-
Three Core Components of Cloud Disaster Recovery
-
The Core Value of Cloud Disaster Recovery
-
Steps to Implement Cloud Disaster Recovery
-
Enhancing Cloud Disaster Recovery with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
-
Cloud Disaster Recovery FAQs
-
Conclusion
In modern IT environments, Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS) is rapidly becoming the ideal solution for businesses leveraging cloud computing to address disaster recovery challenges. As organizations become increasingly dependent on data, disaster recovery becomes more complex—not only due to natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes but also because of cyberattacks, ransomware, human errors, and insider threats. Additionally, the exponential growth of data and high expectations for fast recovery make disaster recovery even more challenging.
However, disaster recovery budgets have not kept pace with these growing demands, prompting businesses to seek more cost-effective solutions. Cloud-based disaster recovery has emerged as a key option. This article explores the fundamentals of cloud disaster recovery, its essential components, how businesses can develop a cloud disaster recovery plan, and the specific steps for implementation.
Three Core Components of Cloud Disaster Recovery
A company’s data protection strategy typically consists of three components: backup, archiving, and recovery. In the cloud environment, the roles and applicability of these elements differ.
Backup: Short-Term Data Protection
Backup involves creating copies of data to restore it in the event of loss or system failure. Most businesses maintain backup retention periods of 3 to 7 years. While cloud backup reduces on-premises storage needs, the cost of long-term cloud storage rentals can be higher than maintaining local storage. Thus, businesses must balance storage costs with the convenience of cloud recovery.
Archiving: Long-Term Data Storage
Archiving focuses on long-term data retention, often for compliance requirements, with retention periods extending 10 years or more. An ideal archiving strategy includes copies stored in at least two separate locations and in different formats. Since archived data is rarely accessed, long-term cloud storage may not be cost-effective, leading many businesses to prefer on-premises or offline storage for archiving.
Recovery: The Key to Disaster Recovery
Recovery (especially disaster recovery) requires the latest data copies and must restore business operations as quickly as possible. Cloud service providers allow businesses to use on-demand cloud computing resources in case of a disaster, eliminating the need to maintain backup servers and storage at remote locations. As a result, cloud-based disaster recovery (DRaaS) has quickly become a preferred strategy for disaster resilience.
The Core Value of Cloud Disaster Recovery
While cloud computing is not a one-size-fits-all solution, it offers flexibility and cost optimization for disaster recovery.
Cost Optimization and Economies of Scale
Cloud service providers operate large-scale data centers, benefiting from bulk hardware purchases and automated maintenance, making cloud storage and computing more cost-effective than traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Lower Upfront Costs with a Subscription Model
Cloud computing follows a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for businesses to make large upfront investments in IT infrastructure. This is especially beneficial for temporary disaster recovery environments. However, for long-term operations, renting cloud resources may become more expensive than maintaining on-premises infrastructure, requiring careful evaluation of cloud disaster recovery’s viability.
Steps to Implement Cloud Disaster Recovery
To establish an effective cloud disaster recovery plan, businesses should follow three key steps.
Step 1: Migrating Data to the Cloud
The first step in cloud disaster recovery planning is data migration, ensuring storage costs remain optimized by keeping only the most recent data copies. Common data protection methods include:
1. Backup-Based Storage - Most cloud backup solutions store data in proprietary formats, requiring extraction and conversion before recovery.
2. Replication-Based Storage–Data is stored in its original file system format, allowing direct access during disasters. Businesses may opt for high-performance cloud storage for faster recovery.
3. Offline Data Migration–For large-scale data transfers, some cloud providers offer high-capacity NAS devices or tape drives, allowing businesses to copy data locally before physically shipping it to the cloud, bypassing network bandwidth limitations.
Step 2: Executing Disaster Recovery in the Cloud
When disaster strikes, businesses must swiftly switch operations to the cloud to ensure business continuity. The recovery process includes:
1. Local vs. Cloud Recovery–If the disaster affects only a single application, local recovery may be sufficient. However, for complete data center outages, businesses must fail over to the cloud.
2. Prioritizing Critical Services–Essential components like DNS and directory services should be restored first, followed by application servers.
3. Adjusting Network Configurations–Ensuring that remote users can seamlessly access cloud-hosted applications requires network adjustments.
4. Regular Testing–Companies must frequently test disaster recovery procedures to ensure that networks, applications, and user access remain functional during actual disasters.
Step 3: Failing Back to the On-Premises Data Center
Once the disaster has been resolved, businesses need to transition operations back to the on-premises data center—a process known as failback. Given the complexity of moving data back from the cloud, companies should:
1. Use Incremental Data Sync–Instead of replicating all data, only synchronize recent changes to accelerate migration.
2. Preconfigure the On-Premises Environment–Ensure the local infrastructure remains operational during the disaster, allowing for a seamless return.
3. Avoid Vendor Lock-In - Opt for standardized data formats to ensure smooth cloud-to-on-premises transitions without compatibility issues.
Enhancing Cloud Disaster Recovery with Vinchin Backup & Recovery
While cloud platforms provide many advantages, they also present unique challenges related to data availability, speed, and security. In this context, Vinchin Backup & Recovery stands out as an ideal solution for businesses looking to streamline their Cloud DR processes. Vinchin’s comprehensive backup and disaster recovery suite supports a wide range of virtualized environments, including VMware, Proxmox, XenServer, and more, ensuring that data is protected across both on-premises and cloud infrastructures. With features like deduplication, compression, and custom throttling, Vinchin helps businesses optimize their backup storage and bandwidth usage while enhancing recovery speed and reliability.
Vinchin’s support for S3 backups and tape backups will further strengthen Cloud DR strategies by providing flexible, multi-layered backup solutions. These new features will enable organizations to store critical backups securely in cloud platforms like AWS S3, Wasabi, or even offline on tape, ensuring that they are always prepared for unexpected disasters.
It’s quite easy to backup VMs with Vinchin Backup & Recovery:
1. Select the backup object.
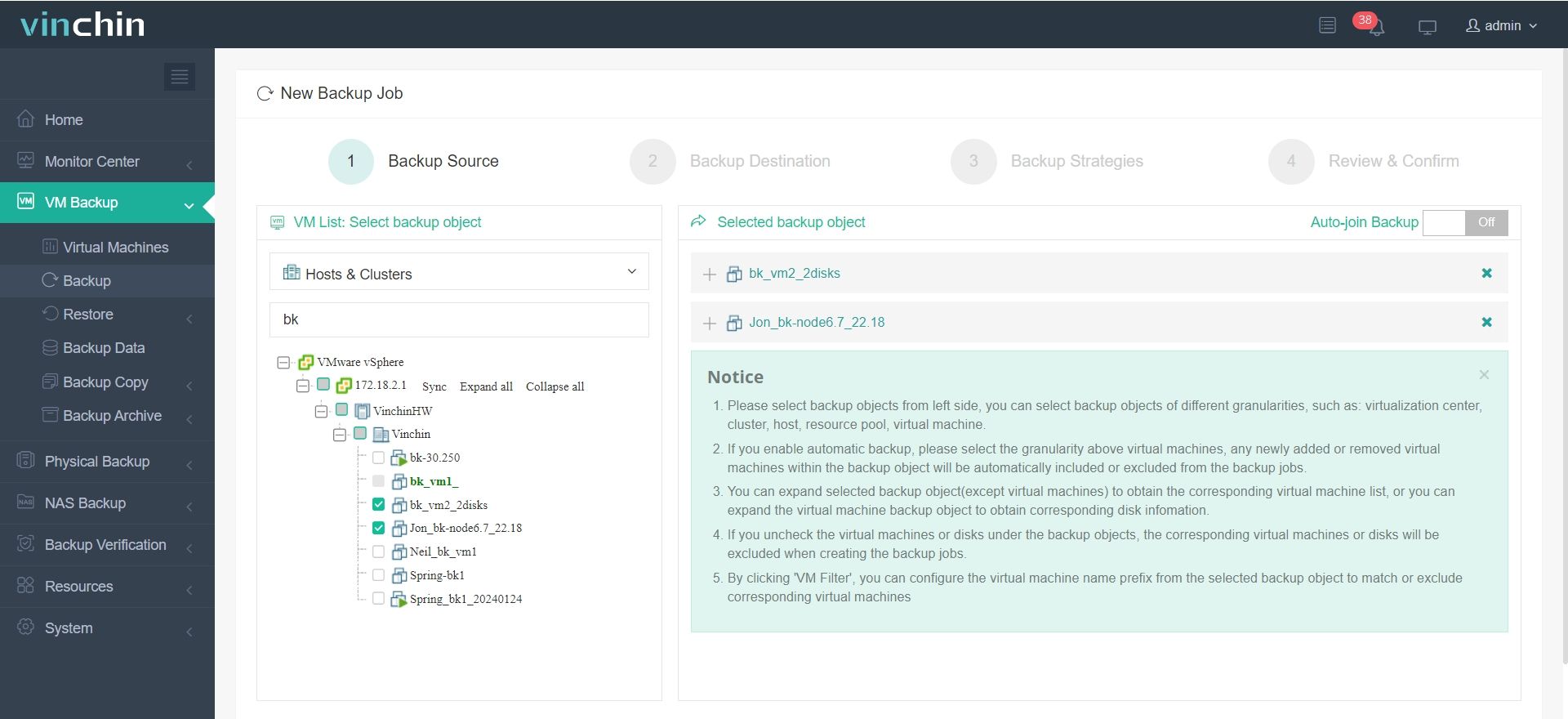
2. Select backup destination.
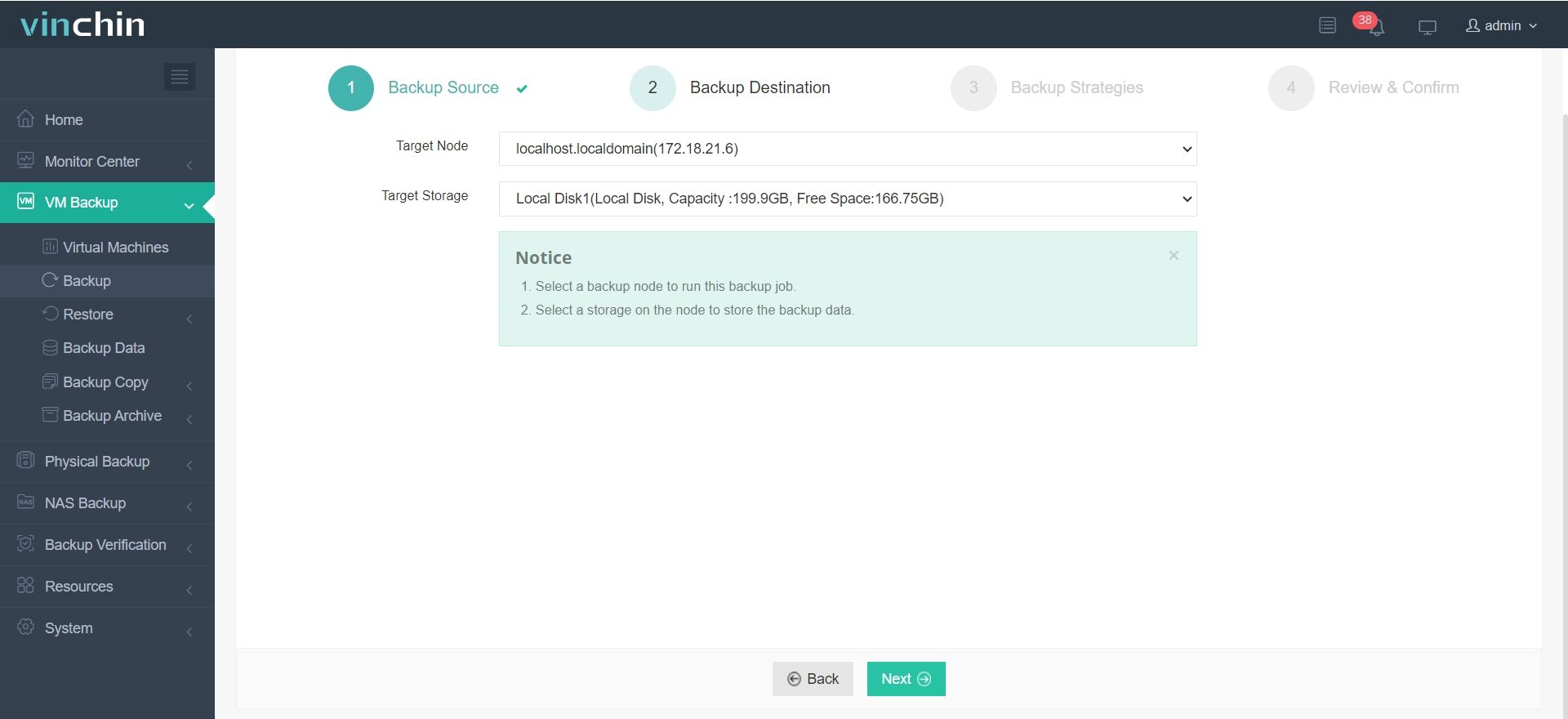
3. Configure backup strategies.
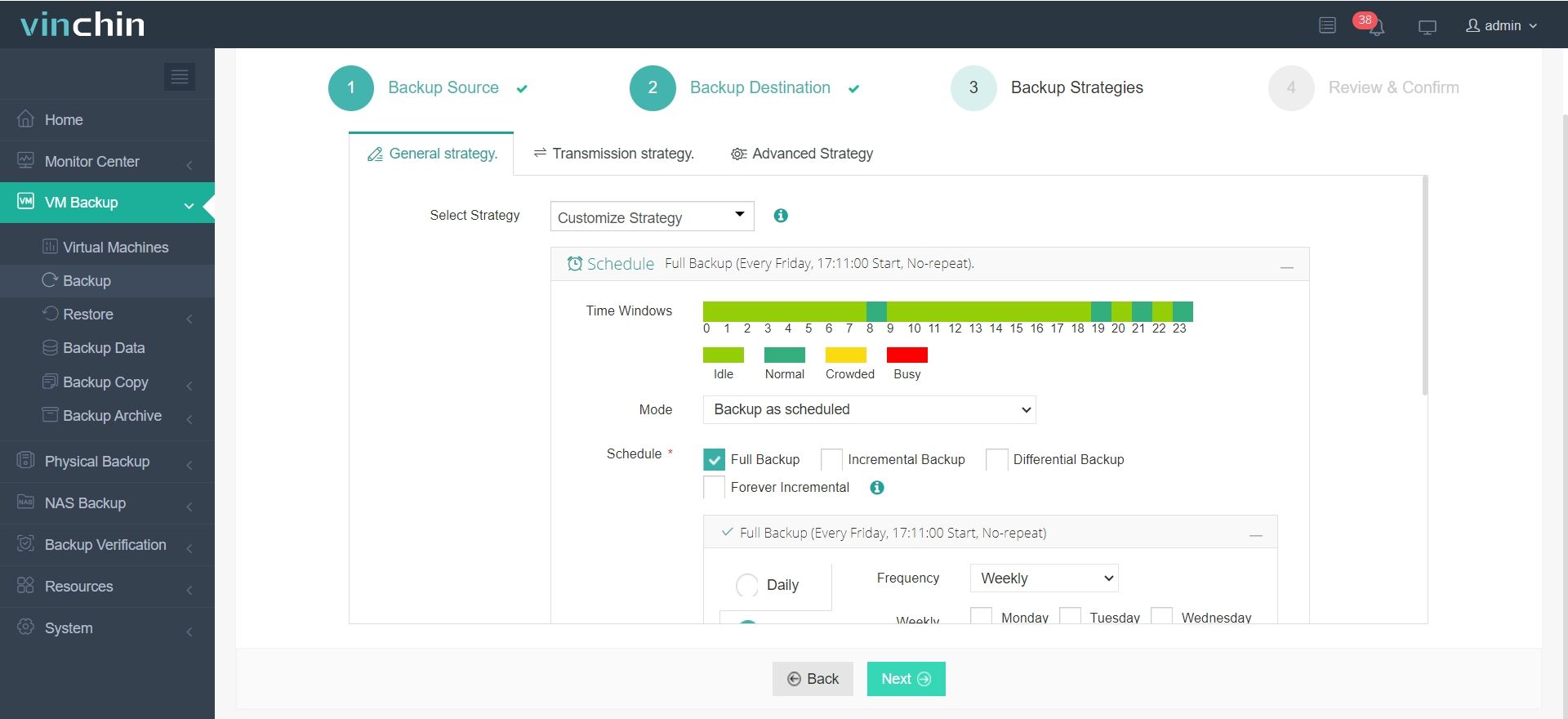
4. Review and submit the job.
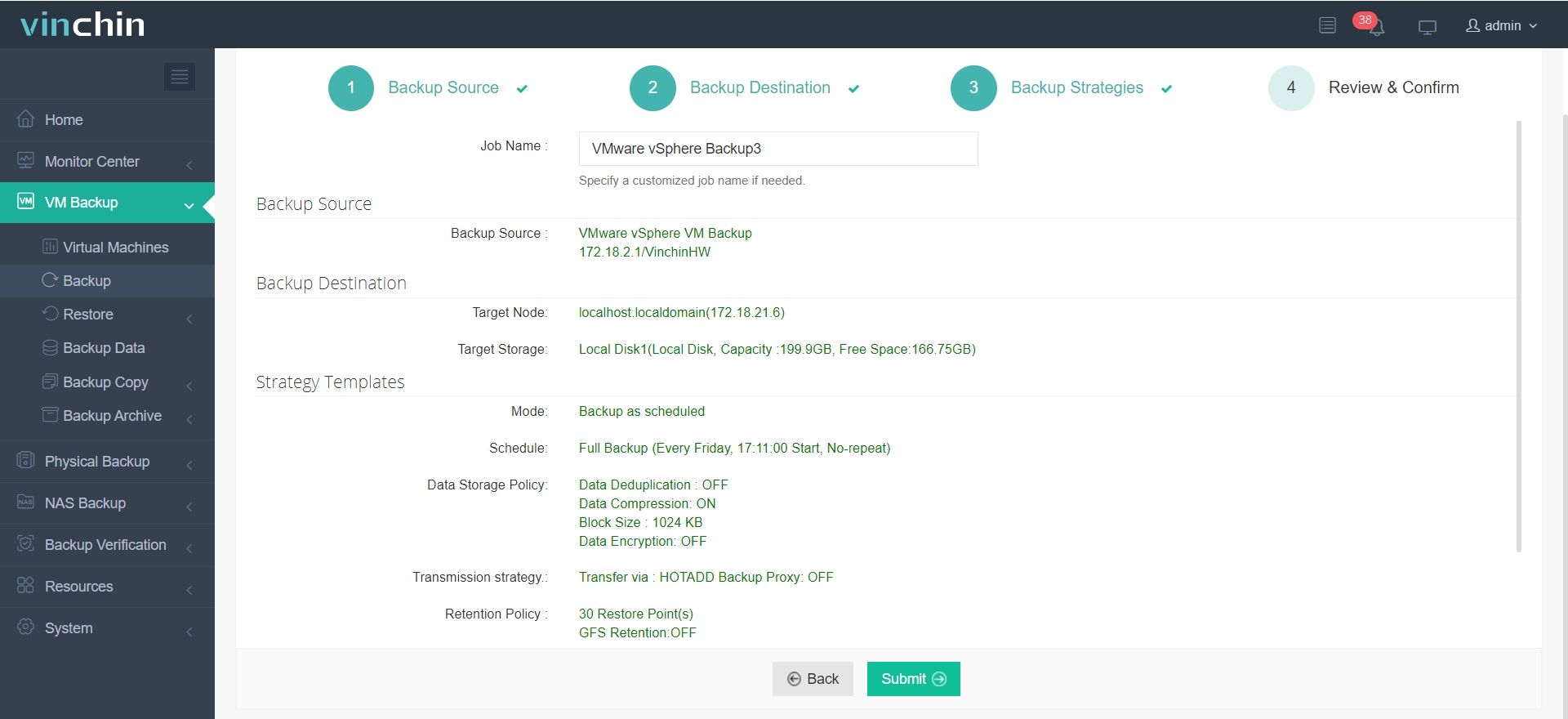
Whether protecting data in the cloud or on-premises, Vinchin Backup & Recovery ensures businesses can recover swiftly and efficiently, minimizing downtime and safeguarding against data loss. Here is a full-featured 60-day trial below! Or, contact us with your requirements, and you will receive a tailored solution for your IT landscape.
Cloud Disaster Recovery FAQs
1. What is a multi-cloud disaster recovery strategy?
A multi-cloud disaster recovery strategy involves using multiple cloud providers to replicate data and applications across different cloud environments. This approach can improve resilience and reduce the risk of downtime if one cloud provider experiences an outage.
2. How can cloud disaster recovery help with business continuity?
By providing fast recovery from data loss, downtime, or system failures, cloud disaster recovery ensures that business-critical applications and services remain operational with minimal interruption, supporting overall business continuity.
Conclusion
Cloud disaster recovery offers businesses a flexible, efficient, and cost-effective solution, but its feasibility depends on business needs and financial considerations. Organizations should carefully plan data storage strategies, cloud recovery workflows, and failback mechanisms to ensure that cloud disaster recovery is not only responsive to emergencies but also remains cost-effective in the long run. Ultimately, regular testing and continuous optimization are key to ensuring that a cloud disaster recovery strategy functions effectively when disaster strikes.
Share on:






