managing virtual machines in Hyper-V, you may encounter situations where a VM needs to be restarted—whether due to system updates, performance issues, or unresponsiveness. Here are 5 effective methods to restart a Hyper-V VM safely and efficiently.
Method 1: Hyper-V Manager to restart VM Hyper-V
Hyper-V Manager is a virtualization management tool that comes with Windows and provides an intuitive graphical user interface to manage and operate VMs. When using Hyper-V Manager to restart a VM, it takes only a few simple steps.
1. Open Hyper-V Manager
In Windows, open Hyper-V Manager in the search box and open the tool.
2. Select a virtual machine
In the virtual machine list of Hyper-V Manager, find the target virtual machine.
3. Menu operation
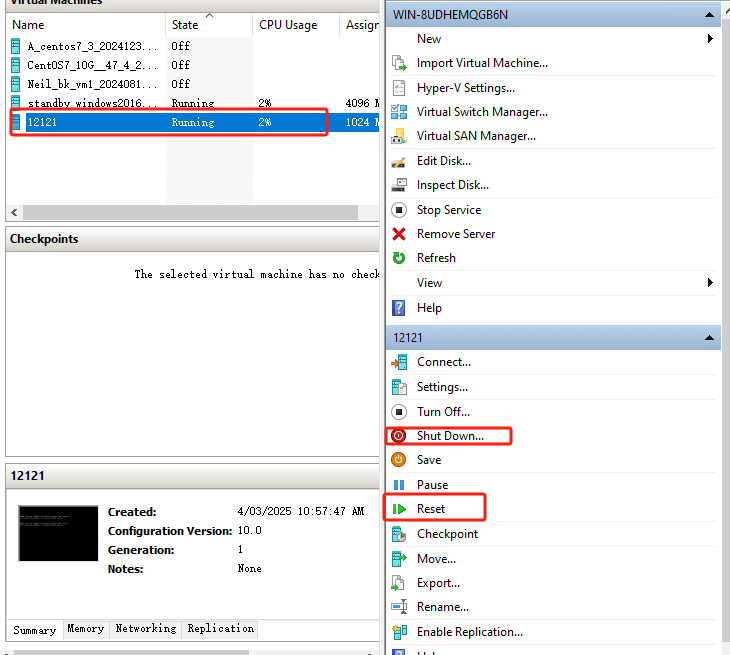
✅ Option 1: Use the “Reset”option (to force a reboot, for unresponsive situations)
Click on the selected VM and select Reset in the menu.
This method is equivalent to a direct power-off reboot, and is suitable for cases where the virtual machine is unresponsive or needs to be forced to reboot.
⚠ NOTE: May result in loss of unsaved data.
✅ Option 2: Use the“Shut down + Start” method (safe reboot, recommended)
Click on the selected VM and select Shut down to let the VM shut down according to the normal process.
After shutting down, right-click again and select Start to start the virtual machine.
Pros: This method is safer and avoids data corruption or system anomalies.
Method 2: Restart the VM using PowerShell commands
For users familiar with command line operations, PowerShell provides a flexible and powerful way to manage virtual machines. PowerShell commands can be used to quickly reboot a virtual machine and are suitable for automated scripting scenarios.
1. Opening PowerShell
In Windows, search for and open“Windows PowerShell” in the search box.
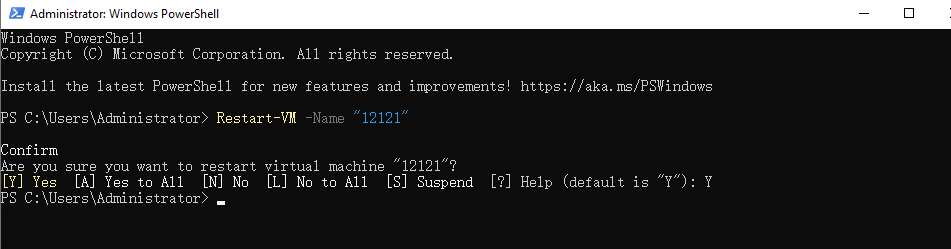
2. Enter the reboot command
Restart-VM -Name "YourVMName"
Restart-VM -Name "12121"
3. Check the status of the virtual machine
You can use the
Get-VM -Name “YourVMName”
command to check the current state of the virtual machine to ensure that the reboot was successful.
Get-VM -Name "12121"
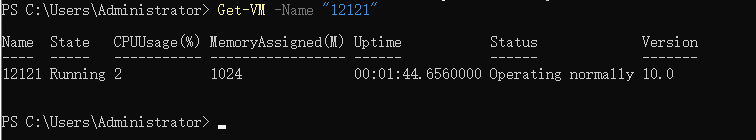
As you can see, the current state of VM 12121 is Running and it is running normally.
Method 3: Reboot virtual machine via Remote Desktop connection
If you have connected to the virtual machine via Remote Desktop, you can reboot it from within the system just as you did with the physical machine.
1. Login to Remote Desktop
Using the Remote Desktop connection tool, log in to the virtual machine that needs to be rebooted.
2. In-system reboot
Inside the virtual machine, click on the“Start”menu and select the“Reboot”option to complete the reboot of the virtual machine.
Method 4: Troubleshooting and solutions
1. Virtual machine can not be restarted
If a virtual machine fails to restart normally, the following reasons are usually possible:
Abnormal VM state: The VM may have been in a hung or unresponsive state.
Solution:
Use the following command to force the virtual machine to shut down.
Stop-VM -Name “YourVMName”
Then, restart the VM using:
Start-VM -Name “YourVMName”
Command example:
Stop-VM -Name "12121" -Force
Start-VM -Name "12121"
2. Permission problems
If you are experiencing permissions issues, it is usually because there are not enough permissions to operate the virtual machine. To resolve this issue:
Ensure that you are using PowerShell or Hyper-V Manager with administrator privileges.
Check that the current user is a member of the Hyper-V Administrators group.
3. Insufficient system resources
A virtual machine restart may fail due to insufficient system resources on the host, especially if there are multiple virtual machines running.
To resolve this issue, check host resources
Ensure that the host has sufficient CPU and memory resources. You can check resource usage using Task Manager or PowerShell.
Get-Process | Sort-Object CPU -Descending | Select-Object -First 10
This command will list the top 10 processes that take up the most CPU.
Free up resources: If the host is running low on resources, consider shutting down other unnecessary virtual machines as well as applications, or adding more physical resources (such as memory and CPU).
4. Other common failures and solutions
Virtual machine cannot start: If the virtual machine cannot start, you can try the following methods:
Check if the virtual machine's disk files are corrupted and try to repair them using Hyper-V Manager.
Ensure that there are no faults or lockups on the host that prevent the virtual machine from booting.
Method 5: Automatic restart configuration
To improve system stability and automated management, virtual machines can be configured to restart automatically under certain circumstances. For example, automatic reboot after a system crash or update.
1. Open Hyper-V Manager
In Hyper-V Manager, right-click the virtual machine you want to configure and select Settings.
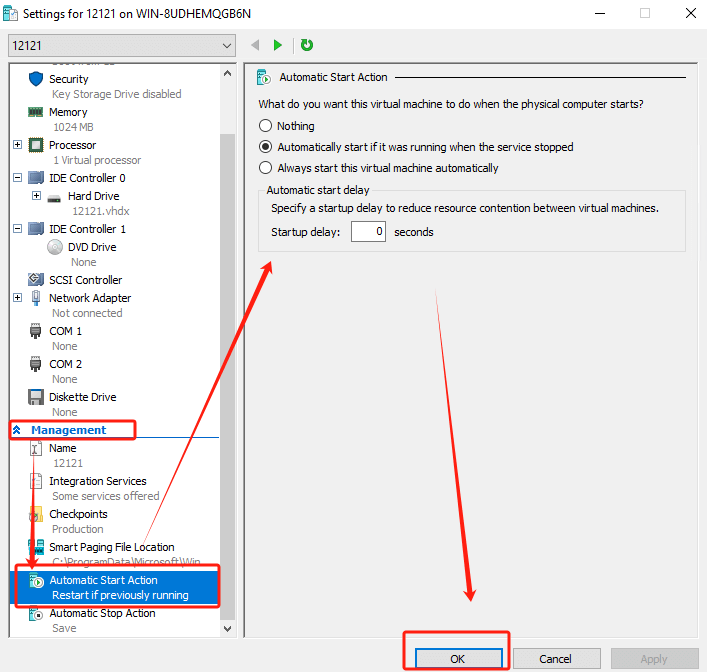
2. Configure Automatic Start Action
In the VM Settings window, find Automatic Start Action, where you can set it:
Nothing: The virtual machine will not start automatically.
Automatically start if it was running when the service stopped: The virtual machine will start automatically only if it was in a running state before the host rebooted.
Always start this virtual machine automatically: The virtual machine is started automatically when the host machine boots, regardless of the state of the virtual machine.
3. Configure automatic start delay
If you wish to avoid resource contention caused by multiple VMs starting at the same time, you can set automatic start delay. This option allows you to set a delay time (e.g., 30 seconds) when a VM starts up to balance the resource utilization of the host machine.
4. Save Settings
When the configuration is complete, click OK to save the settings.
Of course, you can also configure it using PowerShell
Set-VM -Name "YourVMName" -AutomaticStartAction StartIfRunning -AutomaticStartDelay 30
The above command sets the VM to start automatically after the host machine starts and with a delay of 30 seconds.

Recommended: use Vinchin for reliable VM backup
Vinchin Backup & Recovery executes powerful Hyper-V backup and recovery functions, including agentless incremental backup, efficient data deduplication, backup node expansion, and offsite backup copies, to comprehensively protect the Hyper-V environment. It utilizes agentless image-based backup technology to back up Hyper-V VMs directly from the hypervisor data layer without installing any agents on each VM, ensuring easy software deployment with minimal resource consumption in the production environment.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery also supports Hyper-V data recovery at the file level, allowing users to restore specific files from restore points to the production host. If some files are mistakenly deleted, this feature enables quick retrieval of necessary data without restoring the entire virtual machine.
Vinchin Backup & Recovery's operation is very simple, just a few simple steps.
1.Just select VMs on the host
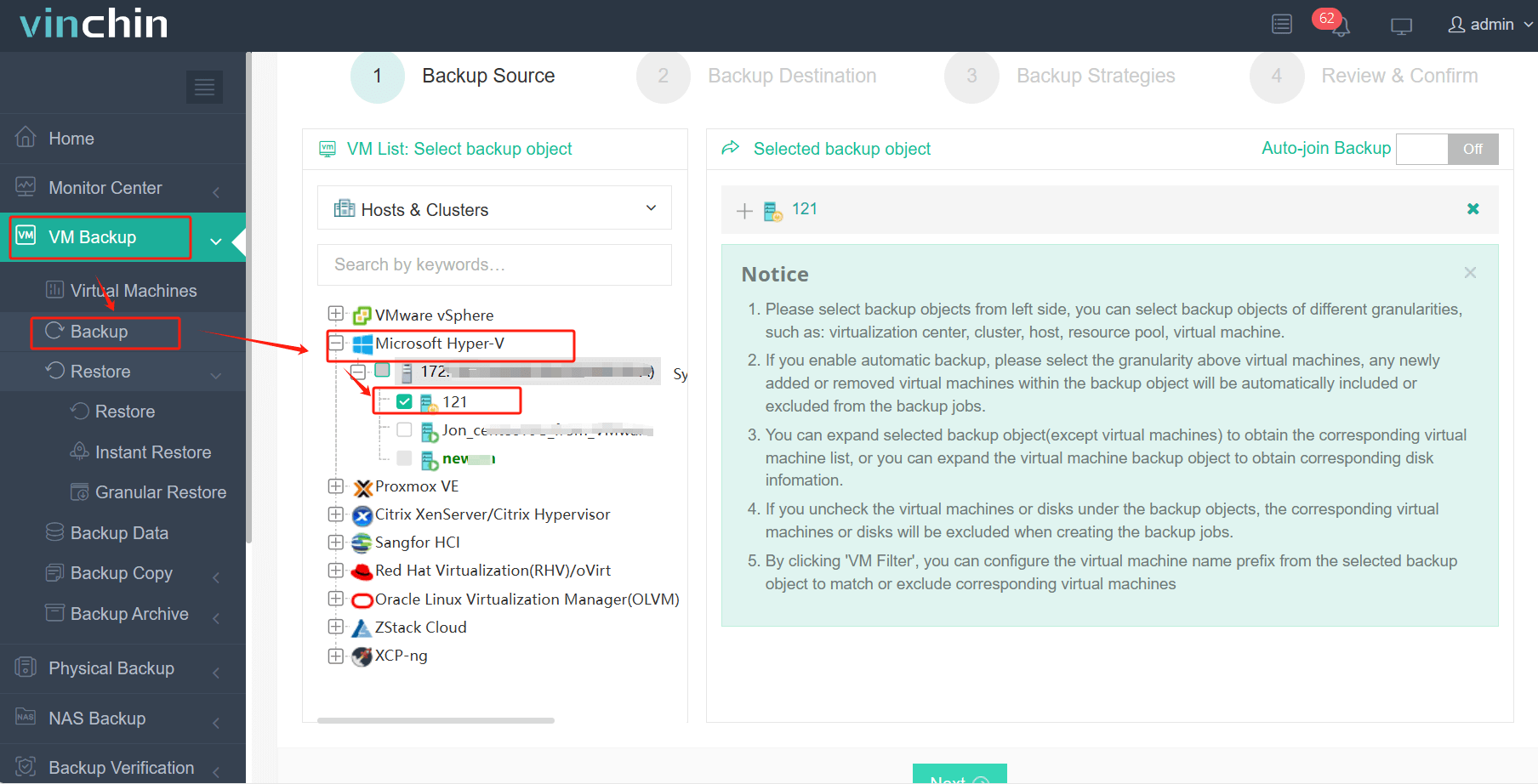
2.Then select backup destination
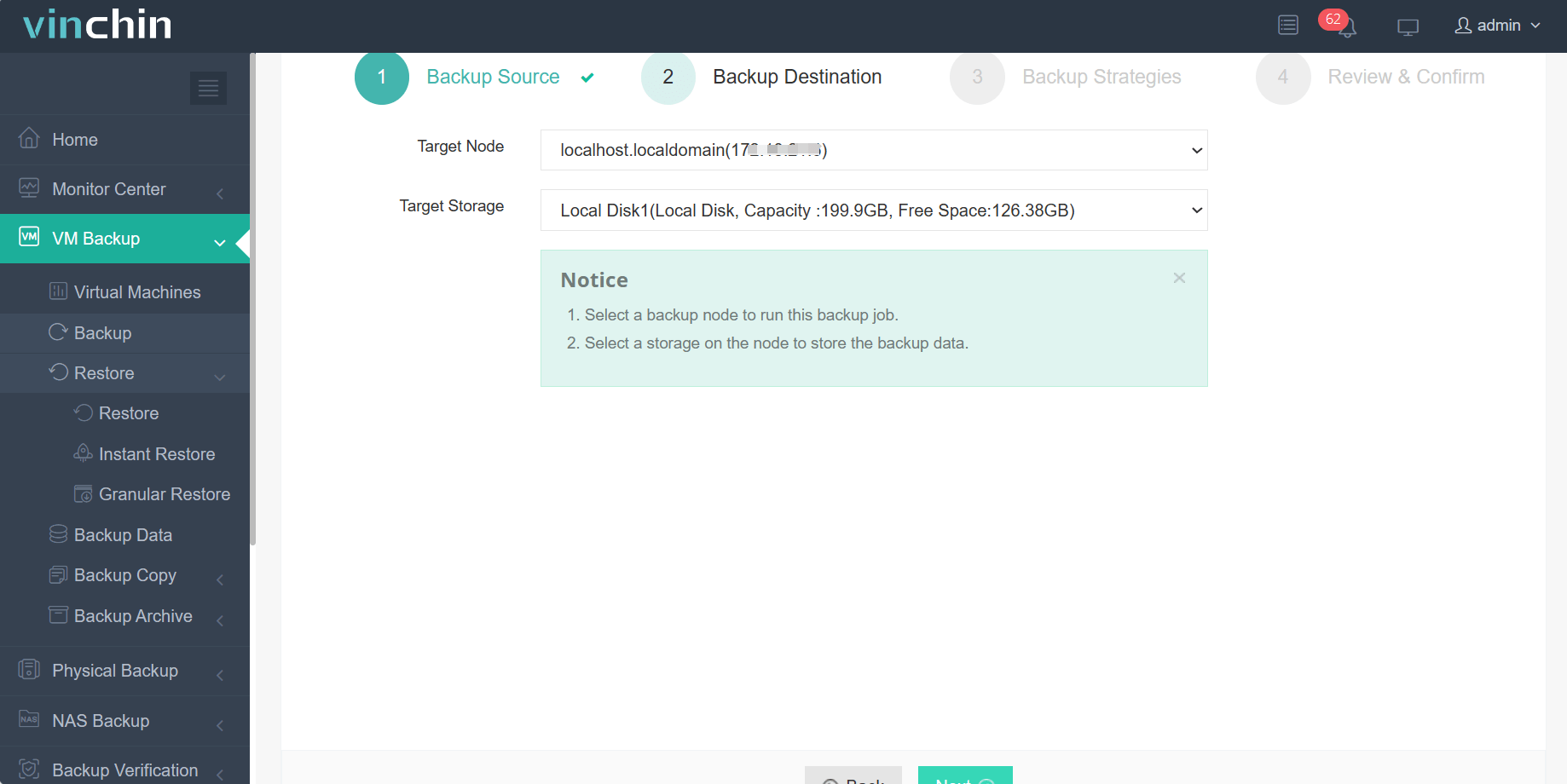
3.Select strategies
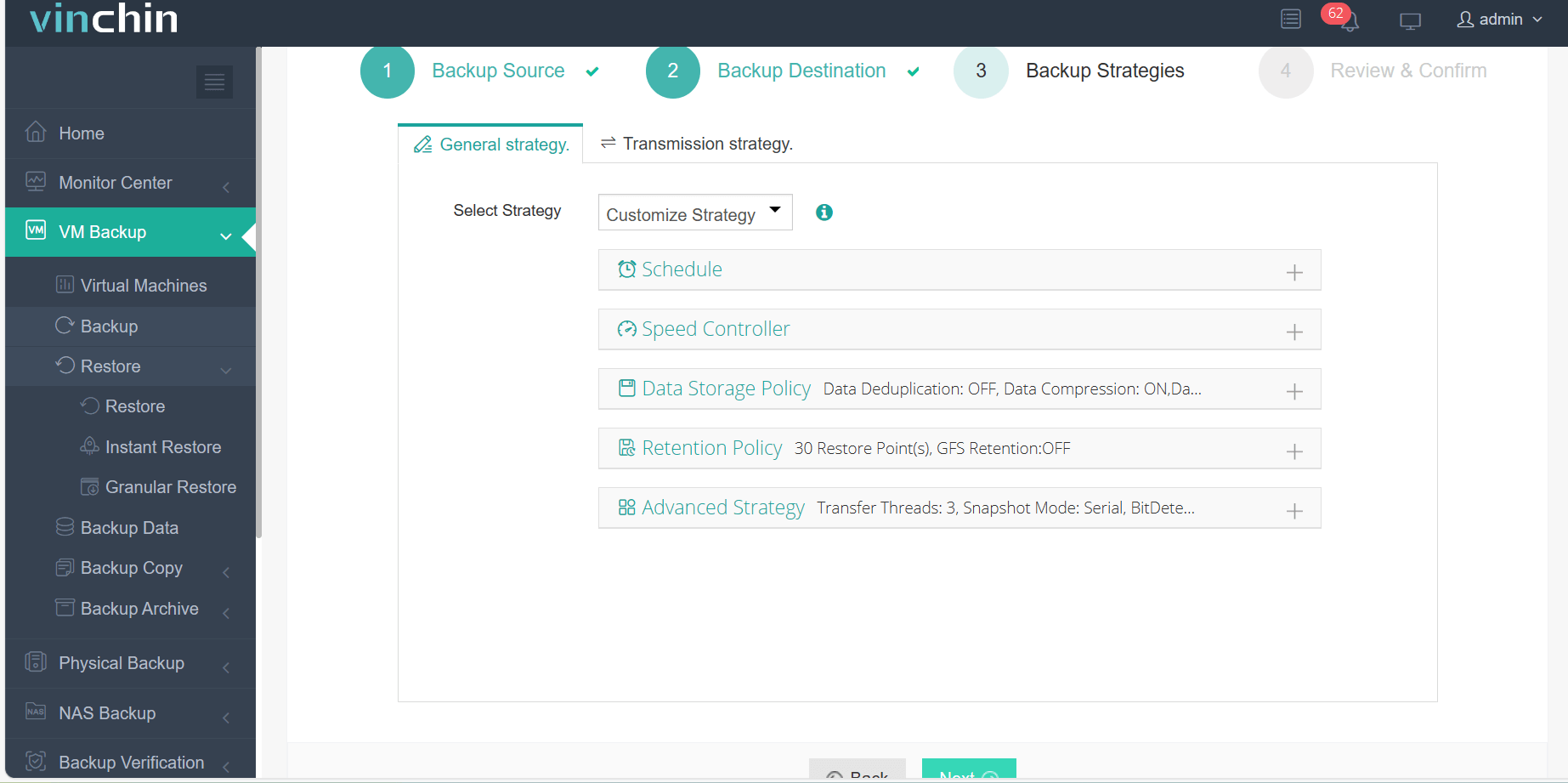
4.Finally submit the job
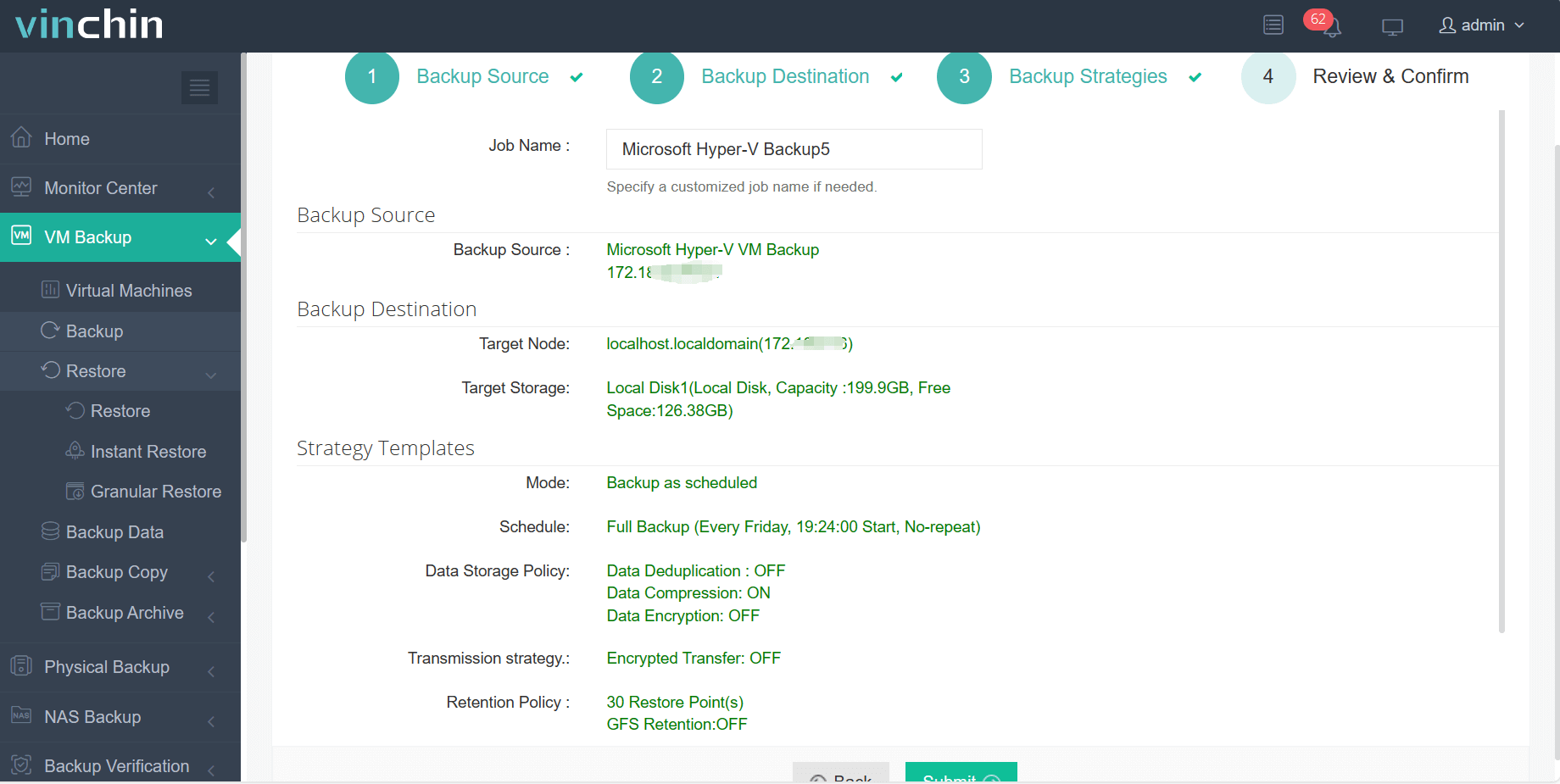
Vinchin offers a free 60-day trial, allowing users to explore its full functionality in real-world scenarios. Users can access 24/7 technical support during the trial period and evaluate key features such as agentless backup, instant recovery, and offsite replication. For further details, please consult Vinchin directly.
Hyper-V restart VM FAQs
Q1: Does restarting a virtual machine affect its performance?
A1: Usually, a normal reboot does not affect the long-term performance of a virtual machine. It helps to clean up memory, end unresponsive processes, and apply necessary security updates, among other things.
However, frequent reboots may temporarily disrupt services, especially for applications and services that need to run continuously.
Q2: How does rebooting a virtual machine differ from saving the state?
A2: A reboot completely powers down a virtual machine and turns it back on again, similar to the process of rebooting a physical computer.
A save state saves the current state of the virtual machine to a file from which it can be quickly resumed without going through the full startup process.
Conclusion
In summary, restarting a Hyper-V virtual machine can be achieved through multiple methods, including Hyper-V Manager, PowerShell, and Remote Desktop. Proper troubleshooting ensures smooth operation. Additionally, Vinchin Backup & Recovery enhances data protection with agentless backup, instant recovery, and offsite replication.
Share on:






